Millennialism facts for kids
Millennialism is a belief held by some religions. It's about a special time, often called a "Messianic Age," that will happen on Earth before the final judgment and the start of eternity. This idea often involves a period of a thousand years.
Both Christianity and Judaism have had groups that believed in a coming earthly kingdom of God. These beliefs sometimes caused big changes or even unrest in society.
Other religions, like Zoroastrianism, also have similar ideas. They talk about different thousand-year periods, each ending in big changes, until evil is finally defeated by a peaceful king.
Scholars also connect this idea to other social and political movements, even non-religious ones.
Contents
Understanding Millennialism in Christianity
Most Christian ideas about millennialism come from the Book of Revelation in the Bible. Specifically, chapter 20 describes a vision where an angel traps Satan for a thousand years.
The Bible says:
He seized the dragon, that ancient serpent, who is the Devil and Satan, and bound him for a thousand years and threw him into the pit and locked and sealed it over him, so that he would deceive the nations no more, until the thousand years were ended. After that, he must be let out for a little while.
After this, the Book of Revelation describes people sitting on thrones as judges. It also talks about the souls of those who died for believing in Jesus. These souls:
came to life and reigned with Christ a thousand years. (The rest of the dead did not come to life until the thousand years were ended.) This is the first resurrection. Blessed and holy are those who share in the first resurrection. Over these the second death has no power, but they will be priests of God and of Christ, and they will reign with him a thousand years
Early Christian Beliefs
In the first few centuries after Jesus, Christians had different ideas about this "thousand-year" period.
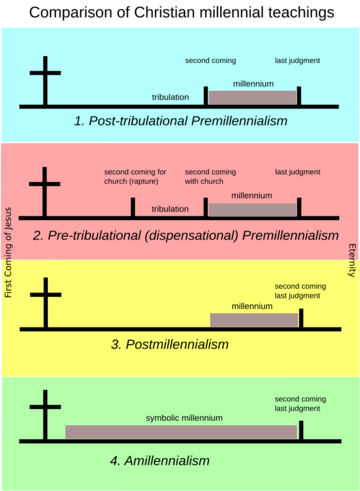
Premillennialism
Some early Christians believed in "Premillennialism." This means they thought Jesus would return to Earth before the thousand-year reign. They believed Jesus would rule physically on Earth during this time. Important figures like Irenaeus and Justin Martyr held these views.
Amillennialism
Other early Christians believed in "Amillennialism." This view says the thousand-year reign isn't a literal time on Earth. Instead, they saw it as a symbolic period, like Jesus's rule through the church right now. Origen and Dionysius of Alexandria were among those who held this view. Later, Augustine, a very influential Christian thinker, also supported amillennialism, which made it very popular.
Millennial Views After the Reformation
After the Protestant Reformation around 1517, Christians started to have many different ideas about the future. They focused more on the Book of Revelation. This book talks about Satan being locked away for 1000 years, then released for a final battle.
Before the Reformation, Catholic and Orthodox churches didn't have one clear idea about what this meant. They mostly believed the world would end suddenly and that an "antichrist" would appear. Millennial theories try to explain what this "1000 years of Satan bound" would be like.
Today, especially among Protestants, there are three main types of millennialism:
- Premillennialism: This view believes Jesus will return before the thousand-year period. He will then rule on Earth physically.
- Postmillennialism: This view believes Jesus will return after the thousand-year period. They think the world will get better and better through the church, leading to a golden age, and then Jesus will return.
- Amillennialism: This view sees the thousand-year kingdom as happening now through the church. It's not a future earthly reign. They believe the new heavens and new earth will appear when Jesus returns.
The Catholic Church generally doesn't support millennialism. They believe that the hope for a perfect kingdom can only happen beyond history, not within it.
Modern Millennial Movements
Bible Student Movement
The Bible Student movement, started by Charles Taze Russell in the late 1800s, believes everyone will have a chance to live forever on Earth during the Millennium.
Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses believe Jesus will rule from heaven for 1,000 years as king over Earth. They think Earth will become a paradise, like the Garden of Eden, and people will become perfect again.
The Church of Almighty God
This group, also known as Eastern Lightning, teaches about an "Age of Millennial Kingdom" that will follow big disasters mentioned in the Bible.
Millennialism in Judaism
Ideas similar to millennialism appeared in Jewish writings during a difficult time called the Second Temple period.
A scholar named Gerschom Scholem wrote about Jewish millennial beliefs from the Middle Ages. He focused on a 17th-century movement led by Sabbatai Zevi, who claimed to be the Messiah.
Millennialism in Islam
Muslims believe that before the Day of Judgment, Jesus will return to Earth. He will become a fair ruler over everyone. This is mentioned in Islamic texts called Hadiths.
Millennialism in the Baha'i Faith
The Baháʼí Faith teaches that God renews the "City of God" about every thousand years. Baháʼu'lláh, the founder, said that a new Manifestation of God (a prophet or messenger) would not appear for 1,000 years after his time (1852–2852 CE). However, his message could last for up to 500,000 years.
Millennialism in Social Movements
Millennial social movements are based on the idea of a thousand-year cycle. These movements don't always have to be religious. They often have a vision of a big change, which can be either a perfect world (utopia) or a terrible one (dystopia).
In progressive millennialism, people believe society will slowly get better, and humans help make that change happen.
In catastrophic millennialism, people think the current society is so bad that it needs to be completely destroyed before a new, good order can be built.
Nazism and the "Third Reich"
One very controversial example linked to millennialism is Adolf Hitler's "Third Reich" (meaning "Third Empire"). Hitler imagined it would last for a thousand years, calling it the "Tausendjähriges Reich" (Thousand-Year Reich). However, it only lasted 12 years (1933–1945).
A German thinker named Arthur Moeller van den Bruck came up with the phrase "Third Reich." He looked at German history and saw three ages, similar to the ideas of a 12th-century theologian named Joachim of Fiore:
- The Holy Roman Empire (starting around 800 AD) was the "First Reich."
- The German Empire (1871–1918) was the "Second Reich."
After a period of democracy, the "Third Reich" was supposed to follow. Even though van den Bruck didn't like Hitler, the Nazis used the term "Third Reich" for the powerful state they wanted to create.
Many Germans in the early years of the Third Reich even called Hitler the "German Messiah." This was especially true during his big rallies in Nuremberg.
Hitler himself spoke about building a "millennial city" for a "thousand-year-old people" with a "thousand-year-old history."
After Hitler's attempt to create a thousand-year reign failed, the Holy See (the Vatican) officially stated that literal millennial claims couldn't be taught safely. They said that the scriptures in Revelation should be understood spiritually, not literally.
Utopianism
Early Christian ideas about millennialism also influenced the concept of utopia (a perfect society).
The Italian monk Joachim of Fiore (who died in 1202) saw human history in three ages:
- The Age of the Father (Old Testament times).
- The Age of the Son (New Testament times).
- The Age of the Holy Spirit (which he believed would start around 1260). He thought that in this age, all believers would live like monks, full of praise for God, for a thousand years until Judgment Day.
Joachim of Fiore's ideas also influenced the New Age movement. They connected his "Three Ages" to astrological ideas. For example, the Age of the Father became the Age of Aries, the Age of the Son became the Age of Pisces, and the Age of the Holy Spirit was called the Age of Aquarius. The current "Age of Aquarius" is supposedly a time of great changes for humankind, similar to some millennial beliefs.
Images for kids
See also
- Christian eschatology
- Christian Zionism
- Millenarianism
- New religious movement