Medical school facts for kids
A medical school is a type of university or college that teaches medicine. It's where people go to train to become doctors. At the end of their studies, students earn a special degree that allows them to work as physicians.
Some of the degrees a medical school can award are a Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (often shortened to MBBS or MBChB), a Doctor of Medicine (MD), or a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO). Many medical schools also offer other advanced degrees, like a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), for students who want to focus on medical research.
Besides teaching, medical schools are also important centers for medical research. They often run their own teaching hospitals where students get hands-on experience. Getting into medical school is usually very difficult. Schools look for students with top grades and high scores on special entrance exams. They also like to see that applicants have experience as leaders.
In many countries, students can go to medical school right after high school. But in the United States and Canada, you usually have to finish a four-year university degree first before you can even apply.
Contents
What is studying at medical school like?
Studying to be a doctor takes a long time, usually five or more years. The first few years are often called "pre-clinical." During this time, students learn the science behind medicine. They study subjects like anatomy (the parts of the body), physiology (how the body works), and pharmacology (how medicines work).
The later years are the "clinical" years. This is when students start working in hospitals and clinics with real patients. They do this under the supervision of experienced doctors. These hands-on experiences are called rotations. Students rotate through different areas of medicine, such as:
- Internal medicine: Dealing with diseases inside the body.
- Surgery: Learning how to perform operations.
- Pediatrics: Caring for babies and children.
- Psychiatry: Focusing on mental health.
- Obstetrics and gynecology: Caring for women, including during pregnancy and childbirth.
After graduating, a new doctor can't just start working. They must get a license from the government. This often involves passing another big exam and completing several years of extra training in a hospital. This training period is called a residency.
Medical Schools Around the World
How medical schools work can be very different from one country to another. Here are a few examples.
North America
In Canada and the United States, medical school is a graduate program. This means students must first earn a bachelor's degree, which usually takes four years. After that, they can apply to a medical school, which is another four years of study.
Admission is very competitive. Applicants need a high grade point average (GPA), a good score on the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT), and experience volunteering in healthcare.
The first two years of medical school focus on basic sciences in the classroom. The last two years are spent doing clinical rotations in hospitals. After graduating with an MD or DO degree, doctors must complete a residency program, which can last from three to seven years, depending on the specialty they choose.
Europe
In most European countries, students can enter medical school directly after finishing high school. The program usually lasts for six years. The first few years focus on pre-clinical science, and the later years are for clinical training in hospitals.
In the United Kingdom, students graduate with a degree called an MBBS or MBChB. After graduating, they must complete a two-year "foundation programme" where they work as junior doctors. Then, they can begin training in a specialty like general practice or surgery.
In Germany, medical school also takes about six years. The program ends with a big national exam. After passing, graduates get a license to practice medicine. To become a specialist, they must complete several more years of residency training.
Asia and Oceania
In countries like Australia and New Zealand, medical education is similar to the system in the United Kingdom. Students can often enter a six-year medical program after high school. After graduating, they must complete an internship in a hospital before they can become fully licensed doctors.
In India, getting into medical college is extremely competitive. Students take a national entrance exam called the NEET. The program is five and a half years long, followed by a one-year internship.
In China, medical school is usually a five-year bachelor's degree. After graduating, students must work in a hospital for one to three years before they can take the national exam to become a licensed physician.
Africa
Across Africa, most medical schools were established after 1970. Today, there are over 100 schools on the continent.
In countries like Ghana, Nigeria, and Kenya, medical education is typically a six-year program that students enter after high school. After graduating, new doctors must complete a one or two-year internship in a hospital. In many countries, they also have to spend time working in rural areas where there are fewer doctors.
In South Africa, most medical schools follow the British model of a six-year undergraduate degree. After graduating, doctors must complete a two-year internship and one year of community service to get their license.
Latin America

In many Latin American countries, such as Argentina and Brazil, medical school is a six-year program that students can enter after high school. The first few years are dedicated to basic sciences, followed by clinical training.
In Brazil, after graduating, doctors can work as general practitioners. To become a specialist, they must pass another competitive exam to get into a residency program.
In Chile, the program is seven years long, with the last two years being a full-time internship. After graduating, doctors must pass a national exam to be able to practice medicine.
Medical Students
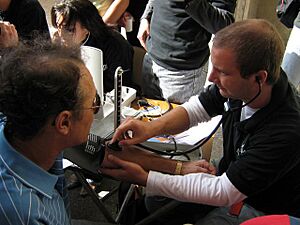
A person who is accepted into and studying at a medical school is called a medical student. The journey to becoming a doctor is long and challenging. Medical students often face a lot of stress due to the difficult classes, long hours of studying, and the emotional challenges of working with sick patients.
It is important for medical schools to provide support for their students' mental health and well-being.
Images for kids
-
Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine at the University of Hong Kong
-
Centro Hospitalario at the Eastern Central University in San Pedro de Macorís, Dominican Republic.
-
Უნივერსიტეტის-ფასადი-(1).jpg
The European University (Georgia)
-
The Dr. Guillermo Grant Benavente Regional Clinical Hospital at the University of Concepción in Chile
-
The College of Medicine at the National University of Colombia College in Bogotá
-
Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, or the Faculty of Health Sciences, the medical school at the Latin University of Panama in Panama City
-
The Hospital Clinic Manuel Quintela at University of the Republic in Montevideo
-
The Hospital Universitario de Caracas, part of the Central University of Venezuela in Caracas
-
King Edward Medical University, fourth oldest medical school in South Asia
-
Jackson Memorial Hospital in Miami, the primary teaching hospital of the University of Miami's Miller School of Medicine and the largest hospital in the United States, with 1,547 beds
-
The Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine in Philadelphia
See also
 In Spanish: Facultad de medicina para niños
In Spanish: Facultad de medicina para niños
- American Medical College Application Service (AMCAS)
- Flexner Report
- International medical graduate
- List of medical schools
- List of university hospitals
- Medical College Admission Test (MCAT)
- University Clinical Aptitude Test (UCAT)
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |





















