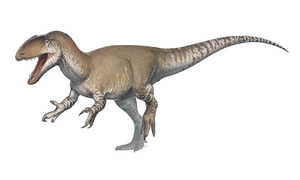Neovenator facts for kids
Quick facts for kids NeovenatorTemporal range: Lower Cretaceous, 125 mya
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Restored skeleton | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: |
Carcharodontosauridae/
Neovenatoridae |
| Genus: |
Neovenator
|
Neovenator was a large, meat-eating dinosaur that lived about 125 million years ago. This was during the early Cretaceous period. It is related to a group of dinosaurs that includes the well-known Allosaurus.
Scientists found Neovenator fossils on the Isle of Wight in the UK. Since its discovery, it has become one of the most famous large meat-eating dinosaurs found in Europe.
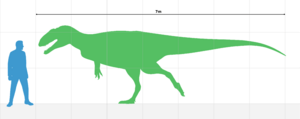
Neovenator was usually about 7.5 meters (24.5 feet) long. It had a slim body and weighed between 1000 and 2000 kilograms (2,200 to 4,400 pounds). Some fossil pieces suggest it might have grown up to 10 meters (33 feet) long.
About Neovenator
Neovenator was a top predator in its time. It lived alongside other dinosaurs like Baryonyx, Polacanthus, and Iguanadon. Its name means "new hunter," which fits its role as a powerful dinosaur.
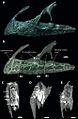
Scientists have studied Neovenator fossils carefully. They found that it had a long snout with five teeth right at the very front. The back bones in its neck were also connected to its neck ribs.
Sensing the World
In 2015, scientists discovered something interesting about Neovenator's snout. It had a complex system of tiny tunnels inside. These tunnels held nerves and blood vessels. This system might have helped Neovenator sense things around it.
Some dinosaurs, like Spinosauridae, had similar systems. They used them to find prey in water. However, scientists are not sure if Neovenator used its snout in the same way.
Unique Features
At first, some features of Neovenator were thought to be unique to it. For example, its large nostrils or certain bone structures. But later research showed that other meat-eating dinosaurs also had these traits.
For instance, having air-filled back bones was common for its dinosaur family. Also, the small bumps on its teeth, called denticles, were not just on Neovenator. Even the raised bumps on its nose were similar to those on Allosaurus.
Images for kids
-
A mounted skeleton and fossils at Dinosaur Isle.
-
A reconstructed skeleton at World Museum Liverpool.