Nagual facts for kids
A nagual (pronounced nah-WAL) is a person in Mesoamerican folk religion who can shapeshift into their special animal partner. This animal is called their tonal. Nagualism is the belief that people can gain power and spiritual understanding by connecting with their inner animal spirit.
What Does "Nagual" Mean?
The word nagual comes from the Nahuatl word nāhualli. This word was used to describe a native religious person, whom the Spanish sometimes called a 'magician'.
In English, nagual is often translated as "transforming witch." However, other meanings that are not negative include "transforming trickster" or simply "shape shifter."
Beliefs About Naguals
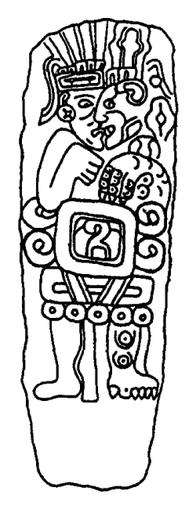
Naguals can use their special powers for good or for bad, depending on who they are. The idea of nagualism is found across many ancient Mesoamerican cultures. It is connected to old shamanistic practices from groups like the Olmec and Toltec. Ancient art shows people changing into animals, which many believe are depictions of naguals.
This belief system is also linked to the Mesoamerican calendars. These calendars were used for telling the future. A person's birth date often helped decide if they could become a nagual. Nagualism is also connected to the belief called tonalism. This idea says that every person has an animal partner, and their life force is connected to this animal.
A person gets the nagual trait when they are born, along with other traits linked to their birth day. Each day is connected to an animal that has both strong and weak qualities. For example, someone born on "Dog Day" would have both strong and weak "dog" traits. In Nahuatl, the word tonalli means both a day and the animal linked to that day.
Naguals are seen as different from the tonal. The tonal is like the spirit of the day itself. The nagual is more like a special spirit that helps the person. It is thought that the tonal represents the daytime side, and the nagual represents the nighttime side of the tonalli. People who practiced powerful magic were often born on days linked to strong or powerful animals. These animals might include the jaguar or puma. In Aztec mythology, the god Tezcatlipoca was seen as a protector of nagualism. This was because his animal partner was the jaguar.
In modern rural Mexico, the word nagual sometimes means a person who can change into an animal at night. These animals are often a dog, owl, bat, wolf, or turkey. They might use their powers to cause mischief or play tricks.
In some native communities, the nagual is an accepted part of their religious leaders. The community knows who is a nagual and respects them, though they might also fear them. Sometimes, naguals are asked to remove bad spells cast by other naguals. However, in other communities, if someone is accused of being a nagual, it can lead to attacks against them.
Western studies of nagualism began with Daniel Garrison Brinton. In 1894, he wrote a book called Nagualism: A Study in Native-American Folklore and History. He wrote about how the word was understood and about people who practiced nagualism in Mexico. He found different beliefs about nagualism among groups like the Mixe, Nahua, Zapotec, and Mixtec.
Since then, many studies have described nagualism in other Mesoamerican cultures. These include the Zoques, Jakaltek, K'iche', Q'eqchi', and Tzeltal Maya. Among the Jacaltek, naguals help protect their native culture. They may punish those who work too closely with non-native Ladinos.
In 1955, Gustavo Correa suggested that nagualism might not be ancient. He thought it came from Europe, comparing it to medieval beliefs in werewolves. However, stories about shapeshifting are found in many cultures around the world, not just Europe. For example, ancient stories like the Epic of Gilgamesh and East Asian tales of Huli Jing also feature shapeshifters.
Researcher Kaplan found that in Oaxaca, Mexico, many people believe naguals are evil shapeshifting individuals. But he also noted that the belief in animal spirit companions is mainly found among native groups. However, for some groups like the Mixes or Chinantecos, those who can control their nagual or alter ego are seen as protectors of their people, nature, and culture. These naguals are highly respected, but also feared.
The idea of the nagual became well-known through the shamanism books written by Carlos Castaneda.
Nagual Practices
The practice of Nagualism often involved using special plants. These plants were believed to help people gain new ways of seeing and understanding things during nagual rituals.
See also
 In Spanish: Nahual para niños
In Spanish: Nahual para niños
- Cat People (1982 film)
- Familiar
- Huay Chivo
- Power animal
- Skin-walker
- Totem
- Tutelary spirit
- Wayob
- Werecat
- Werehyena
- Werejaguar
- Werewolf