Longitude facts for kids
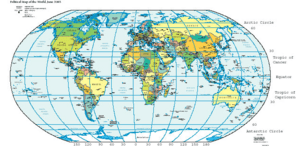
Longitude is a special way to describe exactly where a place is on our Earth. Imagine lines running from the North Pole all the way to the South Pole. These lines are called meridians. Longitude tells you how far east or west a location is from a very important starting line called the Prime Meridian.
We measure longitude using degrees, just like you measure an angle. The Prime Meridian is set at 0° (zero degrees). As you move east or west from this line, the degrees increase. The farthest you can go is 180° east or 180° west. Unlike latitude, which has the equator as a natural starting point, there isn't a natural starting line for longitude. However, most scientists and countries now agree to use the Prime Meridian.
Contents
Finding Your Location: The History of Longitude
For hundreds of years, sailors and navigators at sea found it very hard to figure out their exact longitude. Knowing your longitude was tricky because it depended on knowing the precise time at a starting point (like the Prime Meridian) and comparing it to your local time.
Solving the Longitude Puzzle
The big problem was solved in the early 19th century. This happened when people started making much better clocks, called chronometers. These special clocks were accurate enough to keep the correct time even on a rocking ship. With a reliable clock, sailors could finally calculate their longitude accurately.
How Longitude Lines Work
Longitude lines, also known as meridians, are different from latitude lines. Latitude lines are always the same distance apart. However, longitude lines are farthest apart at the equator and come closer together as they reach the North Pole and South Pole.
This means that near the poles, you don't have to travel very far to cross many degrees of longitude. For example, a short walk near the North Pole could take you across several longitude lines!
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Longitud (cartografía) para niños
In Spanish: Longitud (cartografía) para niños