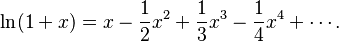Nicholas Mercator facts for kids
Nicholas Mercator (born around 1620 in Holstein, died 1687 in Versailles) was an important mathematician from the 1600s. His German name was Kauffmann. He is famous for his work with logarithms and for helping design the beautiful fountains at the Palace of Versailles.
Contents
Early Life and Education
Nicholas Mercator was born in Eutin, a town in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. He went to university at Rostock and Leyden. After his studies, he lived in the Netherlands from 1642 to 1648.
A Traveling Mathematician
Mercator was a well-traveled scholar. He taught at the University of Copenhagen from 1648 to 1654. Later, he lived in Paris for a few years, from 1655 to 1657. He even worked as a math tutor for Joscelyne Percy, who was the son of a noble family in England.
From 1658 to 1682, Mercator taught mathematics in London. While there, he made an important observation. On May 3, 1661, he watched a transit of Mercury (when the planet Mercury passes in front of the Sun). He did this with other famous scientists like Christiaan Huygens.
Royal Society and Royal Projects
Nicholas Mercator was a respected scientist. On November 14, 1666, he was chosen to be a Fellow of the Royal Society. This is a very old and famous group of scientists in England. He also designed a special clock called a marine chronometer for King Charles II. This clock was meant to help sailors find their location at sea.
Work at Versailles
In 1682, a French minister named Jean Colbert invited Mercator to France. He wanted Mercator to help design and build the amazing fountains at the Palace of Versailles. So, Mercator moved to Versailles to work on this big project.
Mathematical Discoveries
Mercator is best known for his book called Logarithmo-technia, which was published in 1668. In this book, he wrote about logarithms.
The Mercator Series
One of his most famous discoveries is the Mercator series. This is a special way to calculate the natural logarithm of a number using an endless sum:
Nicholas Mercator was also the first person to use the term "natural logarithm."
Contributions to Music
Besides math, Mercator also studied music. He was the first to accurately describe a musical tuning system called 53 equal temperament. This system was important for understanding music theory, even though it wasn't used much in practice.
Nicholas Mercator passed away in Versailles in 1687.
Works
- 1664: Hypothesis astronomica nova, London
- 1666: "Certain problems touching some points of navigation", published in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. This paper discussed challenges in navigation.
- 1668: Logarithmo-technia or Logarithmotechnia. This was his famous book on logarithms.
- 1676: Institutionum astronomicarum, London (reprinted in 1685, Padua). This book was about astronomy.