North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organization facts for kids
The North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organization (NASCO) is an international group. It was started on October 1, 1983. Its main goal is to help protect and manage Atlantic Salmon in the North Atlantic Ocean.
NASCO works like a special team for fishing. It helps countries talk and work together. Their mission is to save, bring back, and wisely manage salmon. They have a 10-year plan to stop the wild North Atlantic salmon from disappearing.
NASCO's main office is in Edinburgh, United Kingdom. It was formed because countries realized they couldn't protect salmon alone. They needed to work together to stop too much fishing. NASCO has made rules and guides for salmon fishing. For example, they limit fishing to areas close to the coast. They also teach people how to properly release fish they catch. This helps the fish survive. Keeping the fish in the water before letting them go is very important.
In 2020, NASCO's budget was about 636,630 British Pounds. Most of this money came from the countries that are members.
Contents
Who Belongs to NASCO?
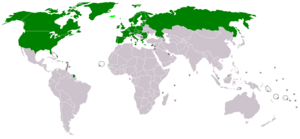
Many countries and groups are part of NASCO. They have been members since 1984:
 Canada
Canada European Union
European Union United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States of America
United States of America Norway
Norway Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands Greenland
Greenland Russian Federation
Russian Federation Iceland
Iceland Denmark (for the Faroe Islands and Greenland)
Denmark (for the Faroe Islands and Greenland)
Iceland left NASCO in 2009 but rejoined in March 2023. They wanted to help save the North Atlantic salmon again.
Also, 34 non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can watch NASCO's yearly meetings. These are groups that are not part of any government.
How NASCO Works
NASCO has different parts that work together to achieve its goals.
Council: This is the main governing body of NASCO. It oversees everything.
- North American Commission (NAC): This group suggests scientific research. It helps members in North America work together. They focus on reducing catches and making rules.
- North-East Atlantic Commission (NEAC): This group helps countries in the North-East Atlantic work together. They focus on saving, bringing back, and managing salmon.
- West Greenland Commission (WGC): This group helps countries work together on salmon in the West Greenland area. They focus on saving and managing salmon stocks.
International Atlantic Salmon Research Board: This board suggests scientific research to the Council and Commissions.
Finance and Administration Committee (FAC): This committee handles NASCO's money and daily operations. One person from each member country is on this committee.
Secretariat: This is a small team led by a Secretary. They help NASCO members carry out their plans.
The Council's main jobs include:
- Being a place to share information about salmon.
- Making sure the different Commissions work well together.
- Working with other fishing and science groups.
- Suggesting ideas for scientific research.
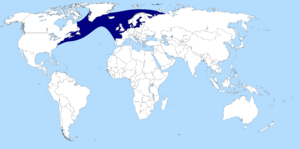
About the Atlantic Salmon
Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) are sometimes called the "King of Fish." They are anadromous fish. This means they live part of their lives in fresh water and part in salt water. Adult salmon lay their eggs in freshwater rivers. After the eggs hatch, the young salmon grow for 1 to 3 years. Then, they travel to the ocean.
Why North Atlantic Salmon Are in Trouble
North Atlantic salmon face many dangers. These dangers have caused their numbers to drop a lot. This is why they need help to recover.
- Overfishing: In the past, too many salmon were caught. This happened because of both commercial fishing (for selling) and recreational fishing (for fun).
- Climate Change: The changing climate affects ocean life. Warmer ocean temperatures, changes in ocean chemistry, and less oxygen in the water can harm salmon. These changes can also make salmon change their migration paths.
- Aquaculture: This is when salmon are raised on farms. Farmed salmon can cause problems for wild salmon. They can spread diseases to wild fish. Also, if farmed salmon escape, they can mix with wild salmon. This can weaken the wild salmon population.
Wild Salmon vs. Farmed Salmon
People around the world want more salmon to eat. Because of this, salmon farming is growing very fast. Salmon farming means raising salmon in large nets close to the shore. The salmon live there for most of their lives. They start in fresh water and then move to salt water until they are big enough to be sold.
A study showed that 70% of Atlantic salmon were produced through fish farming. Farmed salmon might have more toxins. This is because their food can contain certain particles. Some people think salmon farming is a good way to produce protein. However, the extra food waste from these farms can harm ocean life. It can also change the types of plants and animals living in the water.
NASCO's Plan for the Future
NASCO has a Ten-Year Plan to help Atlantic salmon. They want to bring back the healthy salmon populations that once thrived.
NASCO's main goal is to protect, save, and restore wild Atlantic salmon. To reach this goal, they have five main objectives:
- Gather Information: Collect the best scientific information. Make it easy to find. This helps understand the big problems facing wild salmon.
- Share Best Practices: Use the information to create good advice. Make sure this advice is available to anyone who wants to help salmon.
- Promote Good Management: Encourage sustainable ways to manage salmon. Share successful methods. Make sure countries follow NASCO's advice.
- Raise Awareness: Work with other groups and the public. Encourage leaders, people, businesses, and scientists to find solutions for salmon.
- Improve Operations: Make NASCO itself work better. Be efficient, effective, open, and include everyone.
A Plan for Action
A group of experts created a "Call-To-Action" plan for NASCO. This plan has important ideas:
- Find ways to make NASCO stronger. Maybe add new rules to its treaty.
- Work with other fishing groups to reduce accidental catches of salmon.
- Help more with protecting and restoring salmon habitats (their homes).
- Push for specific limits on how many salmon can be caught in each river.
- Make sure these fishing limits are strictly followed.
- Start a project to help salmon populations that are in danger.
- Begin talks for international rules on salmon farming. This would protect wild salmon.
- Find new ways to estimate how many salmon are caught illegally.
- Create a plan with NGOs to decide what research is most important. Also, how to fund it.
- Make a new plan to tell the public about NASCO's work. Be more open. Let NGOs participate more.
- Publish a yearly report on the health of Atlantic salmon populations.