Monoamine oxidase inhibitor facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Monoamine oxidase inhibitor |
|
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
Ribbon diagram of human monoamine oxidase B, from PDB 1GOS
|
|
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | MAOI, RIMA |
| Use | Treatment of major depressive disorder, atypical depression, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders |
| ATC code | N06AF |
| Mechanism of action | Enzyme inhibitor |
| Biological target | Monoamine oxidase enzymes: MAO-A and/or MAO-B |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D008996 |
| Legal status | |
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a type of medicine. They work by stopping the activity of certain enzymes in the body. These enzymes are called monoamine oxidases. There are two main types: MAO-A and MAO-B.
MAOIs are well known for helping people with depression, especially when other treatments haven't worked. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and Parkinson's disease.
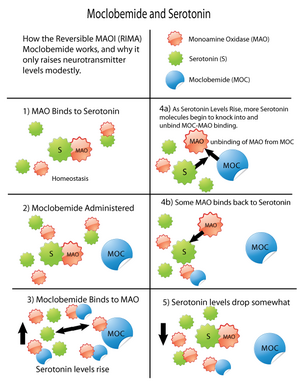
Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a special kind of MAOI. They only affect the MAO-A enzyme and their effect can be reversed. RIMAs are used to treat depression and a milder form of depression called dysthymia.
Contents
What MAOIs Are Used For
MAOIs can help with many conditions. They are effective for panic disorder and social anxiety. They also help with certain types of depression, like atypical depression.
Some people with bulimia or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) might also use MAOIs. There are reports that MAOIs can help with bipolar depression.
MAOIs are also used to treat Parkinson's disease. For this, they mainly target the MAO-B enzyme. They can also help prevent migraine headaches. When both MAO-A and MAO-B are stopped, it helps treat clinical depression and anxiety.
Newer MAOIs, like selegiline and moclobemide, are often safer. They can sometimes be the first medicine a doctor suggests.
Important Things to Know About MAOIs
Food and Drink
People taking MAOIs usually need to be careful about what they eat and drink. Some foods and drinks contain a substance called tyramine. Examples include certain cheeses, soy sauce, and salami.
If someone eats a lot of tyramine while taking MAOIs, it can cause a serious reaction. This reaction is called a hypertensive crisis, which means blood pressure goes dangerously high. This can be very serious. MAOIs stop the body from breaking down tyramine, which leads to this problem.
However, RIMAs are different. They are less likely to cause this problem. This is because tyramine can push RIMAs away from the enzyme. Also, another enzyme (MAO-B) can still break down tyramine. So, people taking RIMAs, like moclobemide, usually don't need to change their diet as much.
Other Medicines
It's very important to tell your doctor about all medicines you are taking. This includes medicines you buy without a prescription, other prescribed drugs, or even some dietary supplements. For example, St. John's wort can be risky with MAOIs.
Mixing MAOIs with certain other medicines can cause serious problems. For this reason, some people who take MAOIs carry a special card. This card tells emergency medical staff which medicines to avoid.
For example, MAOIs should not be mixed with most other antidepressants or stimulants. This includes many cold medicines, like decongestants or cough syrup. Mixing them can lead to a condition called serotonin syndrome, which is dangerous.
MAOIs can also interact with products containing tobacco. This is because tobacco has its own natural MAOI compounds.
Stopping MAOIs
Like many other antidepressants, MAOIs can cause withdrawal symptoms if stopped suddenly. These symptoms can be uncomfortable.
To avoid this, doctors usually suggest slowly lowering the dose over time. This can take days, weeks, or even months. This slow process helps to prevent or reduce any withdrawal symptoms.
See Also
 In Spanish: Inhibidores de la monoamino oxidasa para niños
In Spanish: Inhibidores de la monoamino oxidasa para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |