Red Horn facts for kids
Red Horn is a special hero in the old stories of the Siouan people. These stories come from groups like the Ioway and Ho-Chunk (Winnebago) nations.
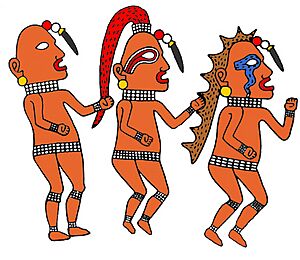
He has a few different names. In Ho-Chunk stories, he is called "Red Horn" (Hešucka). But among both the Ioway and Ho-Chunk, he is also known as "He Who Wears (Man) Faces on His Ears." This name comes from the tiny, living faces on his earlobes. Or, in some stories, they are ear decorations that come alive when he puts them on. He is also called "Red Man" (Wąkšucka) because his whole body is red.
Red Horn was one of five sons of Earthmaker, the Creator. Earthmaker made them to help humanity. While on Earth, Red Horn fought against giants and water spirits. He also led groups of warriors against bad spirits who caused trouble for people.
Some stories say that "He Who Wears Faces on His Ears" is a star. It's not clear which star, though. Red Horn and his sons also lead small hunting spirits called herok'a and "little children spirits." As the chief of the herok'a, Red Horn is sometimes seen as being connected to the arrow itself. Experts think Red Horn might be a figure shown in ancient Mississippian art, found on many special artifacts from that time.
Contents
Red Horn: Son of the Creator
According to old legends, Red Horn was one of five important spirits made by the Creator. They were sent to Earth to make the world safe for humans.
The first spirit, Trickster, was too silly and had to go back. Next came Bladder, who was too proud. Then Turtle, who taught humans about war. Finally, Hare came and defeated all the bad spirits. Hare accidentally brought death, but he also created the Medicine Lodge, where people could find a kind of lasting life.
Red Horn was almost the last hero sent by Earthmaker. He nearly succeeded in his mission. But he was defeated in a wrestling match against the enemies of humans. Even though he was brought back to life, he was eventually called back by Earthmaker.
One story says why he might have been called back: "Then Earthmaker sent down another son, He who Wears Human Heads as Earrings. He talked to people, but they kept looking at his earrings. These tiny heads would wink and make funny faces. In the end, He who Wears Human Heads as Earrings couldn't finish his mission either."
Unlike the other heroes, Red Horn doesn't get his own special place to rule in the afterlife. This makes some experts think he might have been added to these stories later on.
Red Horn's Exciting Adventures
The stories of Red Horn's adventures are called the "Red Horn Cycle." These stories show him with his friends, like Turtle and the thunderbird Storms-as-He-Walks. They fight against a group of giants called Wąge-rucge, or "Man-Eaters," who were harming humans. Red Horn had promised to help the humans.
In one adventure, Red Horn changes himself into an arrow to win a race. After winning, he creates the little faces on his earlobes. He also makes his hair into a long red braid, which is called a he or "horn" in Ho-Chunk. This is how he gets the names "Red-horn" (he-šucka) and "He who Wears (Human) Faces on His Ears" (įco-horúšika).
In another story, the giants challenge Red Horn and his friends to a game of kisik, which is like lacrosse. The giants' best player was a woman with long red hair, just like Red Horn's. The little heads on Red Horn's ears made her laugh so much that she couldn't play well. So, the giants lost the game. Red Horn then married the woman with the red hair.
The giants lost all the other games too. Then they challenged Red Horn and his friends to a wrestling match. The giants won two out of three matches, and Red Horn and his friends were defeated.
Red Horn and the Stars
Many people have wondered if Red Horn is connected to a star. Some experts, like Paul Radin, thought Red Horn might be the Morning Star (the planet Venus). However, Radin changed his mind later, suggesting Red Horn might be the Evening Star.
After a lot of study, one expert, Lankford, said it's safest to think of Red Horn and other Ho-Chunk gods as possibly being stellar figures, but without a clear star name.
However, at the very end of one story, Red Horn, in his "Wears Faces on His Ears" form, is called a fixed star. This star is likely Alnilam, one of the stars in Orion's Belt. The story says: "The one star that is shining most greatly of the trio, it is he. The greatly shining white one, and the blue one, and the red one; and Icohorúšika was the yellowish one. And the other ones, his older brothers, are also stars. They are the trio that are bunched together [the Belt Stars of Orion ?]."
The Morning Star is not a fixed star, so this shows they are different. In another Ho-Chunk story, Polaris (the North Star) has hummingbirds as earrings, which is similar to Red Horn's living ear decorations.
Red Man, Chief of the Herok'a
In the Red Horn stories, a human chief offers his daughter as a prize in a race. Many fast spirits come to compete. But a stranger wins the race by turning himself into an arrow and shooting himself forward. The winner says his name is "Red Horn," but spirits know him as "Wears Man-Faces on His Ears." This shows that Red Horn has a special connection to arrows.
Another story, "The Baldheaded War Club," tells us more about Red Horn and the herok'a spirits. Trickster, a hero, gathered a war party to fight evil spirits. Red Horn was part of this group. When the evil spirits attacked, a different leader stepped forward.
This leader had a single red horn on his forehead. He took it off and struck the water, making it burn up all the bad spirits. He then said, "From now on, you will not call me 'One Horn.' I used my horn to help humans, so humans will call me 'Without Horns,' because I made myself without any." This is why the herok'a are called "ones without horns."
In this story, Red Horn is first called "One Horn" (Hejąkiga), then "Without Horns" (Herok'aga). This last name is sometimes given to his son, showing how Red Horn and his sons are connected across generations.
The word he, meaning "horn," in names like He-jąki-ga ("One Horn") and He-šuc-ka ("Red Horn") can also mean "arrow." In the myth "The Brown Squirrel," a hero points a red cedar "horn" at a bad spirit. This "horn" is later called a "protruding horn." At the end of the myth, the bad spirit is told that boys will shoot him with "protruding horns" (arrows). This means arrows are seen as "horns," especially "red horns." So, the name Hešucka ("Red Horn") refers to his red braid and his special connection to the arrow. It also explains why the spirits he leads are called "without horns"—because they shoot their bows without needing an arrow. Red Horn wins races because he himself is the arrow he shoots to victory.
Red Horn in Ancient Art
Some images found in the SECC area might show Red Horn, his friends, and his sons. Many ancient ear decorations have been found that look like faces. These would have made the wearer look a lot like the mythical Red Horn.
Other artifacts, like the bilobed arrow, might explain an old name Red Horn had: "He Who is Hit with Deer Lungs." Beautifully carved pipes have also been found. One, called "Big Boy," is widely believed to be Red Horn. There are also many pictures of a bird with human features, called "Birdman." Some experts think this "Birdman," who often wears face-like ear decorations, is also a form of Red Horn.
Pictures found in caves have also been linked to Red Horn. One expert, Salzer, thinks a scene in the Gottschall Rockshelter cave shows Red Horn and his friends facing the giants. At Picture Cave, another site, a main figure wears face-like ear decorations, suggesting it might be an early image of Red Horn.
Face-like Ear Decorations as Ancient Artifacts
In the Ioway version of the Red Horn story, "Wears Man-Heads in His Ears" puts on special ear decorations that come to life. These face-like ear ornaments have been found in many places where the SECC culture lived. They are called "Long-nosed god maskettes." They were usually made of valuable materials like copper or shell.
Today, the Ho-Chunk word for special shell beads (wampum) also means earrings. This suggests that some earrings were once considered valuable wampum. These ancient artifacts look very similar, except for the nose size, which can be short or very long. The face is shaped like a shield, and the eyes are large and round, like an owl's.
The first of these was found in St. Louis in 1870, next to a skull in a grave. Since then, almost forty of these artifacts have been found across at least ten states. Ancient SECC art shows figures wearing these long-nosed god maskettes on their ears, just like Red Horn and his sons. One carved pipe, called "Big Boy," shows a young man wearing short-nosed ear decorations.
These artifacts were called "Long-Nosed God" maskettes because they looked like a god with a very long nose. Some even have a bilobed arrow attached to their hair and a single long braid, which are all features linked to Red Horn. However, many of these ear decorations have only a short nose. This has led some experts to believe they represent the Twins, and were worn by war captives who were joining a new tribe.
The "Big Boy" Pipe
"Big Boy" is a large carved pipe found at Spiro Mounds. It weighs over 11 pounds and is probably made of a red rock called bauxite. It might have been a sculpture first, then turned into a pipe.
The figure is unclothed, with his hair tied in a bun at the back and a long braid over his left shoulder. He wears a cape on his back that has a "spade" or feather design. He also wears a flat cap with a special design. Around his neck is a fancy necklace made of three strands of beads.
His most interesting feature is a pair of face-like ear ornaments, which are the short-nosed type. Because of his long red braid and these ear decorations, many experts believe "Big Boy" represents Red Horn. One expert, James A. Brown, agrees but warns that it's hard to be completely sure because of how old the art is.
However, some experts think the ear decorations represent the Twins and were worn by captives joining a tribe. So, they see "Big Boy" as a picture of such a captive, not Red Horn himself.
The Bird Man
Another figure in ancient SECC art is a bird with a very human-like face. This "Birdman" is often shown wearing face-like ear decorations. Some experts also believe this Birdman is another form of Red Horn.
The Gottschall Cave Pictures
Gottschall Rockshelter in Wisconsin has about forty ancient pictures. In 1982, Robert J. Salzer began studying the site. He found a special group of pictures, Panel 5, which seemed to show a single event. These pictures are believed to be from the tenth century A.D.
Experts suggested that one figure in Panel 5 looked like Red Horn. Salzer identified other figures as two giants, one of whom was the woman Red Horn later married. Other pictures seemed to be Turtle and Storms-as-He-Walks. All these figures were together for a big lacrosse game between the good spirits and the giants.
Salzer believes the figure on the far right is Red Horn himself. The face-like ear decorations are not visible because part of a bird's tail was painted over Red Horn's ears. Most experts agree that this panel tells a story from the Red Horn myths.
Picture Cave
In Missouri, there's a place called "Picture Cave" because it has many ancient drawings. One drawing has been identified as the Ho-Chunk spirit Red Horn (Wears Faces on His Ears). Other drawings in the cave are from about 915 AD to 1066 AD. The age of the "Red Horn" drawing isn't known yet, but it looks different and might be older.
Mainly because of the face-like ear decoration, experts connect the main figure in this scene to Red Horn. One expert describes the figure as "Morning Star (known by the Winnebago as Red Horn)." He also thinks the Red Horn in Picture Cave is holding the head of Morning Star, which he sees as an act of bringing himself back to life.