Heterochrony facts for kids

Heterochrony (say: het-uh-ROCK-ruh-nee) means "different time." It's a big idea in how living things grow and change. It describes any change in the timing of how an animal or plant develops. Think of it like a clock for growth!
This idea helps us understand why animals that are closely related can look very different. Even if they have similar DNA instructions, small changes in when things start, stop, or how fast they happen during growth can lead to big differences in shape and size. For example, a giraffe's long neck is a result of heterochrony.
Contents
What is Heterochrony?
Heterochrony is all about timing. It looks at when a certain feature appears in an organism's life. It also looks at how quickly a feature grows. For instance, a bone might grow for a longer time, making it much bigger. Or a feature might appear earlier or later than usual.
Types of Heterochrony
There are different ways that timing can change development. Here are some important types:
Paedomorphosis
Paedomorphosis (say: pee-doe-MOR-foh-sis) happens when an adult animal keeps features that were only seen in its young (juvenile) form. It's like an adult still looking like a baby! This happens because of changes in their genetic instructions.
Neoteny
Neoteny (say: nee-OT-uh-nee) is a type of paedomorphosis. In neoteny, the body's growth slows down, but the animal's ability to reproduce keeps developing at a normal speed. This means the animal can become a parent while still looking like a juvenile or a larva.
A great example is the Axolotl. These salamanders often stay in their larval, water-dwelling form their whole lives. They keep their feathery gills and fins, even though they are old enough to have babies. Most other salamanders would lose these features and move onto land as adults.
Progenesis
Progenesis (say: pro-JEN-uh-sis) is another type of paedomorphosis. With progenesis, the development of an animal stops early. It reaches sexual maturity (can reproduce) before it has fully grown into its adult size or shape.
Postdisplacement
Postdisplacement (say: pohst-diss-PLAYSS-ment) happens when the start of a development process is delayed. Imagine a part of the body that usually starts growing at a certain age. With postdisplacement, it starts growing later than it normally would.
How Heterochrony Explains Animal Differences
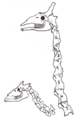
Heterochrony helps us understand how animals change over time. For example, Giraffes and okapi are related. They both have seven neck vertebrae (bones in the neck), just like humans! But giraffes have incredibly long necks. This is because the growth period for their neck bones is much longer during their development. The bones grow for more time, making them longer, instead of adding more bones.
Images for kids
-
Even though their necks are very different lengths, giraffes (right) have the same number of neck bones (7) as their relatives, the okapi (left). The bones just grow longer.
-
The Irish elk was a giant deer that lived long ago. Its huge antlers, which could span 2.7 meters (9 feet), are another example of how growth timing can lead to extreme features.
-
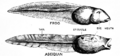
In 1928, a scientist named Walter Garstang suggested that vertebrates (animals with backbones) might have come from a creature similar to a tunicate larva (left) through neoteny. The frog tadpole (right) is a vertebrate larva.
-
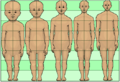
Neoteny can also be seen in human development. We keep some features from our younger stages, like our relatively large heads compared to our bodies, for longer than many other animals.
See also
 In Spanish: Heterocronía para niños
In Spanish: Heterocronía para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |