Probability density function facts for kids
In the world of probability and statistics, a probability density function (often called a PDF) is a special function. It helps us understand how likely it is for a continuous random variable to fall within a certain range of values. Think of it like a smooth curve that shows where numbers are more likely to appear.
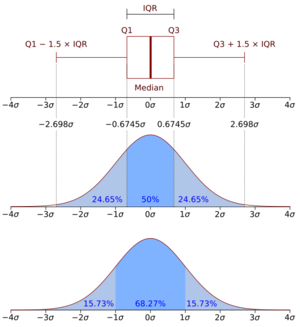
For example, if you measure the heights of many people, you'll find that most people are around an average height, and fewer people are very short or very tall. A probability density function can show this pattern. The area under the curve of this function between two points tells you the probability that a random measurement (like a person's height) will be between those two points.
A key rule for a probability density function is that it must always be positive or zero. Also, if you add up the probabilities for all possible values (which means finding the total area under the curve), it must always equal 1. This makes sense because the total probability of something happening is always 100%.
Contents
Probability Density vs. Probability Mass
It's important to know the difference between a probability density function and a probability mass function.
Continuous Data
A probability density function is used for continuous data. Continuous data can take any value within a range. For example, a person's height could be 170 cm, 170.5 cm, 170.53 cm, and so on. There are endless possibilities between any two numbers.
Imagine measuring the exact height of every student in your school. No two students would have the exact same height down to the smallest fraction of a millimeter. A probability density function helps us work with these kinds of measurements. It lets us find the probability that a student's height is, say, between 150 centimetres (59 in) and 155 centimetres (61 in).
Discrete Data
In contrast, a probability mass function is used for discrete data. Discrete data can only take specific, separate values. For example, when you roll a standard dice, the only possible outcomes are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. You can't roll a 3.5.
For discrete data, you can directly find the probability of a specific value. For example, the probability of rolling a 4 on a fair dice is  . But for continuous data, the probability of getting one exact value (like exactly 170.00000000 cm tall) is practically zero because there are infinitely many possibilities. That's why we use a probability density function to find probabilities over a range of values instead.
. But for continuous data, the probability of getting one exact value (like exactly 170.00000000 cm tall) is practically zero because there are infinitely many possibilities. That's why we use a probability density function to find probabilities over a range of values instead.
Related pages
- Cumulative distribution function
See also
 In Spanish: Función de densidad de probabilidad para niños
In Spanish: Función de densidad de probabilidad para niños