Passenger car facts for kids

A car is a wheeled vehicle that carries its own engine. It is used for transporting people and goods. Cars usually have four wheels and are designed to run on roads. In British English, a car can also be called a motor car or an automobile. Cars have changed the way people live, work, and travel around the world.
Contents
The Story of Cars
Cars have a fascinating history, starting with early ideas for self-moving machines. For centuries, people dreamed of vehicles that didn't need horses.
Early Ideas for Self-Moving Machines
Long before modern cars, inventors tried to create vehicles that could move on their own.
- In 1678, a Jesuit missionary named Ferdinand Verbiest built a small steam-powered machine. It was more like a toy and couldn't carry a driver.
- Later, in 1769, Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot built a full-sized steam-powered vehicle. It was designed to move heavy cannons. This vehicle was very slow and hard to steer.
The First True Cars
The first cars that looked a bit like modern ones appeared in the late 1800s. These early cars used gasoline engines.
- In 1886, Karl Benz in Germany created what is widely considered the first true automobile. It was called the Benz Patent-Motorwagen.
- This three-wheeled vehicle had a gasoline engine and could carry people. Karl Benz's wife, Bertha Benz, made the first long-distance car trip in 1888. She drove about 65 miles to prove the car could work.
- Around the same time, other inventors like Gottlieb Daimler and Carl Benz were also developing their own gasoline-powered vehicles in Germany.
- In France, pioneers like Émile Levassor and Armand Peugeot also played big roles in early car development.
Making Cars for Everyone
At first, cars were very expensive and only wealthy people could afford them. This changed with the idea of mass production.
- Ransom E. Olds founded Olds Motor Vehicle Company (Oldsmobile) in 1897. He was one of the first to use assembly line methods to build cars.
- Henry Ford took mass production to a new level in the early 1900s. He founded the Ford Motor Company in 1903.
- Ford's most famous car was the Ford Model T, introduced in 1908. It was built on a moving assembly line, which made it much faster and cheaper to produce. This meant more people could buy a car.
- In Japan, Kiichiro Toyoda founded the Toyota Motor Corporation in 1937. Toyota also became famous for its efficient mass production methods.
How Cars Work
Most cars today run on gasoline or diesel fuel, but electric cars are becoming more common.
- A car's engine burns fuel to create power. This power turns the wheels, making the car move.
- Drivers use pedals to control speed and brakes. They use a steering wheel to guide the car.
- Cars have many important parts, including a transmission (gears), brakes, lights, and safety features like airbags.
- Fuses and circuit breakers protect the car's electrical system from damage.
Different Kinds of Cars
Cars come in many shapes and sizes to fit different needs.
- Small cars like the Smart Fortwo are great for city driving and parking. They are very light, weighing around 730 kg (1,609 lb).
- Larger vehicles like Chevrolet Suburban SUVs can carry many passengers or a lot of cargo. They can weigh over 3,266 kg (7,200 lb).
- Some cars, like the Toyota Corolla, are known for being very reliable and are among the best-selling cars of all-time.
Electric Cars
Electric cars use electricity instead of gasoline. They have a battery and an electric motor.
- Electric cars produce no exhaust fumes, which is better for the environment.
- The Nissan Leaf is an example of a popular electric car.
- The first electric automobile shown in public was Gustave Trouvé's tricycle in 1881.
Cars and Our World
Cars have had a huge impact on society, both good and bad.
Benefits of Cars
- Cars give people freedom to travel where and when they want.
- They help businesses transport goods and allow people to commute to work.
- Cars have created many jobs in manufacturing, sales, and repair.
Challenges with Cars
- Traffic: Many cities face road congestion, meaning too many cars on the roads, causing delays.
- Pollution: Cars that burn gasoline or diesel release pollutants into the air, which can harm the environment and people's health.
- Accidents: Car collisions can be very serious and cause injuries.
The Future of Cars
The future of cars is exciting, with new technologies being developed.
- Self-driving cars: These cars can drive themselves using sensors and computers. They could make roads safer and travel easier.
- More electric cars: As technology improves, electric cars are expected to become even more common.
- Shared transport: Services like bike-sharing systems, like the Vélib' in Paris, offer alternatives to owning a car, especially in cities.
Images for kids
-
Steam Machine Of Verbiest, in 1678 (Ferdinand Verbiest)
-
Bertha Benz, the first long distance driver
-
Ransom E. Olds founded Olds Motor Vehicle Company (Oldsmobile) in 1897.
-
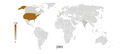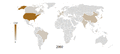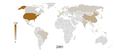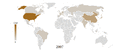
Vehicles in use per country from 2001 to 2007. It shows the significant growth in BRIC.
See also
 In Spanish: Automóvil para niños
In Spanish: Automóvil para niños