Pinus maximartinezii facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Pinus maximartinezii |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Pinus |
| Subgenus: | P. subg. Strobus |
| Section: | P. sect. Parrya |
| Subsection: | P. subsect. Cembroides |
| Species: |
P. maximartinezii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pinus maximartinezii Rzedowski
|
|
 |
|
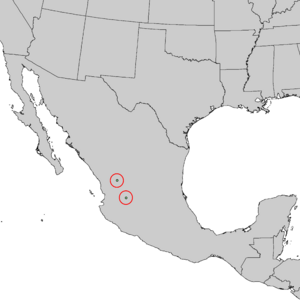
| Natural range of Pinus maximartinezii | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Pinus maximartinezii, also known as the Martinez pinyon or big-cone pinyon, is a special type of pine tree. It belongs to the pinyon pine family and grows only in a small part of west-central Mexico. This tree is famous for its incredibly large cones and seeds!
Contents
What Makes the Martinez Pinyon Special?
Size and Appearance
The Martinez pinyon is a small tree. It usually grows to be about 5 to 15 meters (16 to 49 feet) tall. Its trunk can be up to 50 centimeters (20 inches) wide. The bark is thick and brown, with cracks near the bottom of the trunk.
Leaves, Cones, and Seeds
The leaves of this pine are called 'needles'. They grow in groups of five, like a small bunch. Each needle is thin and about 7 to 13 centimeters (3 to 5 inches) long. They are deep green or blue-green. The needles have tiny pores called stomata on their inner surfaces. These pores look like a bright white stripe.
The cones of the Martinez pinyon are huge! They are shaped like an oval and can be 15 to 27 centimeters (6 to 11 inches) long. They are also very wide, about 8 to 14 centimeters (3 to 5 inches) across. A closed cone can weigh up to 2 kilograms (4.4 pounds). When they are young, the cones are green. They turn yellow-brown when they are about 26 to 28 months old. The cones have very thick, woody scales. There are usually 30 to 60 fertile scales on each cone. These scales are quite stiff, which is unusual for a pine in its group. When the cones are ready, they open up to 10 to 15 centimeters (4 to 6 inches) wide.
The seeds inside these cones are also very big. They are 2 to 3 centimeters (about 1 inch) long. Each seed has a thick shell. They have a tiny, undeveloped wing, only 1 to 2 millimeters long. When a Martinez pinyon seed sprouts, it grows many first leaves, called cotyledons. It can have 18 to 24 cotyledons, which is the most found in any plant!
Why Its Seeds Are Important
The Martinez pinyon stands out from other pinyon pines because of its massive cones and large seeds. Like other pinyon pines, its seeds are safe to eat. People often collect these seeds. This can be a problem for the tree's survival. When too many seeds are harvested, fewer new pine trees can grow naturally.
Where Does This Pine Live?
Its Home in Mexico
The Martinez pinyon only grows in a very small area. It is found in two specific places in the southern Sierra Madre Occidental mountains in Mexico. These places are the Sierra de Morones in southern Zacatecas and La Muralla in Durango.
It grows at medium heights, from about 1,800 to 2,400 meters (5,900 to 7,900 feet) above sea level. The climate where it lives is warm, mild, and dry.
Why It's Endangered
Because there are so few of these trees, the Mexican government has officially declared the Martinez pinyon an endangered species. This means it is at high risk of disappearing forever if we don't protect it.
How Was This Tree Discovered?
For a long time, this special pine tree was unknown to scientists. It grew in a very remote area. In 1964, a Mexican botanist named Jerzy Rzedowski made an interesting discovery. He saw some unusually large pine nuts, called piñones, being sold in local village markets. He decided to investigate where these big nuts came from. His search led him to find the Pinus maximartinezii tree!
Growing the Martinez Pinyon
Recently, people have started to grow the Martinez pinyon in other places. It is becoming a popular and beautiful tree for gardens and parks.
See also
 In Spanish: Piñón de Martínez para niños
In Spanish: Piñón de Martínez para niños


