Ransomware facts for kids
Ransomware is a type of malware, which is a short name for "malicious software." It's a harmful computer program that tries to stop you from using your computer or accessing your files. To get your computer back, the people who created the ransomware demand a payment, often called a ransom.
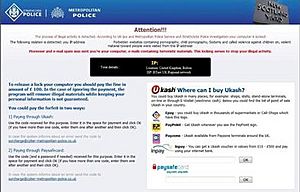
Some ransomware programs are very tricky. They can encrypt (or scramble) the files on your computer's hard disk, making them unreadable. Other types might just lock your screen and show scary messages. These messages try to convince you that you must pay money to unlock your computer.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is like a digital kidnapper for your computer. It takes your files or your whole computer hostage. The people behind it then ask for money, usually in digital currency, to give you back control. If you don't pay, they might threaten to keep your files locked forever or even delete them.
How Ransomware Spreads
Ransomware often spreads through tricky methods. You might get an email with a fake link or an attachment that looks harmless. If you click on it, the ransomware can secretly install itself on your computer. It can also spread through infected websites or by exploiting weaknesses in software.
A Brief History of Ransomware
Ransomware first became well-known in Russia. Over time, these types of scams started to spread all over the world. In 2013, a company called McAfee found a huge increase in ransomware samples. They saw more than double the number compared to the year before!
One famous example was a ransomware program called CryptoLocker. It appeared in late 2013 and was a type of Computer worm. A computer worm is a program that can copy itself and spread to other computers. CryptoLocker managed to collect about $3 million USD from people before authorities (like law enforcement) were able to shut it down.
See also
 In Spanish: Ransomware para niños
In Spanish: Ransomware para niños