Probability distribution facts for kids
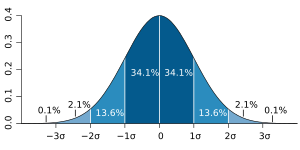
A probability distribution is a way to show all the possible results of a random event. It also tells us how likely each result is. Think of it like a map that tells you the chances of different things happening. It's used in mathematics to understand things that have random outcomes.
Imagine you're flipping a coin or rolling a dice. You don't know exactly what will happen each time. A probability distribution helps us predict what should happen over many tries. It's different from a frequency distribution, which just tells you what did happen in the past.
Probability distributions can be for things that have a specific number of outcomes. For example, rolling a dice can only give you 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. These are called discrete distributions. Or they can be for things that can have any value within a range. For example, measuring someone's height. These are called continuous distributions.
Contents
Understanding Dice Roll Probabilities
Let's look at rolling a normal 6-sided dice. Each side has an equal chance of landing face up.
| Result | 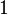 |
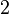 |
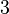 |
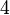 |
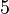 |
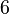 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probability of result |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
This table shows that for each number (1 to 6), the chance of it appearing is 1 out of 6. If you roll a dice 60 times, you would expect each side to appear about 10 times on average.
Different Types of Distributions
There are many different types of probability distributions. Each one is useful for different situations. They all have their own strengths and weaknesses. Some common probability distributions include:
- Binomial distribution
- Cauchy distribution
- Chi-square distribution
- Exponential distribution
- Gumbel distribution
- Normal distribution
- Poisson distribution
- Student's t-distribution
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Distribución de probabilidad para niños
In Spanish: Distribución de probabilidad para niños