Lipid facts for kids
A lipid is a type of molecule found in all living things. Think of them as oily or waxy substances. Fats are a common example of lipids. You can find lipids in many foods like algae, seeds, meat, cheese, butter, and fish.
Lipids are important because they help our bodies in many ways. They are a big part of cell membranes, which are like the protective walls of our cells. Lipids also store energy for us to use later, and they help send signals around the body.
What Are Lipids?
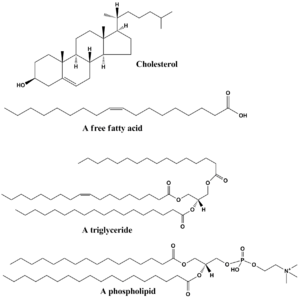
Lipids are a group of natural molecules. They include things like fats, waxes, and sterols. Even some important vitamins, like vitamins A, D, E, and K, are types of lipids because they dissolve in fat. Other lipids include glycerides and phospholipids.
How Lipids Are Built
Lipids are usually long chains made mostly of carbon and hydrogen atoms. These chains can be simple or more complex. For example, steroids and phospholipids are types of complex lipids.
Some lipids don't mix well with water; they are called hydrophobic. This means "water-fearing." Other lipids are amphipathic, which means they have one part that likes water and another part that doesn't. This special quality helps them form cell membranes.
What Do Lipids Do?
Lipids have several super important jobs in living things:
- Storing Energy: Lipids are great at storing energy. Our bodies can save energy in the form of fat, which can be used when we need it. This is why animals often store fat for winter or long journeys.
- Building Cell Membranes: One of the most important jobs of lipids is to form lipid bilayers. These are the main parts of cell membranes. Cell membranes act like a protective skin around every cell, controlling what goes in and out.
- Sending Signals: Some lipids act like messengers, helping cells talk to each other. This process is called signal transduction. They can tell cells to grow, divide, or do other important tasks.
Images for kids
-
Example of an unsaturated fat triglyceride. It shows glycerol and three fatty acids: palmitic acid, oleic acid, and alpha-linolenic acid.
-
Structure of the saccharolipid Kdo2-lipid A. This complex lipid has Glucosamine and Kdo parts, along with acyl chains and phosphate groups.
See also
 In Spanish: Lípido para niños
In Spanish: Lípido para niños