Norm (mathematics) facts for kids
In mathematics, a vector is like an arrow. It has a size (how long it is), which we call its magnitude, and it points in a certain direction. For example, if you describe how far and in what direction you walked, that's a vector.
The norm of a vector is simply its length. It tells you how 'big' a vector is. Think of it as measuring the distance from the start of the vector to its end. For simple numbers, the norm is just the absolute value (how far a number is from zero). For vectors in more complex spaces, the norm is a special way to measure length.
Contents
What is a Vector Norm?
A vector norm is a special rule or function that helps us find the length or "size" of a vector. We write the norm of a vector 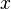 as
as 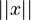 . It has three main rules:
. It has three main rules:
- Scaling: If you make a vector twice as long, its norm (length) also becomes twice as big.
- Triangle Inequality: If you add two vectors, the length of the new vector is never longer than adding the lengths of the two original vectors separately. Imagine walking: the shortest path between two points is a straight line.
- Zero Vector: A vector only has a length of zero if it's the "zero vector" (a vector with no length and no direction).
How to Calculate a Vector Norm
For a vector 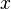 with several parts (like
with several parts (like 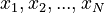 ), we often use something called the L
), we often use something called the L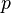 norm. The formula looks a bit complex, but it's a way to combine all the parts of the vector to find its total length:
norm. The formula looks a bit complex, but it's a way to combine all the parts of the vector to find its total length:
![||x||_p = \sqrt[p]{x_1^p+x_2^p+...+x_N^p}](/images/math/7/3/c/73c83a3f8df38938eac5dbf7a3b35910.png)
The most common way to find a vector's length is using the Euclidean norm. This is like using the Pythagorean theorem to find the distance between two points.
Different Types of Vector Norms
There are several ways to calculate the norm, each useful for different situations:
The One-Norm (L1-Norm)
The one-norm is the simplest to understand. You just add up the absolute values of all the parts of the vector. 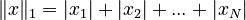 Imagine you're walking on a city grid, like in Manhattan. To get from one corner to another, you can only walk along the streets (north-south or east-west). The one-norm tells you the total distance you'd walk by adding up all the blocks you go in each direction.
Imagine you're walking on a city grid, like in Manhattan. To get from one corner to another, you can only walk along the streets (north-south or east-west). The one-norm tells you the total distance you'd walk by adding up all the blocks you go in each direction.
The Euclidean Norm (L2-Norm)
This is the most common norm and is also called the standard distance formula. It's what you usually think of as "distance." 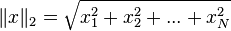 This norm is like finding the straight-line distance between two points in space. If you have a vector in 2D or 3D space, this is how you'd calculate its actual length.
This norm is like finding the straight-line distance between two points in space. If you have a vector in 2D or 3D space, this is how you'd calculate its actual length.
The Maximum Norm (Infinity Norm)
The maximum norm looks for the largest absolute value among all the parts of the vector. 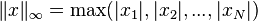 So, if your vector is (3, -7, 2), the maximum norm would be 7, because |-7| is the largest absolute value.
So, if your vector is (3, -7, 2), the maximum norm would be 7, because |-7| is the largest absolute value.
Frobenius Norm
When we talk about the Euclidean norm for matrices (which are like grids of numbers), it's called the Frobenius norm.
L0 Norm
The L0 norm isn't really a "norm" in the strict mathematical sense, but it's often used. It simply counts how many parts of a vector are not zero. For example, if a vector is (5, 0, -2, 0, 1), its L0 norm would be 3, because three of its parts are not zero.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Norma vectorial para niños
In Spanish: Norma vectorial para niños

