Long-tailed duck facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Long-tailed duck |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Male | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Anseriformes |
| Family: | Anatidae |
| Genus: | Clangula Leach, 1819 |
| Species: |
C. hyemalis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Clangula hyemalis (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The long-tailed duck (Clangula hyemalis) is a medium-sized sea duck. It's the only living member of its group, called Clangula. These ducks are known for their unique look and interesting habits.
Contents
What Do Long-Tailed Ducks Look Like?
Adult long-tailed ducks have white feathers on their bellies. Their other feathers change color throughout the year.
The male duck has a long, pointed tail that can be about 10 to 15 centimeters (4 to 6 inches) long. He has a dark gray beak with a pink band across it.
- In winter, the male has a mostly white head and neck with a dark patch on his cheek. His chest is dark, and his body is mostly white.
- In summer, the male's head, neck, and back are dark, but he has a white patch on his cheek.
The female duck has a brown back and a shorter, pointed tail.
- In winter, her head and neck are white with a dark top (crown).
- In summer, her head is dark.
Young ducks look a lot like adult females in the autumn, but their cheek patch is lighter and not as clear.
Male long-tailed ducks are quite noisy! They make a musical, yodeling sound that sounds like ow, ow, owal-ow.
Where Do Long-Tailed Ducks Live and What Do They Eat?
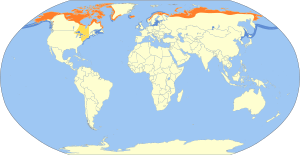
Long-tailed ducks breed in cold, open areas called tundra. They like pools and marshes, but also live along sea coasts and big mountain lakes. You can find them in places like the North Atlantic, Alaska, northern Canada, northern Europe, and Russia.
Their nests are built on the ground near water. They use plants and soft feathers (down) to make them cozy.
These ducks travel long distances. They spend their winters along the eastern and western coasts of North America, on the Great Lakes, and along the coasts of northern Europe and Asia. The Baltic Sea is a very important winter home for them, with about 4.5 million ducks gathering there!
Long-tailed ducks like to be with other ducks. They form large groups in winter and when they are migrating. They find their food by diving underwater. They mostly eat mollusks (like clams and snails), crustaceans (like crabs and shrimp), and some small fish.
They usually feed close to the surface, but they are amazing divers! They can dive up to 60 meters (200 feet) deep. Some reports even say they can dive as deep as 146 meters (480 feet)! They are the only ducks that use their wings to help them dive, which allows them to go much deeper than other ducks.
Why Did Their Name Change?
In North America, the long-tailed duck was sometimes called oldsquaw. However, this name is not used much anymore because the word "squaw" can be offensive to some Native American people.
To make sure the name was respectful and to match how the bird is known in other parts of the world, scientists officially changed the name to "Long-tailed Duck." The scientific name, Clangula hyemalis, comes from Latin words: clangere means "to resound" (which fits their loud call!), and hyemalis means "of winter."
Conservation Status
The long-tailed duck is part of an agreement called the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA). This agreement helps protect birds that migrate across Africa, Europe, and Asia, making sure they have safe places to live and travel.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Pato havelda para niños
In Spanish: Pato havelda para niños






