Conservation of energy facts for kids
The law of conservation of energy is a super important rule in physics and chemistry. It says that the total amount of energy in a closed system always stays the same. Think of a closed system as a bubble where nothing can get in or out.
This means energy can't be made or destroyed. It can only change from one form to another, or move from one place to another. For example, when a stick of dynamite explodes, the chemical energy stored in it turns into other types of energy. You get kinetic energy (movement) from the flying pieces, plus heat and sound. If you add up all these new forms of energy, they will exactly match the chemical energy that was used up.
Long ago, people thought mass and energy were separate. But thanks to Albert Einstein's theory of special relativity, we now know they are connected by the famous equation E = mc². This means mass itself is a form of energy! So, scientists now say that mass-energy as a whole is always conserved.
A cool result of this law is that a perpetual motion machine can't exist. This is a machine that could run forever and give out endless energy without needing any fuel. The law of conservation of energy tells us this is impossible!
Contents
How We Learned About Energy Conservation
The idea that something fundamental stays the same has been around for a long time. Ancient thinkers like Thales wondered what everything was made of. But their ideas were different from our modern understanding of energy.
Early Discoveries
In 1638, Galileo Galilei studied how things move. He looked at a swinging pendulum. He noticed that as the pendulum swung, its height and speed changed. This showed how potential energy (energy of position) could turn into kinetic energy (energy of motion) and back again. Galileo didn't use these exact terms, but his work helped set the stage.
Later, in the late 1600s, Gottfried Leibniz from Germany tried to describe the energy of motion using math. He called this "vis viva," meaning "living force." He saw that in systems without friction, a certain quantity related to mass and speed stayed constant. This was an early step towards understanding kinetic energy.
Heat and Motion Connection
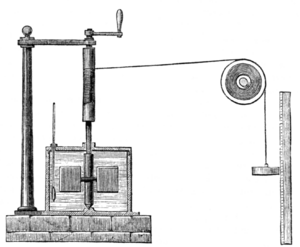
A big breakthrough happened in 1843 with James Prescott Joule. He did many experiments to show that mechanical energy (like motion) could turn into heat. In his most famous experiment, called the "Joule apparatus," a weight fell and turned a paddle in water. He found that the energy lost by the falling weight was almost exactly equal to the heat gained by the water. This proved that heat is just another form of energy.
Images for kids
-
Emmy Noether (1882-1935) was a very important mathematician who helped us understand abstract algebra and theoretical physics.
See also
 In Spanish: Conservación de la energía para niños
In Spanish: Conservación de la energía para niños