List of kings of Jordan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids King of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan |
|
|---|---|

Arms of His Majesty the King of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
|
|
| Incumbent | |
 |
|
| Abdullah II since 7 February 1999 |
|
| Details | |
| Style | His Majesty |
| Heir apparent | Hussein, Crown Prince of Jordan |
| First monarch | Abdullah I |
| Formation | 25 May 1946 |
| Residence | Raghadan Palace (official) Beit Al Urdun Palace (private) |
The King of Jordan is the leader of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. He is the head of state and leads the country's royal family, known as the Hashemites. People address the King as His Majesty.
Jordan is a constitutional monarchy. This means the country has a king, but his powers are guided by a constitution. In Jordan, the King has more power than many other constitutional monarchs. He is the main leader of the Jordanian Armed Forces. He also chooses the Prime Minister of Jordan and the heads of security groups. The King also appoints members of the upper house of parliament, called the Senate, and judges for the Constitutional Court.
The current King is Abdullah II. He became King on February 7, 1999. This happened after his father, Hussein, passed away.
Contents
Jordan's Royal History
- Further information: History of Jordan
The story of Jordan's monarchy began after World War I. The sons of Hussein bin Ali, who was the Grand Emir and Sharif of Mecca, became kings in both Iraq and Jordan. This happened after the Arab Revolt.
The Jordanian monarchy started in 1921. At that time, Abdullah I became the Emir of the Emirate of Transjordan. He held this role from April 11, 1921. Transjordan became an independent country on May 25, 1946. It was then called the Hashemite Kingdom of Transjordan. After gaining independence, Abdullah I became the country's first King. The country's name was later shortened to the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan on April 26, 1949. This change happened after the kingdom gained control of both sides of the Jordan River following the 1948 Arab–Israeli War.
Who Becomes King?
- Further information: Succession to the Jordanian throne
The way a new king is chosen in Jordan follows specific rules. Usually, the oldest son of the King inherits the throne. This system ensures a clear line of succession for the Hashemite family.
Kings of Jordan (1921–present)
Emirs of Transjordan (1921–1946)
| Name | Lifespan | Reign start | Reign end | Notes | Family | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Abdullah I
|
2 February 1882 – 20 July 1951 (aged 69) | 11 April 1921 | 25 May 1946 | Son of Hussein bin Ali | Hashemite |  |
Kings of Jordan (1946–present)
| Name | Lifespan | Reign start | Reign end | Notes | Family | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Abdullah I
|
2 February 1882 – 20 July 1951 (aged 69) | 25 May 1946 | 20 July 1951 (assassinated) |
Proclaimed King of Palestine by the Jericho Conference in 1948 | Hashemite |  |
Talal
|
26 February 1909 – 7 July 1972 (aged 63) | 20 July 1951 | 11 August 1952 (abdicated) |
Son of Abdullah I | Hashemite |  |
Hussein
|
14 November 1935 – 7 February 1999 (aged 63) | 11 August 1952 | 7 February 1999 | Son of Talal | Hashemite |  |
Abdullah II
|
30 January 1962 | 7 February 1999 | Incumbent | Son of Hussein | Hashemite |  |
Timeline of Jordanian Monarchs
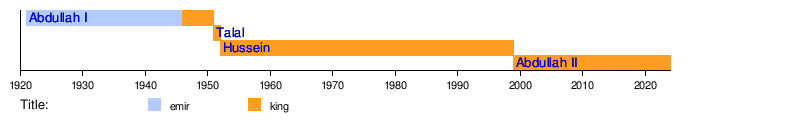
Royal Flag
More to Explore
- History of Jordan
- Royal Hashemite Court
- Crown Prince of Jordan
- List of Jordanian royal consorts
- List of Sunni dynasties
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Reyes de Jordania para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Reyes de Jordania para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |


