Nerve impulse facts for kids
A nerve impulse is like a tiny electrical message. It's how your nerve cells, called neurons, talk to each other. These messages are mostly electrical signals. They travel along parts of the neuron called dendrites. This creates what scientists call an action potential.
Think of an action potential as a quick burst of electricity. It happens when tiny charged particles, called ions, move in and out of the nerve cell. The main ions involved are potassium (K+) and sodium (Na+). Special doors in the cell membrane, called potassium channels and sodium channels, let these ions move. There's also a "sodium-potassium pump" that helps move them.
How Nerve Impulses Travel
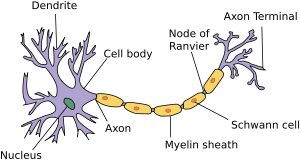
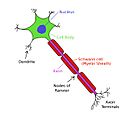
Nerve impulses travel very quickly along the long part of a neuron called the axon. This movement is like a wave of electrical change. It starts at one end of the neuron and moves all the way to the other end.
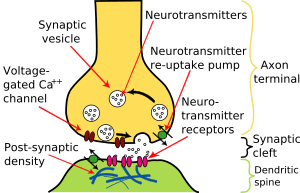
When an impulse reaches the end of an axon, it needs to jump to the next neuron. This jump happens at a tiny gap called a synapse. At most synapses, the electrical signal changes into a chemical signal. This chemical signal then crosses the gap to the next neuron.
Super-Fast Connections: Electrical Synapses
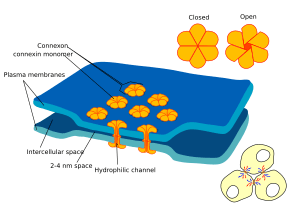
Some nerve cells have a special way to connect that is even faster. These are called electrical synapses. They are used when speed is super important. For example, they help with quick escape reflexes. They are also found in your retina (the back of your eye) and in your heart.
Electrical synapses are faster because they don't need to use slow neurotransmitter chemicals. Instead, the nerve cells are connected directly. When an electrical message arrives, the electrical currents flow right from one cell to the next. This happens through tiny tunnels called connexons. So, the electrical signal jumps straight to the next cell, making the response almost instant!
Images for kids
-
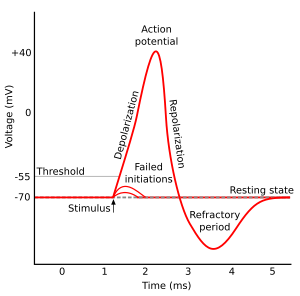
As an action potential (nerve impulse) travels down an axon there is a change in electric polarity across the membrane of the axon. In response to a signal from another neuron, sodium- (Na+) and potassium- (K-) gated ion channels open and close as the membrane reaches its threshold potential. Na+ channels open at the beginning of the action potential, and Na+ moves into the axon, causing depolarization. Repolarization occurs when the K+ channels open and K+ moves out of the axon, creating a change in electric polarity between the outside of the cell and the inside. The impulse travels down the axon in one direction only, to the axon terminal where it signals other neurons.
-
In saltatory conduction, an action potential at one node of Ranvier causes inwards currents that depolarize the membrane at the next node, provoking a new action potential there; the action potential appears to "hop" from node to node.
-
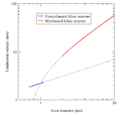
Comparison of the conduction velocities of myelinated and unmyelinated axons in the cat. The conduction velocity v of myelinated neurons varies roughly linearly with axon diameter d (that is, v ∝ d), whereas the speed of unmyelinated neurons varies roughly as the square root (v ∝√d). The red and blue curves are fits of experimental data, whereas the dotted lines are their theoretical extrapolations.
-
As revealed by a patch clamp electrode, an ion channel has two states: open (high conductance) and closed (low conductance).
-
Tetrodotoxin is a lethal toxin found in pufferfish that inhibits the voltage-sensitive sodium channel, halting action potentials.
-
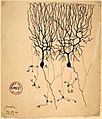
Image of two Purkinje cells (labeled as A) drawn by Santiago Ramón y Cajal in 1899. Large trees of dendrites feed into the soma, from which a single axon emerges and moves generally downwards with a few branch points. The smaller cells labeled B are granule cells.
-
Ribbon diagram of the sodium–potassium pump in its E2-Pi state. The estimated boundaries of the lipid bilayer are shown as blue (intracellular) and red (extracellular) planes.