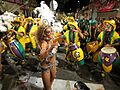Montevideo facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Montevideo
Ciudad de San Felipe y Santiago de Montevideo
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
|
||
| Motto(s):
Con libertad ni ofendo ni temo
With liberty I offend not, I fear not. |
||
| Country | ||
| Department | Montevideo | |
| Established | 1726 | |
| Founded by | Bruno Mauricio de Zabala | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Strong mayor | |
| Area | ||
| • Capital city | 201 km2 (77.5 sq mi) | |
| • Metro | 1,640 km2 (633 sq mi) | |
| The department area is 530 square kilometers (200 sq mi) and the conurbated built-up area 350 square kilometers (140 sq mi). | ||
| Elevation | 43 m (141 ft) | |
| Population
(2011 Census)
|
1,319,108 | |
| • Density | 6,726/km2 (17,421/sq mi) | |
| • Urban | 1,719,453 | |
| • Metro | 1,947,604 | |
| • Department | 1,319,108 | |
| Demonyms | montevideano (m) montevideana (f) Montevidean (English) |
|
| GDP (PPP, constant 2015 values) | ||
| • Year | 2023 | |
| • Total | $41.7 billion | |
| • Per capita | $23,500 | |
| Time zone | UTC−03:00 (Uruguay Time) | |
| • Summer (DST) | (Not Observed) | |
| Postal code |
11#00 & 12#00
|
|
| Dial plan | (+598) 2XXX XXXX | |
| HDI (2017) | 0.841 – very high | |
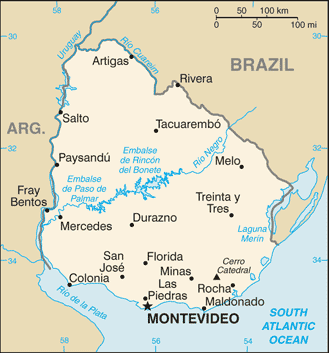
Montevideo is the capital and largest city of Uruguay. In 2011, about one-third of Uruguay's total population lived here. Montevideo is located on the southern coast of the country, along the Río de la Plata.
The city was founded by a Spanish soldier, Bruno Mauricio de Zabala, in 1726. Before that, Portuguese soldiers had set up a fort there in 1723, but the Spanish quickly took over. Montevideo was also briefly under British rule in 1807, but the Spanish soon won it back.
Today, Montevideo is an important city in Latin America. It hosts the main offices for Mercosur and ALADI, which are big trade groups in the region. It's often compared to Brussels in Europe because of its important role. Since 2005, Montevideo has been ranked as having the best quality of life in Latin America. It's known for its beautiful European-style buildings, especially those with Art Deco designs. The city is also a major center for business, education, and culture in Uruguay. In 1930, Montevideo hosted all the matches for the very first FIFA World Cup.
Contents
What's in a Name?
There are a few ideas about where the name Montevideo came from. Everyone agrees that "Monte" refers to the Cerro de Montevideo, which is a hill across the Bay of Montevideo. But the "video" part is a bit of a mystery!
- Monte vide eu ("I saw a mount"): This is the most popular story. It suggests that a Portuguese sailor from Fernando de Magallanes's trip shouted "I saw a mount!" when he saw the Cerro de Montevideo. However, most experts don't think this is likely because it mixes different languages.
- Monte Vidi: This idea comes from a sailor's diary from 1520. He wrote about a "mountain like a hat" that they called "Montevidi." This is the oldest Spanish record with a name similar to Montevideo.
- Monte-VI-D-E-O (Monte VI De Este a Oeste, meaning "Mount 6 from East to West"): A history professor, Rolando Laguarda Trías, suggested that Spanish sailors might have marked the hill as the 6th mountain they saw when sailing from east to west along the coast. Over time, these words might have combined to form "Montevideo." We don't have strong proof for this idea.
- Monte Ovídio (Monte Santo Ovídio): This less common idea suggests a religious origin. It might come from an old map that mentioned "Santo Vidio," possibly referring to a saint named Auditus of Braga. Since the Portuguese were involved in the area's early history, some think this name might have changed into "Montevideo."
When the Portuguese took over the region for a while, they called the city Montevidéu.
A Look Back: Montevideo's History
 Spanish Empire 1724–1807
Spanish Empire 1724–1807 British Empire 1807
British Empire 1807 Spanish Empire 1807–1814
Spanish Empire 1807–1814 Río de la Plata 1814–1815
Río de la Plata 1814–1815 Federal League 1815–1817
Federal League 1815–1817 U.K. of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves 1817–1822
U.K. of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves 1817–1822 Empire of Brazil 1822–1828
Empire of Brazil 1822–1828 Uruguay 1828–present
Uruguay 1828–present
Early Days
In the late 1600s, Portugal built a city called Colonia do Sacramento near where Montevideo is now. Spain didn't like this. In 1723, Portugal built a fort in Montevideo. But in 1724, a Spanish expedition from Buenos Aires, led by Bruno Mauricio de Zabala, forced the Portuguese to leave.
The Spanish then started settling the area. Families from Buenos Aires and the Canary Islands moved in. In 1724, a count of the people showed over 100 families, plus many Guaraní people and some enslaved people from Africa. The city was named San Felipe y Santiago de Montevideo.
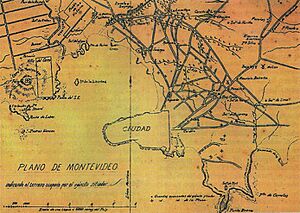
Montevideo quickly became an important city for trade in the region, even competing with Buenos Aires. It was a key port for the Spanish, especially for defending against Portuguese attacks. Until the late 1700s, Montevideo was a strong, fortified area, known today as Ciudad Vieja (Old City).
The 1800s
In 1807, British troops took over Montevideo, but the Spanish quickly won it back. After this, there were disagreements between Spanish leaders. When the Peninsular War started in Spain, the Spanish colonial government moved to Montevideo.
In 1810, a revolution began in the Rio de la Plata region. A Uruguayan revolutionary, José Gervasio Artigas, joined forces with others from Buenos Aires against Spain. They tried to take Montevideo, but the siege was lifted. The Spanish governor was finally kicked out in 1814.
In 1816, Portugal invaded the area, and in 1821, it became part of Brazil. But in 1825, a group called the Treinta y Tres Orientales (Thirty-Three Orientals) fought for independence. Uruguay became an independent country in 1828, with Montevideo as its capital. In 1829, the city's old walls were torn down to allow the city to grow.
The 1830s were a time of conflict between two leaders, Manuel Oribe and Fructuoso Rivera. Their followers became known as the Blancos (whites) and Colorados (reds). This led to a long civil war called the Guerra Grande (Great War), which lasted from 1843 to 1851. Montevideo was under siege for eight years during this war. The city was very diverse, with many Italians, Spanish, and Argentines living there.
After the war, Montevideo began to grow rapidly. New things like stagecoach bus lines, natural gas street lights, and public sanitation were introduced. The Solís Theatre opened in 1856. In the 1860s, areas like Aguada and Cordón became part of the city. An underwater telegraph line connected Montevideo with Buenos Aires in 1866. Horse-drawn trams started running in 1868, connecting the city to other towns. The first railway line opened in 1869. Public water supply was established in 1871. Electric street lights replaced gas lights in 1886. The new port was built in 1894, and the Central Railway Station opened in 1897.
The 1900s
In the early 1900s, many Europeans, especially from Spain and Italy, moved to Montevideo. The city grew quickly, adding new neighborhoods like Villa del Cerro and Pocitos. Important places like Rodó Park and the Estadio Gran Parque Central were built. Uruguay also saw big social changes, like women getting the right to divorce (1907) and the right to vote.
The 1910s brought more changes, including the building of Montevideo's Rambla (coastal avenue) and the start of electric trams. In 1913, the city limits expanded to include more areas.
During the 1920s, the Legislative Palace was built, and the Estadio Centenario was started in 1929 and finished in 1930 for the first FIFA World Cup.
World War II and After
During World War II, a famous event happened near Montevideo. A German warship, the Admiral Graf Spee, was damaged in a battle and went to Montevideo's port, which was neutral. To avoid losing his crew in another fight, the captain decided to sink the ship himself in 1939.
After the war, Uruguay's economy slowed down in the mid-1950s, and Montevideo faced challenges. There was social and political unrest starting in 1968, and a military dictatorship from 1973 to 1985. Many people were affected by political violence. In 1980, the people of Uruguay voted against a new constitution proposed by the military, which helped bring back democracy in 1985.
In the 1980s, Pope John Paul II visited Montevideo twice.
The 2000s
Montevideo has seen good economic growth since the early 2000s. The city continues to be ranked as having the best quality of life in Latin America.
Montevideo's Location
Montevideo is located on the northern shore of the Río de la Plata. This is a large arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Uruguay from Argentina. Buenos Aires, Argentina, is about 230 kilometers (140 mi) to the west. The Santa Lucía River forms a natural border to the west of Montevideo. To the north and east, the city borders Canelones Department.
The coastline of Montevideo has both rocky areas and sandy beaches. The Bay of Montevideo is a natural harbor, which is the largest in Uruguay and very important for the country's economy and trade. Several small rivers flow through the city and into the bay. The city's average height above sea level is 43 meters (141 ft). The highest points are the Cerro de Montevideo and Cerro de la Victoria, with the Cerro de Montevideo's peak reaching 134 m (440 ft), topped by the Fortaleza del Cerro.
Weather in Montevideo
Montevideo has a Humid subtropical climate with four seasons. The weather is generally mild, meaning it doesn't get extremely cold or extremely hot. There are often thunderstorms, but no tropical cyclones. Rain falls regularly throughout the year.
- Winters (June to August) are cool, wet, and often cloudy. Temperatures are usually between 10 °C (50 °F) and 18 °C (64 °F) during the day. Sometimes, cold winds can make it feel chilly, but temperatures rarely drop below −2 °C (28 °F) because the ocean helps keep it warmer. Snow is extremely rare.
- Summers (December to February) are warm and humid. Daytime temperatures are usually between 24 °C (75 °F) and 32 °C (90 °F). A gentle sea breeze often cools the city in the evenings. Heat waves can occur, with temperatures rising above 35 °C (95 °F), often followed by thunderstorms that bring cooler air.
- Autumn (March to May) is usually pleasant, with daytime temperatures around 20 °C (68 °F).
- Spring (September to November) has similar temperatures to autumn but can be windier and have more sudden weather changes.
The average yearly temperature in Montevideo is 16.7 °C (62.1 °F). The coldest temperature ever recorded was −5.6 °C (21.9 °F), and the hottest was 42.8 °C (109.0 °F).
| Climate data for Montevideo (Prado) 1991–2020, extremes 1901–2020 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 42.8 (109.0) |
40.3 (104.5) |
38.4 (101.1) |
36.7 (98.1) |
32.0 (89.6) |
27.8 (82.0) |
29.8 (85.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.7 (90.9) |
35.8 (96.4) |
38.2 (100.8) |
40.8 (105.4) |
42.8 (109.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 27.8 (82.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
22.0 (71.6) |
18.5 (65.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
14.7 (58.5) |
16.7 (62.1) |
17.9 (64.2) |
20.7 (69.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
26.4 (79.5) |
21.4 (70.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 23.3 (73.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
21.2 (70.2) |
18.1 (64.6) |
14.8 (58.6) |
11.9 (53.4) |
11.0 (51.8) |
12.6 (54.7) |
13.9 (57.0) |
16.5 (61.7) |
19.2 (66.6) |
21.8 (71.2) |
17.3 (63.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 18.8 (65.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
17.1 (62.8) |
14.1 (57.4) |
11.0 (51.8) |
8.1 (46.6) |
7.3 (45.1) |
8.5 (47.3) |
9.9 (49.8) |
12.4 (54.3) |
14.7 (58.5) |
17.1 (62.8) |
13.1 (55.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
6.8 (44.2) |
3.8 (38.8) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
2.5 (36.5) |
5.0 (41.0) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 94.6 (3.72) |
93.8 (3.69) |
105.8 (4.17) |
111.1 (4.37) |
83.4 (3.28) |
89.4 (3.52) |
93.2 (3.67) |
89.9 (3.54) |
92.1 (3.63) |
102.2 (4.02) |
95.9 (3.78) |
91.3 (3.59) |
1,142.7 (44.99) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 79 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70 | 73 | 76 | 77 | 79 | 81 | 80 | 78 | 76 | 74 | 72 | 70 | 76 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 294.5 | 234.5 | 220.1 | 162.0 | 161.2 | 126.0 | 142.6 | 164.3 | 180.0 | 226.3 | 249.0 | 282.1 | 2,442.6 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 9.5 | 8.3 | 7.1 | 5.4 | 5.2 | 4.2 | 4.6 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 7.3 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 6.7 |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 14.2 | 13.3 | 12.3 | 11.2 | 10.3 | 9.8 | 10.1 | 10.9 | 11.9 | 13 | 14 | 14.5 | 12.1 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 12 | 11 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 7 |
| Source 1: Instituto Uruguayo de Metereología | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Instituto Nacional de Investigación Agropecuaria (sun and humidity 1980–2009), NOAA (precipitation 1991–2020)
Source 3: Weather Atlas(daylight-UV) |
|||||||||||||
| Sea temperature data for Montevideo | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average sea temperature °C (°F) | 24.2 (75.6) |
23.4 (74.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
19.0 (66.2) |
15.9 (60.6) |
13.1 (55.6) |
11.3 (52.3) |
12.1 (53.8) |
13.3 (55.9) |
17.2 (63.0) |
19.8 (67.6) |
21.9 (71.4) |
17.8 (64.0) |
| Source: Weather Atlas | |||||||||||||
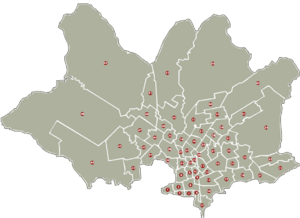
City Areas and Neighborhoods
Montevideo is divided into 8 political areas called Municipios, each with its own elected mayor. This helps local people have a say in how their city is run.
More importantly, the city is divided into 62 barrios, which are like neighborhoods or districts. Many of these neighborhoods, such as Sayago and Pocitos, used to be separate towns that grew and became part of Montevideo. Others grew around factories. Each barrio has its own unique feel and activities. The Ciudad Vieja (Old City) is very important because it has many old buildings from when the city was first founded.
- Ciudad Vieja
- Centro
- Barrio Sur
- Aguada
- Villa Muñoz, Goes, Retiro
- Cordón
- Palermo
- Parque Rodó
- Tres Cruces
- La Comercial
- Larrañaga
- La Blanqueada
- Parque Batlle – Villa Dolores
- Pocitos
- Punta Carretas
- Unión
- Buceo
- Malvín
- Malvín Norte
- Las Canteras
- Punta Gorda
- Carrasco
- Carrasco Norte
- Bañados de Carrasco
- Flor de Maroñas
- Maroñas – Parque Guaraní
- Villa Española
- Ituzaingó
- Castro – Pérez Castellanos
- Mercado Modelo – Bolívar
- Brazo Oriental
- Jacinto Vera
- La Figurita
- Reducto
- Capurro – Bella Vista, Arroyo Seco
- Prado – Nueva Savona
- Atahualpa
- Aires Puros
- Paso de las Duranas
- Belvedere
- La Teja
- Tres Ombúes – Pueblo Victoria
- Villa del Cerro
- Casabó – Pajas Blancas, Rincón del Cerro
- La Paloma – Tomkinson
- Paso de la Arena – Los Bulevares – Santiago Vázquez
- Nuevo París
- Conciliación
- Sayago
- Peñarol – Lavalleja
- Colón Centro y Noroeste
- Lezica – Melilla
- Colón Sudeste – Abayubá
- Manga – Toledo Chico
- Casavalle, Barrio Borro
- Cerrito de la Victoria
- Las Acacias
- Jardines del Hipódromo
- Piedras Blancas
- Manga
- Punta de Rieles - Bella Italia
- Villa García – Manga Rural
Famous Landmarks

Montevideo's buildings show a mix of styles, from old Neoclassical buildings to modern skyscrapers like the World Trade Center Montevideo and the ANTEL Telecommunication Tower. The old town's buildings reflect the many European immigrants who came to the city.
Legislative Palace

The Legislative Palace is where the Uruguayan Parliament meets. It's north of the city center. Construction began in 1904 and it was designed by Italian architects. Many artists helped create its beautiful interior.
World Trade Center Montevideo
The World Trade Center Montevideo is a modern business complex that opened in 1998. It has several towers and buildings, including a large central square called Towers Square. This square is used for business events, art shows, and music performances. It also connects the different buildings. A sculpture by the famous Uruguayan artist Pablo Atchugarry is located here.
Telecommunications Tower
The Telecommunications Tower, also known as Antel Tower, is the tallest building in Uruguay. It's 158 meters (518 ft) tall and has 37 floors. It's the headquarters for Uruguay's government-owned phone company, ANTEL. It was finished in 2000.
Old City (Ciudad Vieja)
The Ciudad Vieja is the oldest part of Montevideo. It has many colonial buildings and historical sites. Today, it's a lively area with banks, offices, museums, art galleries, restaurants, and nightclubs. Uruguay's main port is also located here.
Montevideo's most important square is Plaza Independencia. It sits between the Old City and downtown. At one end, you can see the old gateway of the city's original wall. Many important buildings are around this plaza.
The Solís Theatre is Uruguay's oldest theater, built in 1856. It was renovated and reopened in 2004. The plaza also has the offices of the President of Uruguay. In the center of the plaza is the Artigas Mausoleum, where José Gervasio Artigas, a hero of Uruguay's independence, is buried. Guards stand watch there.
The Palacio Salvo, a tall building with an antenna, stands at the edge of Plaza Independencia. It was finished in 1925 and was designed by an Italian architect. It's built where a famous tango song, "La Cumparsita", was written.
Another important square in the Old City is Plaza de la Constitución. Here you'll find the Cabildo, which was the government seat during colonial times, and the Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral. The cathedral is where many famous Uruguayans are buried.
Parque Batlle
Parque Batlle is a large public park in Montevideo. It's one of the city's main green spaces. The park and the area around it form one of Montevideo's 62 neighborhoods. This neighborhood is close to the coast and has many people living there.
The park is named after José Batlle y Ordóñez, a former President of Uruguay. It was designed by a French landscape architect. In 1975, it was made a National Historic Monument Park. The park covers about 60 hectares (150 acres) and is considered the "lung" of the city because of its many trees.

The Estadio Centenario, Uruguay's national football stadium, is located in Parque Batlle. It opened in 1930 for the first World Cup. Uruguay won that World Cup! The stadium has 70,000 seats and is considered one of the classic football stadiums in the world. There's also a museum inside the stadium.
You can also find the "La Carreta" monument in the park, which is a bronze statue of oxen pulling a wagon. The Obelisk of Montevideo, a tall granite monument, is also in Parque Batlle. It honors those who created Uruguay's first Constitution.
Parque Prado
Parque Prado is the largest of Montevideo's main public parks, created in 1873. It's in the northern part of the city, with a stream flowing through it.
Popular spots in the park include the Rosedal (a rose garden with 12,000 roses imported from France), the Botanical Garden, and the area around the Hotel del Prado. The Rural del Prado is a fairground for farm animals. There are also paths for jogging along the Miguelete river.
The President's official home is located behind the Botanical Gardens. The Juan Manuel Blanes Museum, which has a Japanese garden, is also in the park.
Parque Rodó
Parque Rodó is both a neighborhood and a park in Montevideo. It's named after José Enrique Rodó, a famous Uruguayan writer. The park has an amusement park, a football stadium, and an artificial lake with a children's library inside a small castle.
On the east side of the park is the National Museum of Visual Arts. A street market is held here every Sunday. West of the park is Ramirez Beach. The Edifício Mercosur, where the parliament of the Mercosur countries meets, is also located near the park.
Historic Forts
Montevideo has a history of forts built to protect it. The first forts were planned by the Portuguese in the early 1700s to stop Spanish attacks.
Fortaleza del Cerro
The Fortaleza del Cerro overlooks the Bay of Montevideo. An observation post was first built here in the late 1700s. The fortress itself was built between 1809 and 1839. It has been part of many historical events and has been taken over by different groups over time. Since 1916, it has been a military museum and is now a popular tourist spot.
Punta Brava Lighthouse
The Punta Brava Lighthouse, also known as Punta Carretas Lighthouse, was built in 1876. It's 21 meters (69 ft) tall and its light can be seen from 24 km (15 mi) away. It helps guide ships into the harbor.
The Rambla
The Rambla is a long avenue that runs along the entire coastline of Montevideo. It's a very important place for fun and relaxation in the city. People go there to walk, jog, bike, roller skate, fish, and even skateboard. Its 27-kilometer (17 mi) length makes it one of the longest coastal paths in the world.
Montevideo is also known for its beaches, which are very popular, especially in summer. Some of the best-known beaches are Ramírez, Pocitos, Carrasco, Buceo and Malvín.
Cemeteries
Montevideo has five large cemeteries. The largest is the Cementerio del Norte. The Central Cemetery is one of Uruguay's oldest, founded in 1835. Many famous Uruguayans are buried there.
The British Cemetery Montevideo is another old cemetery, located in the Buceo neighborhood. Many important people are buried there, including sailors from different countries.
People of Montevideo
In 1860, Montevideo had about 58,000 people, including many of African origin who had been brought as slaves and later became free. By 1880, the population had grown a lot due to European immigration. In the 1900s, many more Europeans, especially from Spain and Italy, moved to the city.
According to the 2011 census, Montevideo had 1,319,108 people. The population has changed over time, with fewer births and some people moving away, but it remains the largest city in Uruguay.
| 1860 | 1884 | 1908 | 1963 | 1975 | 1985 | 1996 | 2004 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58,000 | 164,028 | 309,331 | 1,202,890 | 1,176,049 | 1,251,511 | 1,303,182 | 1,269,552 | 1,319,108 |
Source: Instituto Nacional de Estadística de Uruguay
Culture and Fun

Montevideo is a city with a rich culture, including architecture, writers, artists, and musicians. The city is part of the UNESCO Creative Cities Network for Literature.
The Arts
Uruguayan tango is a special dance that started in Montevideo in the late 1800s. Tango, candombe, and murga are the main music styles here. The city is also a center for Uruguayan films. There are many movie theaters and theaters for plays. The Solís Theatre is the most famous theater in Uruguay and the oldest in South America.
Visual Arts
Montevideo has many art museums and galleries. The Virtual Museum of Contemporary Uruguayan Art shows exhibitions online. During a time of military rule in the 1970s, art suffered, but artists found ways to continue their work.
Literature
Montevideo has a long history of literature. The first public library was created in 1815. The National Library of Uruguay has about 900,000 books.
In the early 1900s, Montevideo was called the "Athens of the Rio de la Plata" because of its many great writers like José Enrique Rodó and Delmira Agustini. Later, famous authors like Juan Carlos Onetti and Eduardo Galeano came from Montevideo.

Music
Tango, milonga, and vals criollo are very popular in Montevideo. Many famous songs, like "La Cumparsita", were created here. There are many places in the city where you can enjoy tango music and dance. Montevideo also hosts a Jazz Festival.
Food in Montevideo
The Mercado del Puerto (Port Market) is a great place to find traditional Uruguayan food. Beef is a very important part of Uruguayan cooking. A torta frita is a popular fried cake eaten throughout the city. Montevideo has many different types of restaurants, from local dishes to Japanese food.
Fun and Recreation
Museums
Montevideo has many interesting museums. The Montevideo Cabildo was the government building during colonial times. It's now a museum that shows artifacts from Uruguay's history.
The Palacio Taranco is a beautiful palace that is now the Museum of Decorative Arts. It has collections of European paintings, ancient Greek and Roman art, and Islamic ceramics.
The National History Museum of Montevideo shows items related to Uruguay's history. It also includes several historical houses in the city, like the home of Giuseppe Garibaldi, a famous Italian general who lived in Montevideo in the 1840s.
The Museo Torres García displays the unique paintings of Joaquín Torres García, a famous Uruguayan artist.
Other museums include the Centro de Fotografía de Montevideo (for photography), the National Museum of Visual Arts (with Uruguay's largest painting collection), and the Juan Manuel Blanes Museum (focused on Uruguayan patriotic art). There's also the Museo del Gaucho y de la Moneda, which shows the culture of Uruguay's cowboys (gauchos), and the Museo Naval, which covers Uruguay's maritime history.
Festivals
Montevideo hosts many festivals, including a Gaucho festival where people ride horses in traditional cowboy clothes. The biggest annual event is the Montevideo Carnival. It's part of a national festival that lasts for two days, but many businesses close for the whole week because it's so important. During Carnival, there are many outdoor performances and competitions. The "Desfile de las Llamadas" (Parade of the Calls) is a big parade where people march with drums.
Sports
The Estadio Centenario, the national football stadium, is in Parque Batlle. It opened in 1930 for the first World Cup, which Uruguay won! The stadium is considered one of the classic football stadiums in the world.
Montevideo is home to many football teams in Uruguay's top leagues, including Nacional and Peñarol.
The city also hosts major international basketball tournaments. Most of Uruguay's basketball teams are from Montevideo. Rugby, horse racing, golf, and yachting are also popular sports in the city.
Religion
Most people in Montevideo are Roman Catholic. The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Montevideo was created in 1830. The main Catholic church is the Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral, located in the Old City. It was consecrated in 1804.
Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral
The Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral is the main Roman Catholic church in the city. It's in the Old City, across from Constitution Square. It was built in the late 1700s and early 1800s. Important ceremonies are held here, and it was once a burial place for famous people.
Nuestra Señora del Sagrado Corazón
Nuestra Señora del Sagrado Corazón, also known as Punta Carretas Church, was built between 1917 and 1927. It has a Romanesque Revival style.
Economy and Business
Montevideo is the economic and political heart of Uruguay. Many of the country's largest businesses have their main offices here. Since the 1990s, the city has grown economically, with new buildings like the World Trade Center Montevideo and the Telecommunications Tower.
The Port of Montevideo is one of the most important ports in South America. It's growing quickly and is very important for Uruguay's trade with other countries. The city has received money to modernize the port and make it more efficient.
Many important state-owned companies in Uruguay are based in Montevideo, including those for railways, energy, ports, and telecommunications. Banking is also a strong part of Montevideo's economy, with many local and international banks operating here.
Tourism
Tourism is a big part of Uruguay's economy. In Montevideo, tourism often focuses on the Ciudad Vieja (Old City), with its old buildings, museums, and nightclubs. Sarandí Street and the Mercado del Puerto are popular spots.
Plaza Independencia is another key tourist area, surrounded by sights like the Solís Theatre and the Palacio Salvo. It's also the start of 18 de Julio Avenue, a major street for shopping and sightseeing, known for its Art Deco buildings and public squares.
Along the coast, the Fortaleza del Cerro, the Rambla (coastal avenue), and the sandy beaches attract many visitors. Most tourists come from Argentina, Brazil, and Europe, but more and more visitors are coming from other parts of Latin America and the United States.
Shopping
Montevideo is the main shopping center in Uruguay. The city has many modern buildings and shopping malls. In 1985, the first shopping center, Montevideo Shopping, was built. Later, more malls like Shopping Tres Cruces, Portones Shopping, and Punta Carretas Shopping opened. These malls changed how people in Montevideo shopped. Big international fast-food chains are also found here. In 2013, Nuevocentro Shopping opened.
Besides the large malls, you can find many shops along 18 de Julio Avenue in the Centro and Cordón neighborhoods.
Getting Around Montevideo
Public Buses
Montevideo has a large bus network that covers the city and nearby areas. It's managed by the city government and the Ministry of Transport. The Baltasar Brum Terminal in the Old City is the main bus station for city buses.
Taxis
Most taxis in Montevideo are white with a yellow band. They use a meter to calculate the fare based on distance. You can pay with cash or credit card.
Trains
The State Railways Administration of Uruguay (AFE) runs three train lines that connect Montevideo to nearby suburban areas. Within the city, trains stop at several stations. The historic General Artigas Central Station closed in 2003, and a new station near the Telecommunications Tower now handles train traffic. Train service is currently paused for upgrades.
Intercity Buses
The Tres Cruces bus station is Uruguay's main bus terminal for long-distance buses. These buses travel to other parts of Uruguay and to other countries. It opened in 1994 and serves over 12 million passengers each year.
Air Travel
Montevideo is served by the Carrasco International Airport (MVD), located about 19 km (12 mi) from the city center. It handles over 1.5 million passengers annually and is known for being efficient and traveler-friendly.
Ángel S. Adami Airport is a smaller private airport used by charter companies and a flight school.
Port and Ferries

Montevideo also has a ferry system run by the company Buquebus, which connects the port with Buenos Aires, Argentina. Over 2.2 million people travel between the two countries by ferry each year. Some ferries are very fast, reaching speeds of about 80 km/h (50 mph).
The port on Montevideo Bay was a key reason the city was founded. It provides natural protection for ships. The port has grown a lot and is very important for trade. Many businesses related to import/export and naval activities are located near the port.
Cycling
Montevideo has bicycle paths in the Old City, Artigas Boulevard, and city center. There are also bike racks throughout the city. In 2013, a "South Bicicircuito" was opened, connecting university buildings. The city has over 100 bike stations, and in 2014, a bike-sharing system called Movete was launched.
Learning in Montevideo
Public Education
The University of the Republic is Uruguay's largest and most important university. It was founded in 1849 in Montevideo, where most of its buildings are still located. Many famous Uruguayans have studied here. The university has 14 faculties (departments) and various schools.
Private Education
The largest private university in Uruguay, ORT Uruguay, is also in Montevideo. It started as a non-profit organization in 1942 and became a private university in 1996. It focuses on science and technology.
The Montevideo Crandon Institute is an American school with a missionary background, founded in 1879. It's known for being one of the most traditional schools in the city.
The Christian Brothers of Ireland Stella Maris College is a private Catholic school in the wealthy Carrasco neighborhood. It's considered one of the best high schools in the country.
Also in Carrasco is The British Schools of Montevideo, founded in 1908. It aims to give children a complete education based on British school principles.
St. Brendan's School in Cordon is a bilingual school known for being one of the best in the country. It uses a teaching approach that focuses on the whole child and is the only school in Uruguay to offer all three International Baccalaureate Programmes.
Healthcare in Montevideo
Montevideo has both public and private healthcare services, including clinics and hospitals.
Public Hospitals
The Hospital de Clínicas "Dr. Manuel Quintela" is a university hospital connected to the University of the Republic. It's a general hospital for adults.
Hospital Maciel is one of Uruguay's oldest hospitals. It was founded in the late 1700s by a kind person named Francisco Antonio Maciel.
Hospital Pereira Rossell was founded in 1908 as the city's first pediatric (children's) hospital. It later became the first maternity hospital too.
Hospital Vilardebó is Montevideo's only psychiatric hospital, opened in 1880. It was once one of the best in Latin America.
Other public hospitals include Hospital Saint Bois, Pasteur Hospital, and the National Cancer Institute.
Private Healthcare
Many private health insurance companies offer healthcare in Montevideo. They have their own clinics and hospitals. Some well-known private medical facilities include the Hospital Británico and the Italian Hospital of Montevideo.
International Connections
Montevideo is connected with many cities around the world through "twin town" or "sister city" relationships. This means they share culture, ideas, and friendship.
Twin Towns and Sister Cities
 Arica, Chile
Arica, Chile Asunción, Paraguay
Asunción, Paraguay Barcelona, Spain
Barcelona, Spain Berisso, Argentina
Berisso, Argentina Bluefields, Nicaragua
Bluefields, Nicaragua Brasília, Brazil
Brasília, Brazil Cádiz, Spain
Cádiz, Spain Cali, Colombia
Cali, Colombia Ceuta, Spain
Ceuta, Spain Cochabamba, Bolivia
Cochabamba, Bolivia Córdoba, Argentina
Córdoba, Argentina Coroico, Bolivia
Coroico, Bolivia Cumaná, Venezuela
Cumaná, Venezuela Curitiba, Brazil
Curitiba, Brazil El Aaiun, Western Sahara
El Aaiun, Western Sahara Esmeraldas, Ecuador
Esmeraldas, Ecuador Hurlingham, Argentina
Hurlingham, Argentina La Plata, Argentina
La Plata, Argentina Libertador, Venezuela
Libertador, Venezuela Lisbon, Portugal
Lisbon, Portugal Mar del Plata, Argentina
Mar del Plata, Argentina Marsico Nuovo, Basilicata, Italy
Marsico Nuovo, Basilicata, Italy Melilla, Spain
Melilla, Spain Mississauga, Ontario, Canada
Mississauga, Ontario, Canada Montevideo, Minnesota, United States< (relationship began in 1905)
Montevideo, Minnesota, United States< (relationship began in 1905) Paris, France
Paris, France Port-au-Prince, Haiti
Port-au-Prince, Haiti Qingdao, Shandong, China
Qingdao, Shandong, China Quebec City, Canada
Quebec City, Canada Rosario, Argentina
Rosario, Argentina Saint Petersburg, Russia
Saint Petersburg, Russia Santa Cruz, Bolivia
Santa Cruz, Bolivia São Paulo, Brazil
São Paulo, Brazil Satriano di Lucania, Basilicata, Italy
Satriano di Lucania, Basilicata, Italy Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China Talamanca, Costa Rica
Talamanca, Costa Rica Tambo de Mora, Peru
Tambo de Mora, Peru Tianjin, China
Tianjin, China Tito, Basilicata, Italy
Tito, Basilicata, Italy Tumaco, Colombia
Tumaco, Colombia Ulsan, South Korea
Ulsan, South Korea Wrocław, Poland
Wrocław, Poland Wuhu, Anhui, China
Wuhu, Anhui, China
Montevideo is also part of the Union of Ibero-American Capital Cities, a group of capital cities in Latin America, Spain, and Portugal.
Images for kids
-
Pocitos is the most populous Montevideo neighborhood.
-
The Legislative Palace.
-
Obelisk of Montevideo in the Parque Batlle.
-
Solis Theatre in Montevideo
-
The writer Eduardo Galeano.
-
Buquebus high-speed ferries connect Montevideo to Argentina
See also
 In Spanish: Montevideo para niños
In Spanish: Montevideo para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |