Oxytocin facts for kids
Oxytocin is a special chemical, or hormone, made naturally in your brain. It's created in a small area called the hypothalamus. Then, it's released by the pituitary gland, which helps control many hormones in your body. This amazing hormone has been around in animals for a very long time. It helps with important things like social connections, feelings of love, and childbirth.
When a baby is born, oxytocin helps the uterus contract. This makes the birth process faster. It also helps mothers produce milk for their babies. Plus, it helps mothers feel a strong connection with their newborns. Oxytocin is released during special moments like childbirth and when people feel close to each other. It works in a "positive feedback" loop. This means the more it's released, the more the body is encouraged to make even more! For example, during childbirth, each contraction causes more oxytocin to be released. This makes contractions stronger until the baby is born.
Oxytocin is also available as a medicine. Doctors can use it to help with childbirth or milk production.
Contents
What Does the Name "Oxytocin" Mean?
The word "oxytocin" comes from ancient Greek words. "Oxys" means "sharp" or "swift." "Tokos" means "childbirth." So, it literally means "swift birth." Sometimes, people informally call oxytocin the "cuddle hormone" or the "love hormone." This is because it helps with social bonding and feelings of closeness.
A Look Back in Time: Discovering Oxytocin
Scientists first found out that something in the body could make the uterus contract. This happened in 1906. A British scientist named Henry Hallett Dale made this discovery. Later, in 1909, doctors started using this knowledge to help women with difficult births.
By the 1920s, oxytocin was separated from other substances in the pituitary gland. Then, in the early 1950s, an American biochemist named Vincent du Vigneaud figured out its exact structure. He learned it's made of nine tiny building blocks called amino acids. He was even able to create oxytocin in a lab in 1953! This was a huge achievement. For this important work, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1955.
How Oxytocin Works in Your Body
Oxytocin works by attaching to special "receptors" in different parts of your body and brain. Think of receptors like locks and oxytocin like a key. When the key fits the lock, it causes something to happen.
Where is Oxytocin Made?
Oxytocin is made in specific nerve cells in the hypothalamus part of your brain. These cells send out long branches, called axons. These branches reach all the way to the pituitary gland. From there, oxytocin is released into your bloodstream. It then travels throughout your body.
Interestingly, oxytocin isn't just made in the brain. Small amounts of it are also found in other body parts. These include the placenta (during pregnancy), and even the eyes and heart.
How is Oxytocin Created?
Oxytocin starts as a larger, inactive protein. Then, special enzymes (which are like tiny biological scissors) cut this larger protein into smaller pieces. One of these pieces is active oxytocin. This process needs vitamin C to work properly!
What Oxytocin Does in Your Body
Oxytocin has many important jobs. It affects both your body and how you feel and act.
- Helping with Birth and Milk: During childbirth, oxytocin causes the uterus to contract. This helps the baby move out. After birth, it helps the uterus shrink back to its normal size. It also helps stop bleeding. For breastfeeding mothers, oxytocin helps release milk from the mammary glands. This allows the baby to drink it. When a baby sucks, it sends a signal to the brain. This signal tells the brain to release more oxytocin, which then releases more milk.
- Water Balance: Oxytocin is similar to another hormone called vasopressin. Because of this, oxytocin can slightly reduce how much urine your body makes.
- Heart Health: In some animals, oxytocin is found in the heart. It might help the heart develop.
- Brain Protection: Studies in animals suggest that oxytocin might help protect brain cells. It may also improve learning, especially after stress. It might also help reduce inflammation in the brain.
- Appetite: Some research suggests that oxytocin neurons in the brain might help control appetite. They might also tell us when we've had enough to eat.
How Oxytocin Affects Your Feelings and Actions
Oxytocin is often called the "love hormone." This is because it plays a big role in how we connect with others.
- Social Connections: It helps create strong bonds. These include the bond between a mother and her baby, or between romantic partners. Studies show that oxytocin levels can go up when people pet their dogs. This suggests it helps with the bond between humans and pets too! It can make people feel more positive towards those they consider part of their "group" or "team."
- Trust and Generosity: Oxytocin can make people more trusting of strangers. It can also make them more generous in certain situations. It might do this by increasing empathy. Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another.
- Fear and Anxiety: Oxytocin can help reduce feelings of fear and anxiety. It possibly does this by calming down the part of the brain that handles fear responses. However, it's a complex hormone. Its effects can depend on the situation.
- Mood: Some research suggests that oxytocin might help with mood. It could have effects similar to antidepressant medicines.
- Differences Between Genders: Studies show that oxytocin might affect males and females differently. This is especially true in how they react to social situations or threats. For example, estrogen (a female hormone) can affect how oxytocin works in the brain. Also, testosterone (a male hormone) might reduce oxytocin's effects.
The Chemistry of Oxytocin
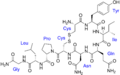
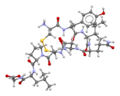
Oxytocin is a small protein, or peptide. It is made up of nine amino acids linked together. It has a special ring shape. This shape is created by a disulfide bridge between two of its amino acids.
Its structure is very similar to another important hormone called vasopressin. They are almost identical! They differ by only two amino acids. This similarity shows how these hormones might have evolved from a common ancestor.
Oxytocin in Medicine
Because of its effects on social behavior, scientists are studying oxytocin. They want to know if medicines that act like oxytocin could help people with social challenges. This includes people with autism.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Oxitocina para niños
In Spanish: Oxitocina para niños