Mut facts for kids
Mut was an ancient Egyptian goddess. Her name can also be spelled Maut or Mout.
Mut was an important goddess in ancient Egypt. She was known as the mother goddess and was worshiped for thousands of years. Her name, "Mut," means "mother" in the ancient Egyptian language. She is associated with the waters from which everything was born.
Let's explore who Mut was, what she represented, and why she was so important to the ancient Egyptians.
Contents
Titles
Mut had many names that showed how important she was. She was called "Mother of the Gods," "World-Mother," and "Queen of the Goddesses."
Family
Mut was part of a special family in Thebes, a city in ancient Egypt. She was the wife of Amun, who was a very important god, and the mother of Khonsu, the moon god. Together, they were known as the Theban Triad.
Appearance
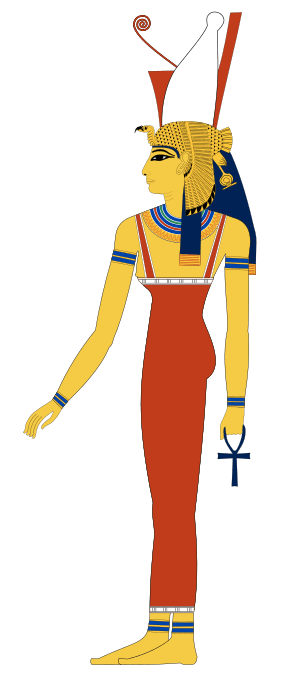
Mut was often shown as a woman wearing a special crown. This crown was made up of the crowns of Upper and Lower Egypt, which showed that she had power over the entire land. Sometimes, she was also shown with the head of a vulture, an animal that the Egyptians thought was very protective and motherly.
What Did Mut Represent?
Mut represented many important ideas to the ancient Egyptians.
- Motherhood: As her name suggests, Mut was the goddess of motherhood. She was seen as the mother of everything in the world and was often shown with a child on her lap.
- Protection: Mut was also a protector. The vulture, which was one of her symbols, was thought to be a very caring and protective mother. Egyptians believed that Mut watched over them and kept them safe.
- Power: Mut was a powerful goddess. She wore the double crown of Egypt, which showed that she had control over the entire country. This made her a symbol of strength and authority.
- The Sky: Mut was also known as the goddess of the sky. This meant that she was connected to everything above the earth, like the sun, moon, and stars.
Symbols
Symbols helped the ancient Egyptians understand and recognize their gods and goddesses. Here are some of Mut's main symbols:
- The Vulture: The vulture was a very important symbol for Mut. Egyptians believed that vultures were very caring mothers, so they used the vulture to represent Mut's motherly qualities.
- The Uraeus: The Uraeus was a cobra symbol that was often worn on the crowns of pharaohs (the rulers of ancient Egypt). It stood for protection and power. Mut was often shown wearing the Uraeus on her crown, which showed that she was a powerful protector.
- The Double Crown: The double crown was made up of the white crown of Upper Egypt and the red crown of Lower Egypt. Wearing this crown showed that Mut had power over all of Egypt.
- The Ankh: The ankh was a symbol that looked like a looped cross. It stood for life. Mut was often shown holding an ankh, which meant that she had the power to give and protect life.
Temples and Worship
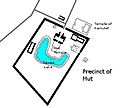
The ancient Egyptians built temples to honor their gods and goddesses. Mut had a very important temple in Thebes, which was one of the most important cities in ancient Egypt.
Mut's temple was part of a larger temple complex called Karnak. This temple was very grand and had many statues, columns, and decorations.
Mut's temple had a special lake called the Isheru. This lake was shaped like a horseshoe and was considered sacred. People would celebrate Mut by sailing on this lake during festivals.
Festivals
The ancient Egyptians held many festivals to honor Mut. One of the most important was the Opet Festival, which celebrated the Theban Triad (Amun, Mut, and Khonsu). During this festival, statues of the gods were carried in a procession through the city.
Myths
In some stories, Mut was said to have been around since the beginning of time. She was sometimes shown as a serpent (a type of snake) who came out of the primordial waters with her father, Amun-Ra.
One of the most important stories about Mut is that she was the mother of Khonsu, the moon god. According to the myth, Mut called for Amun-Ra, and then she gave birth to Khonsu in her temple. The birth of Khonsu was celebrated every year in Thebes.
The Eye of Ra
Sometimes, Mut was called the "Eye of Ra." Ra was the sun god, and his eye was a symbol of his power and protection. By calling Mut the Eye of Ra, people showed that she was a powerful protector, just like Ra.
Mut and the Pharaohs
The pharaohs, who were the rulers of ancient Egypt, also played a role in Mut's worship.
They supported the worship of Mut to show that they had the right to rule. By honoring Mut, they showed that they were connected to the gods and had their support.
One famous pharaoh, Queen Hatshepsut, even claimed that she was descended from Mut. She rebuilt Mut's temple at Karnak to honor the goddess and show her importance.
Egyptian queens often wore the symbol of the vulture on their crowns. This was because the vulture was a symbol of motherhood and protection, and it showed that the queen was a caring and protective figure for the people of Egypt.
Influence
Mut was worshiped for a very long time, and her influence can be seen in many parts of ancient Egyptian culture.
As time went on, Mut became connected to other goddesses, like Isis, Sekhmet, and Bastet. People began to see her as the main goddess, and all the other goddesses were just different parts of her.
When the Greeks came to Egypt, they connected Mut with their own goddess, Hera. This shows that Mut's influence spread beyond Egypt.
Images for kids
-
Relief of the Goddess Mut, c. 1336–1213 B.C.E., 79.120, Brooklyn Museum
-
Precinct of Mut at the Karnak temple complex
See also
 In Spanish: Mut para niños
In Spanish: Mut para niños