Planck (spacecraft) facts for kids
| Names | COBRAS/SAMBA |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Space telescope |
| Operator | ESA |
| Mission duration | Planned: >15 months Final: 4 years, 5 months, 8 days |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Thales Alenia Space |
| Launch mass | 1,950 kg (4,300 lb) |
| Payload mass | 205 kg (452 lb) |
| Dimensions | Body: 4.20 m × 4.22 m (13.8 ft × 13.8 ft) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 14 May 2009, 13:12:02 UTC |
| Rocket | Ariane 5 ECA |
| Launch site | Guiana Space Centre, French Guiana |
| Contractor | Arianespace |
| Entered service | 3 July 2009 |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Decommissioned |
| Deactivated | 23 October 2013, 12:10:27 UTC |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | L2 point (1,500,000 km / 930,000 mi) |
| Regime | Lissajous |
| Main telescope | |
| Type | Gregorian |
| Diameter | 1.9 m × 1.5 m (6.2 ft × 4.9 ft) |
| Wavelengths | 300 µm – 11.1 mm (frequencies between 27 GHz and 1 THz) |
|
Horizon 2000
|
|
The Planck space observatory was a special telescope used by the European Space Agency (ESA). It was active from 2009 to 2013.
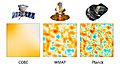
Its main job was to map tiny differences in the cosmic microwave background (CMB). The CMB is like an echo of the Big Bang, the very beginning of our universe. Planck looked at this echo using microwave and infrared light. It did this with great detail and sensitivity.
The Planck mission helped scientists learn a lot about cosmology (the study of the universe) and astrophysics (the study of stars and galaxies). It helped test ideas about how the early universe formed. It also looked at how cosmic structures, like galaxies, first appeared.
After its mission ended, Planck gave us the most exact measurements of several important numbers. These include the average amount of normal matter and mysterious dark matter in the universe. It also helped us figure out the age of the universe. The Planck telescope is now switched off.
Contents
What was the Planck Mission?
The Planck mission was designed to study the very first light in the universe. This light is called the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). It is the oldest light we can see.
Why study the CMB?
Studying the CMB helps us understand what the universe was like when it was very young. It shows us tiny temperature differences. These differences eventually grew into the stars and galaxies we see today.
How did Planck work?
Planck had two main instruments:
- The High Frequency Instrument (HFI)
- The Low Frequency Instrument (LFI)
These instruments measured different types of microwaves. They worked together to create a full map of the CMB. The telescope was a Gregorian type. This means it used two curved mirrors to focus the light.
Where was Planck located?
Planck orbited around a special spot in space called the Lagrangian Point 2. This point is about 1.5 million kilometers (about 930,000 miles) away from Earth. It's a stable "parking spot" where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance out. This allowed Planck to stay cool and have a clear view of space.
What did Planck discover?
Planck gave us the most detailed map of the CMB ever made. This map helped scientists confirm many ideas about the universe.
- Age of the Universe: Planck helped scientists calculate the universe is about 13.8 billion years old.
- Composition of the Universe: It showed us that the universe is made of:
* About 4.9% normal matter (like stars, planets, and us) * About 26.8% dark matter (a mysterious substance we can't see) * About 68.3% dark energy (a force that makes the universe expand faster)
- Early Universe: The data from Planck supported the idea of cosmic inflation. This is a theory that the universe expanded incredibly fast right after the Big Bang.
Images for kids
-
Some of the Herschel-Planck team, from left to right: Jean-Jacques Juillet, director of scientific programmes, Thales Alenia Space; Marc Sauvage, project scientist for Herschel PACS experiment, CEA; François Bouchet, Planck operations manager, IAP; and Jean-Michel Reix, Herschel & Planck operations manager, Thales Alenia Space. Taken during presentations of the first results for the missions, Cannes, October 2009.
See also
 In Spanish: Planck (satélite) para niños
In Spanish: Planck (satélite) para niños