Muffler facts for kids

A muffler (also called a silencer in some places like the UK) is a special part of a vehicle's exhaust system. Its main job is to make the loud noise from an internal combustion engine much quieter. Think of it as a sound-proofing device for your car's engine!
How Mufflers Work
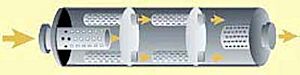
Mufflers are found in the exhaust system of most engines that burn fuel inside, like those in cars and motorcycles. They are designed to be an "acoustic device," which means they work with sound. They lower the loudness of the sound waves made by the engine.
Mufflers use different tricks to quiet sound. Some common ways include:
- Reactive silencing: This uses chambers and passages to bounce sound waves around, making them cancel each other out.
- Resistive silencing: This involves materials that absorb sound energy.
- Absorptive silencing: This often uses materials like fiberglass to soak up sound.
- Shell damping: This makes the outer case of the muffler less likely to vibrate and make noise.
The hot exhaust gas leaving an engine comes out in quick bursts, like little puffs. For example, a four-cylinder engine makes four high-pressure puffs for every full cycle. A six-cylinder engine makes six puffs, and so on. Between these puffs, there's a low-pressure area. This low pressure helps pull out the next batch of exhaust gas from the engine's cylinders.
The exhaust system needs these pressure changes to work well. The more clear and separate these puffs are, the better the exhaust gases are cleared from each cylinder.
Balancing Sound and Performance
Designing exhaust systems and mufflers is a bit of a balancing act. Engineers need to make sure the exhaust gases leave the engine well, but also that the engine doesn't use too much fuel or lose power. And, of course, they need to keep the noise down!
One side effect of making things quieter is that the muffler can slightly block the flow of exhaust gas. This blockage creates something called "back pressure." Too much back pressure can make the engine less efficient. This happens because the exhaust gases have to share the same complex path inside the muffler as the sound waves that the muffler is trying to quiet.
However, a little bit of back pressure can actually be helpful for some engines. It can even help reduce harmful gases like nitrous oxides (NOx) in some cases.
For vehicles where performance is super important, the exhaust pipes and muffler need to be just right. They should be big enough for the engine to "breathe" easily, but also small enough to keep the exhaust flowing quickly. The goal for a high-performance muffler is to tune the pressure waves correctly and keep back pressure as low as possible.
Some mufflers you can buy after a car is made (called "aftermarket" mufflers) claim to make your engine more powerful or use less fuel. They do this by reducing back pressure a little. But this usually means they make more noise! A muffler that lets more gas flow might increase power, but if it flows too much, it won't give extra benefits and might just be louder and more expensive.
Rules About Mufflers
On May 18, 1905, the state of Oregon in the United States made a law. It said that vehicles had to have "a light, a muffler, and efficient brakes." This shows that mufflers have been important for a long time!
Today, changing a vehicle's original exhaust system is often regulated by law. In many countries, like the United States, Canada, and Australia, there are strict rules about what you can change. Sometimes, these changes are even against the law. This is usually to control noise pollution and make sure vehicles are safe.

See also
- Noise control
- Hush kit
- Hush house
- Soundproofing
- Anechoic chamber
- Vibration isolation
- Shock absorber
- Cushioning
- Damped wave
- Damping ratio
- Detuner
- Sound attenuator
- Supressor
- List of auto parts