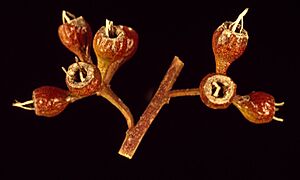Red morrel facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Red morrel |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Eucalyptus longicornis near Southern Cross | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Eucalyptus |
| Species: |
E. longicornis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eucalyptus longicornis |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Eucalyptus longicornis, also known as the red morrel, is a tall tree. It is found only in the southwest part of Western Australia. This tree has rough, stringy bark on its main trunk. Higher up, its bark is smooth and grey. The red morrel grows white flowers in groups of seven or more. Its fruit looks like a small, round woody ball.
Contents
What Does the Red Morrel Look Like?
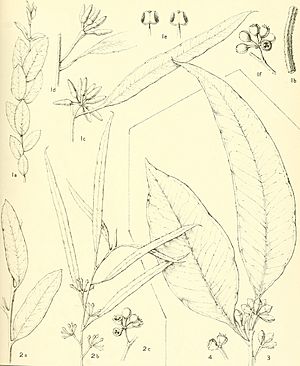
The red morrel tree usually grows to be about 2 to 24 meters (6 to 79 feet) tall. Some can even reach 30 meters (98 feet) high! Its trunk has rough, grey-brown bark that often looks cracked. Higher up, the bark is smooth and can be white or grey.
Young red morrel plants have stems that look a bit waxy or powdery (this is called glaucous). These stems are mostly square. Their leaves are directly attached to the stem (sessile). They are shaped like a spear or an egg, about 20 to 85 millimeters long and 9 to 26 millimeters wide.
Adult leaves grow in an alternating pattern. They are thick and shiny green on both sides. These leaves are narrow and spear-shaped, about 60 to 130 millimeters long and 6 to 13 millimeters wide. They narrow down to a small stem called a petiole, which is about 10 to 15 millimeters long.
The tree's flower buds grow in groups of seven to thirteen. They are found where the leaves meet the stem. Each group of buds sits on a stalk (peduncle) that is 6 to 13 millimeters long. Each individual bud has its own small stem (pedicel) that is 4 to 9 millimeters long.
When the buds are ready, they are oval-shaped, about 9 to 15 millimeters long and 3 to 6 millimeters wide. They have a pointed cap (operculum) that is 7 to 10 millimeters long. The red morrel flowers are white and bloom between December and February.
After flowering, the tree produces woody, round fruits. These fruits are called capsules. They are about 6 to 8 millimeters long and wide. The parts that open to release seeds stick out from the fruit's edge. Each gram of these capsules holds over 200 seeds! The capsules stay on the tree for at least a year, sometimes even longer.
How the Red Morrel Got Its Name
This tree was first officially described in 1878 by a scientist named Ferdinand von Mueller. He first called it Eucalyptus oleosa var. longicornis. He wrote about it in his book Fragmenta Phytographiae Australiae.
Later, in 1919, another scientist, Joseph Maiden, noticed that Mueller had used the name Eucalyptus longicornis in another one of his books, Eucalyptographia, but without a full description. So, Maiden officially published the new name Eucalyptus longicornis in the Journal and Proceedings of the Royal Society of New South Wales. He made sure to give credit to Mueller for first using the name.
The Noongar people, who are the traditional owners of the land where this tree grows, call it morryl, poot, or put.
The second part of the scientific name, longicornis, comes from two Latin words. Longus means "long," and cornu means "horn." This name refers to the long, horn-like shape of the flower buds.
Where Does the Red Morrel Grow?
The red morrel tree is found in the Wheatbelt and southern Goldfields-Esperance areas of Western Australia. It likes to grow in loamy soils, which are a mix of sand, silt, and clay. These soils are often found over limestone or clay loam on flat areas.
The tree grows best in dark red loamy soils. These soils are rich in minerals and can sometimes be a little salty. They form from the breakdown of certain rocks like dolerite gneiss dykes and other rock formations in the Yilgarn Block.
Its Home and Neighbors
The red morrel usually lives in woodland areas. It is often one of the tallest trees (an overstorey tree) in these communities. Sometimes, it grows by itself in a stand of only red morrel trees. Other times, it grows with other types of eucalypts.
Some of its tree neighbors include Eucalyptus salmonophloia, Eucalyptus melanoxylon, Eucalyptus wandoo, Eucalyptus loxophleba, Eucalyptus astringens, or Eucalyptus kondininensis.
Below these taller trees, you might find smaller plants. These are called understorey species. Some of these include Sclerolaena diacantha, Lycium australe, Melaleuca merrallii, Melaleuca pauperiflora, and Rhagodia drummondii.
Is the Red Morrel Endangered?
Good news! The Western Australian Government's Department of Parks and Wildlife says that this eucalypt is "not threatened." This means it is not currently in danger of disappearing.
How People Use the Red Morrel
The red morrel is a tall tree that can grow well in tough conditions. It can handle soils that are very alkaline (like baking soda), salty, or very clayey.
People sometimes plant it as an ornamental tree to make places look nice. It is also used as a windbreak to protect farms or homes from strong winds. It's also helpful for beekeeping because bees like its flowers.
In the past, the wood from the red morrel was used in the mining industry. It was a source of timber and fuel. Today, its fine-textured, reddish-brown wood is seen as valuable. It can be used to make high-quality furniture and craft items.