Paul R. Ehrlich facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Paul R. Ehrlich
|
|
|---|---|

Ehrlich in 1974
|
|
| Born |
Paul Ralph Ehrlich
May 29, 1932 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S.
|
| Education | |
| Known for | The Population Bomb (1968) Simon–Ehrlich wager |
| Spouse(s) | |
| Children | 1 |
| Awards |
|
| Scientific career | |
| Fields |
|
| Institutions | Stanford University |
| Thesis | The Morphology, Phylogeny and Higher Classification of the Butterflies (Lepidoptera: Papilionoidea) (1957) |
| Doctoral advisor | C. D. Michener |
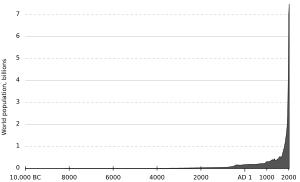
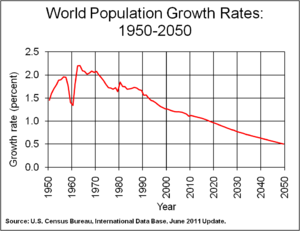
Paul Ralph Ehrlich (born May 29, 1932) is an American biologist and professor at Stanford University. He is famous for his warnings about the problems of a growing human population. He worried that too many people would lead to shortages of food and other resources.
In 1968, he and his wife, Anne H. Ehrlich, wrote a famous book called The Population Bomb. In it, they warned that in the 1970s, hundreds of millions of people would starve. This prediction did not come true, and Ehrlich has been criticized for it. However, he still believes that the world's population is a major issue. He now says that the bigger problem is overconsumption, which is when wealthy countries use too many resources.
Contents
Early Life and Career
Paul Ehrlich was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. As a child, he became interested in collecting and studying butterflies. This led him to become an entomologist, a scientist who studies insects. He earned his Ph.D. from the University of Kansas in 1957.
In 1959, he began working at Stanford University. He became a professor of biology in 1966. With another scientist, Peter H. Raven, he studied how plants and insects evolve together. This idea, called coevolution, was very influential. It helped explain why there are so many different types of plants and insects in the world.
The Overpopulation Debate
In the 1960s, many people were worried about the world's population growing too fast. Ehrlich became a leading voice in this debate. He appeared on television shows many times to share his concerns.
The Population Bomb (1968)
Ehrlich's most famous work is the book The Population Bomb. He wrote it with his wife, Anne, but the publisher only listed his name. The book started with a shocking statement: "The battle to feed all of humanity is over. In the 1970s hundreds of millions of people will starve to death."
Ehrlich argued that the human population was already too large. He said this would lead to terrible famines, the spread of diseases, and social problems. He suggested that countries needed to control their population growth.
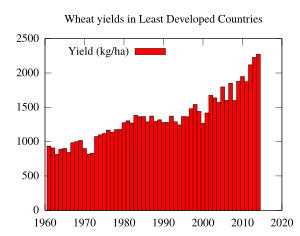
However, the massive famines he predicted did not happen. Many experts criticized the book for being too pessimistic. They pointed out that new farming technologies, known as the Green Revolution, helped produce much more food.
Later Views on Population
Even though his early predictions were wrong, Ehrlich still believes that population is a serious problem. In a 1990 book, The Population Explosion, he argued that the crisis was still happening, just in different ways.
In recent years, Ehrlich has said that his original book was "way too optimistic." He now focuses more on the problem of overconsumption. He argues that wealthy people and nations use a much larger share of the Earth's resources. In his view, this is a major threat to the environment. He believes the ideal population for Earth is between 1.5 and 2 billion people, much lower than the current population of over 8 billion.
Criticism and Praise
Ehrlich's ideas have always been controversial. Some people agree with his warnings, while others strongly disagree.
Failed Predictions
Many critics point out that Ehrlich's specific predictions did not come true. For example, he once said that by the year 2000, the United Kingdom would be a poor country with 70 million hungry people. When this didn't happen, he admitted he was wrong about the details but said that countries like the U.K. still face serious problems.
Critics like journalist Dan Gardner say that Ehrlich takes credit for general warnings that came true, like the rise of new diseases or climate change, but doesn't admit his specific mistakes.
The Simon–Ehrlich Wager
One of Ehrlich's biggest critics was an economist named Julian Simon. Simon believed that humans were creative enough to solve problems like resource shortages. He argued that resources were not running out.
To prove his point, Simon made a famous bet with Ehrlich in 1980. Ehrlich chose five metals that he thought would become more expensive over the next ten years because they were running out. Simon bet that their prices would go down. Ten years later, the prices of all five metals had dropped. Ehrlich lost the bet and paid Simon.
Ehrlich's Response
Ehrlich agrees that the Green Revolution helped prevent the famines he predicted. However, he argues that it only delayed the problem. He says that a growing population and high consumption are still damaging the planet. He points to problems like the loss of animal species, overfishing, and climate change as proof that humanity is using resources unsustainably.
Personal Life
Ehrlich married Anne Howland in 1954. She has co-authored many of his books and is a respected scientist herself. They have one daughter, Lisa Marie. Ehrlich is a patron of the organization Population Matters, which campaigns for a sustainable human population.
Awards and Honors
Despite the controversy, Ehrlich is a highly respected scientist. He has won many major awards for his work in ecology and environmental science, including:
- The Crafoord Prize (1990), a top award in ecology
- The Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement (1998)
- The Blue Planet Prize (1999)
- Fellow of the Royal Society of London (2012)
Images for kids
See also
- Demography
- Population Connection
- Moral panic