Protoceratops facts for kids
Quick facts for kids ProtoceratopsTemporal range: Upper Cretaceous
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Protoceratops skeleton at Wyoming Dinosaur Center. | |
| Conservation status | |
|
Fossil
|
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Infraorder: | |
| Family: |
Protoceratopsidae
|
| Genus: |
Protoceratops
|
| Groups | |
|
P. andrewsi (type) |
|
Protoceratops was a fascinating plant-eating dinosaur that lived in what is now Mongolia. This dinosaur is famous for a fossil that shows it in a fierce battle with a Velociraptor. Imagine two dinosaurs frozen in time during a fight!
Contents
What Did Protoceratops Look Like?
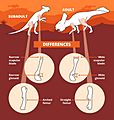
Protoceratops was a four-legged dinosaur with a unique look. It had a special bony frill at the back of its head. This frill had two big holes in it. The exact size and shape of the frill were different for each Protoceratops. Some had short frills, while others had frills almost half the length of their entire skull! Scientists think these differences might be because of age or even whether the dinosaur was male or female.
This dinosaur was about 1.8 meters (5.9 feet) long and 0.6 meters (2 feet) tall at the shoulder. A full-grown adult Protoceratops would have weighed around 82.7 kilograms (182 pounds). Many Protoceratops fossils have been found together. This suggests that they probably lived in large groups, like herds.
Protoceratops had a relatively small body but a very large head. Its jaws were strong and filled with many teeth. These teeth were perfect for chewing tough plants. Its skull also had a big beak at the front, like a parrot. It had large eye sockets, about 50 millimeters (2 inches) wide.
Discovery and Different Types
The first Protoceratops fossils were found in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia. This happened in 1922 during an American expedition. The team was looking for early human ancestors, but instead, they found many amazing dinosaur fossils! They discovered many Protoceratops skeletons, along with Velociraptor and Oviraptor.
Scientists Walter Granger and W. K. Gregory officially described the first species in 1923. They named it P. andrewsi after the expedition leader, Roy Chapman Andrews. These fossils are about 75 to 71 million years old. When they were found, scientists thought Protoceratops might be the ancestor of the famous Triceratops. The fossils were so well preserved that even delicate eye bones were still there!
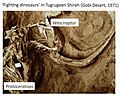
One of the most famous Protoceratops fossils was found in 1971. It shows a Velociraptor and a Protoceratops locked in a fight. Scientists believe they died together, perhaps buried by a sandstorm or a collapsing sand dune.
In 2001, another type of Protoceratops was discovered in China. It was named P. hellenikorhinus. This species was bigger than P. andrewsi and had a slightly different frill. It also had small horns over its nostrils.
In 2011, a Protoceratops fossil was found with its own footprint preserved next to it! This was the first time a dinosaur was found with its footprint right there.
How Protoceratops Lived
Reproduction and Family Life

In the 1920s, the first dinosaur eggs ever found were discovered in the Gobi Desert. Each egg was about 8 inches long. Because many Protoceratops fossils were found nearby, scientists first thought these eggs belonged to Protoceratops.
Later, a fossil of an Oviraptor was found near a nest of these eggs. Scientists thought the Oviraptor was trying to steal the eggs. They even thought a Protoceratops mother might have fought the Oviraptor to protect her nest. However, in 1993, scientists found an embryo inside one of these eggs. It turned out to be an Oviraptor embryo! This meant the Oviraptor was actually the parent, sitting on its own nest, not stealing eggs.
In 2011, a nest with 15 young Protoceratops andrewsi was found in Mongolia. This was the first true Protoceratops nest ever discovered. This amazing find suggests that Protoceratops parents likely cared for their young. They probably stayed with their babies in the nest when they were very young. Since Protoceratops is an early type of ceratopsian, this discovery also suggests that other ceratopsians might have cared for their young too.
Daily Activities
Protoceratops had large eyes, which made some scientists think it was active at night. However, by comparing its eye bones to those of modern birds and reptiles, scientists now think Protoceratops was active throughout the day in short bursts. This means the famous fight between Protoceratops and Velociraptor might have happened during twilight or in low light conditions.
Classification: Where Does Protoceratops Fit?
Protoceratops was the first dinosaur named in its group, the Protoceratopsidae. This family includes plant-eating dinosaurs that are more advanced than some early ceratopsians but not as advanced as the big horned dinosaurs like Triceratops. Dinosaurs in this group often had smaller frills and no large horns. They also had limbs that were good for running.
Scientists use a "family tree" called a cladogram to show how dinosaurs are related. Protoceratops is an important part of understanding the evolution of horned dinosaurs.
The Myth of the Griffin
A historian named Adrienne Mayor has an interesting idea about the mythical creature called the griffin. Griffins were described as creatures with a lion's body, big claws, and a bird-like beak. They were said to lay eggs in nests on the ground.
Mayor suggests that ancient people found the amazing fossils of Protoceratops in Central Asia. These fossils might have inspired the idea of the griffin. The area where many Protoceratops fossils are found, in Mongolia and China, is also rich in gold. This fits with the ancient stories of griffins guarding gold deposits. Greek writers started describing griffins around 675 B.C., which is when they first met the nomads who lived in these areas.
However, some people disagree with this idea. They point out that there are older pictures and stories of griffins from before the Greeks met these nomads.
Images for kids
-
Flaming Cliffs of Mongolia. This area in the Gobi Desert is where the first Protoceratops fossils were found.
-
A classic drawing of a mythical griffin.
See also
 In Spanish: Protoceratops para niños
In Spanish: Protoceratops para niños