Nucleophilic substitution facts for kids
A nucleophilic substitution is a special kind of chemical reaction. Think of it like a swap! In this reaction, one chemical group, called a nucleophile, replaces another group on an atom. The group that leaves is called a leaving group.
This type of reaction is very important in chemistry. It helps scientists understand how different molecules are built and how they change.
Contents
What is a Nucleophile?
A nucleophile is a chemical group that "loves" positive charges. It has extra electrons that it wants to share. Because of this, a nucleophile is attracted to parts of molecules that have a slight positive charge. When it finds such a spot, it can attach itself there, pushing another group away.
How Does Substitution Work?
Imagine you have a toy car with a special wheel. A nucleophilic substitution is like taking off that special wheel and putting on a different, but similar, wheel. The old wheel is the "leaving group," and the new wheel is the "nucleophile" that replaces it.
In chemistry, this happens when a nucleophile attacks an atom that is connected to a leaving group. The nucleophile forms a new bond with that atom, and at the same time, the leaving group breaks its bond and moves away.
Types of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
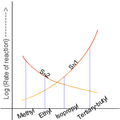
There are different ways nucleophilic substitution can happen. The two main types are called the SN1 reaction and the SN2 reaction. The letters "SN" stand for "Substitution, Nucleophilic." The number (1 or 2) tells us about how many molecules are involved in the slowest step of the reaction.
SN1 Reactions
In an SN1 reaction, the leaving group leaves first. This creates a temporary, positively charged atom called a "carbocation." After the carbocation forms, the nucleophile then attacks it and forms a new bond. This type of reaction happens in two main steps.
SN2 Reactions
In an SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks the atom at the same time the leaving group is leaving. It's like a single, smooth movement where one bond forms as another breaks. This type of reaction happens in one main step.
The type of nucleophilic substitution that occurs depends on the specific atoms and molecules involved. Scientists study these reactions to predict how chemicals will behave and to create new substances.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sustitución nucleófila para niños
In Spanish: Sustitución nucleófila para niños