Photon facts for kids
Photons are tiny particles that carry light. The word "photon" comes from the Greek word for "light." In physics, photons are the basic units of light. They are also their own anti-particles. In quantum mechanics, each photon has a specific amount of energy.
Photons have no rest mass, meaning they don't have mass when they are still. However, Albert Einstein's theory of relativity shows that they do have momentum. Before they were called photons, Einstein suggested that light was made of separate packets of energy. These packets later became known as photons.
A photon is usually shown with the symbol γ (gamma).
Contents
What Are Photons Like?
Photons are fundamental particles. This means they are not made of smaller parts. While they can be created and destroyed, they last forever once they exist.
In a vacuum (empty space), all photons travel at the speed of light, which is about 299,792,458 meters (or 300,000 kilometers) per second. This speed is often called c.
Frequency and Wavelength
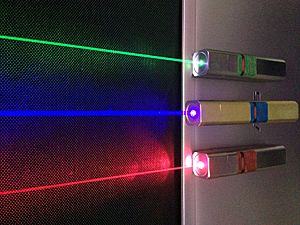
A photon has a certain frequency, which helps decide its color. For example, different frequencies of light create different colors we see. Radio technology uses frequency a lot.
The frequency of a photon is linked to its energy. This is shown by the Planck constant equation: E = h × f. Here, 'E' is energy, 'h' is Planck's constant, and 'f' is frequency.
Another important feature of a photon is its wavelength. Frequency (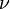 ), wavelength (
), wavelength (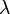 ), and the speed of light (c) are connected by the equation:
), and the speed of light (c) are connected by the equation: 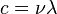 . Wavelength is used in many types of technology.
. Wavelength is used in many types of technology.
The energy of different photons is used in things like infrared cameras. It's also important for visible light and higher energy radiation like X-rays. This is because these photons have enough energy to ionize atoms, which means they can knock electrons out of atoms.
Polarity and Spin
Photons also have a property called polarity. Imagine a giant photon coming at you. It might look like a wave moving up and down, side to side, or somewhere in between.
Polarized sunglasses work by blocking photons that are swinging up and down. This helps reduce glare because light bouncing off surfaces often moves in that direction. LCD screens also use polarity to control which light passes through. Some animals can even see light polarization.
Finally, light has a spin. A photon's spin is a subtle feature that needs special equipment to detect.
Photons and Electromagnetism
In particle physics, photons are responsible for the electromagnetic force. This force combines electricity and magnetism. One common way we experience electromagnetism every day is through light. Electromagnetism also causes charge, which is why you can't push your hand through a solid table.
Since photons carry the electromagnetic force, they are also called gauge bosons. Some matter, like dark matter, is not thought to be affected by electromagnetism. This means dark matter would not have a charge and would not give off light.
How Light Is Made
Light is often created when energy hits an electron. This energy can come from heat, movement, or other forms. When an electron gains energy, it can jump to a higher energy level in its atom. This higher level is unstable, and the electron wants to return to its lowest energy state. (Think of dropping a pencil; it falls to the ground, which is a lower energy state).
When the electron drops back down, it must release the extra energy it gained. This follows the conservation of energy rule, which says energy cannot be created or destroyed. Electrons release this energy as photons. When many photons are released with enough intensity, we can see them as visible light.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Stimulated emission is when photons "clone" themselves. This idea helped lead to the creation of the laser.
See also
 In Spanish: Fotón para niños
In Spanish: Fotón para niños
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |