Outer Mongolia facts for kids
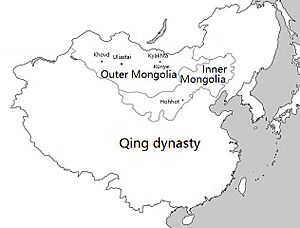
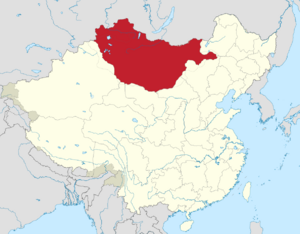
Outer Mongolia was a historical region in Asia. It was part of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. Today, this area mostly matches the independent country of Mongolia. It also includes the Russian republic of Tuva.
This historical region became independent from Qing China around 1911. This happened during a big change called the Xinhai Revolution.
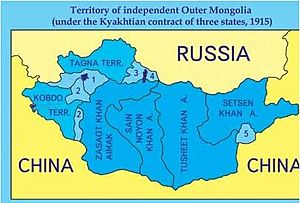
During the Qing dynasty, Outer Mongolia included four main areas of the Khalkha people. Later, the term "Outer Mongolia" also included other groups like the Oirats and the region of Tannu Uriankhai.
After the Qing dynasty ended, the Republic of China claimed Outer Mongolia. They saw it as part of their country. This claimed area was sometimes called "Mongolia Area." However, most of Outer Mongolia was actually controlled by the Bogd Khanate. This new Mongolian state was not widely recognized by other countries.
The Republic of China briefly took control of most of the region from 1919 to 1921. Later, the Mongolian People's Republic was formed in 1924. China officially recognized Mongolia's independence in 1946. This was partly due to pressure from the Soviet Union. However, this recognition was later taken back by the Chinese government in 1953. Today, the People's Republic of China fully recognizes Mongolia as an independent country.
Contents
Understanding the Names of Outer Mongolia
The name "Outer Mongolia" is often compared to Inner Mongolia. Inner Mongolia is a region within China today. The Qing court managed Inner Mongolia more directly. Outer Mongolia was further from the capital city of Beijing. Because of this, it had more freedom within the Qing empire.
There are a few other names for this region. These include Ar Mongol and Mobei Mongol.
Ar Mongol: The "Back Side" of Mongolia
The term Ar Mongol or Mobei Mongol is sometimes used in Chinese and Mongolian languages. It means "North-of-the-Desert Mongolia." This name helps to show a geographic difference between North and South Mongolia. It avoids focusing on the history of Qing rule. Instead, it highlights the areas where Mongols lived on the Mongolian Plateau. You might also hear it called Northern Mongolia in English.
In the Mongolian language, the word ar means the back side of something. It can also mean the northern side of a mountain or a traditional tent called a yurt. The word öbür means the front or south side. So, the difference between South Mongolia and the Mongolian state is like the difference between the northern and southern sides of a mountain.
In contrast to Mobei Mongol (North of the Desert), there is also Monan Mongol. This means "South of the Desert Mongolia." It generally refers to the region now known as South Mongolia.
How "Outer Mongolia" Is Used Today
Today, "Outer Mongolia" is sometimes still used informally. It can refer to the independent country of Mongolia. To avoid confusion, Chinese sources usually call the country "State of Mongolia." This is the official name in Mongolian, which is Монгол Улс. They do this instead of just saying "Mongolia," which could mean the whole Mongolian region.
In English, "Outer Mongolia" is also sometimes used as a saying. It means a place that is very far away.
See also
- Mongolia under Qing rule
- Tannu Uriankhai
- Dzungaria
- Outer Northwest China
- Outer Manchuria
- Mongolia–Taiwan relations
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |