Plastid facts for kids
A plastid is a tiny part inside the cells of plants and algae. Think of them like small factories or storage units within a cell. They can make or store important chemicals that the plant needs to live and grow. Each plastid can also make copies of itself. The special DNA inside a plastid is called a plastome.
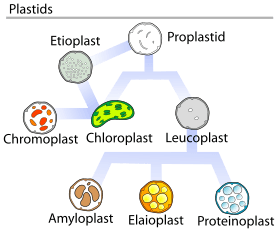
There are different types of plastids, and each has a special job:
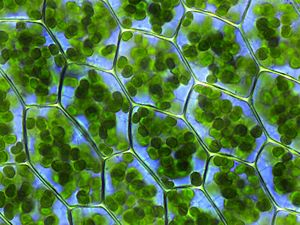
- Chloroplasts: These are the most famous plastids. They are green and help plants make their own food using sunlight, a process called photosynthesis. Other types of plastids might have grown from chloroplasts. If a chloroplast hasn't been exposed to light yet, it's called an etioplast.
- Chromoplasts: These plastids make and store pigments, which give plants their bright colors, like in flowers and fruits.
- Leucoplasts: These plastids are colorless. They can make substances like resin. Some leucoplasts can even change into more specialized types:
Plastids in Algae and Hornworts
Plastids in algae and hornworts can be a bit different from those found in plants. In algae, the word "leucoplast" is used for any plastid that doesn't have color, and their jobs are different from plant leucoplasts.
For example, a type of algae called glaucocystophytic algae has muroplasts. These are like chloroplasts but have a special cell wall, similar to very simple living things called prokaryotes. Rhodophytic algae have rhodoplasts, which are red chloroplasts. These red plastids allow the algae to do photosynthesis even in very deep water, up to 268 meters below the surface!
How Plastids Evolved
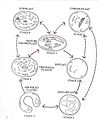
Plastids are just one of many tiny parts, or organelles, inside a cell. Scientists believe that plastids originally came from tiny bacteria called cyanobacteria. This idea is part of the endosymbiont theory. It was first suggested in 1905 by a scientist named Mereschkowsky. Another scientist, Schimper, had already noticed in 1883 that chloroplasts looked a lot like cyanobacteria.
Most chloroplasts today are thought to have come from a single event where a plant cell "swallowed" a cyanobacterium a very long time ago. This is similar to how Mitochondria (the powerhouses of the cell) also came from a type of symbiosis. However, chloroplasts are only found in plants and some protists.
A chloroplast has two layers of membranes around it, with a space in between. Inside, it has many folds and its own DNA. This DNA contains instructions for making special proteins that help with electron transport during photosynthesis.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Plasto para niños
In Spanish: Plasto para niños
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |