Rufous hummingbird facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Rufous hummingbird |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Adult male | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Genus: | Selasphorus |
| Species: |
S. rufus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Selasphorus rufus (Gmelin, 1788)
|
|
 |
|
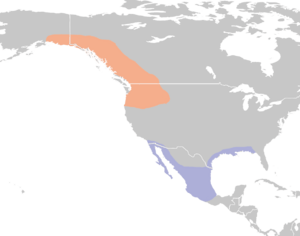
| Summer, breeding range Winter range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The rufous hummingbird (Selasphorus rufus) is a small, amazing bird. It's about 8 cm (3.1 in) long and has a long, straight, and thin bill. These tiny birds are famous for their incredible flying skills. They can fly over 2,000 mi (3,200 km) when they migrate! The rufous hummingbird is one of seven types of birds in the Selasphorus group.
Contents
What Does the Rufous Hummingbird Look Like?
Adult male rufous hummingbirds have a white chest. Their face, sides, and tail are a reddish-brown color called rufous. They also have a bright, shiny orange-red patch on their throat, which is called a gorget. This patch can look like it changes color in different light, which is called iridescence. Some males might even have a bit of green on their back or head.
Female rufous hummingbirds are mostly green and white. They have some shiny orange feathers in the middle of their throat. Their tail is dark with white tips and a rufous (reddish-brown) base.
Females are a little bigger than males. It can be very hard to tell a female rufous hummingbird apart from an Allen's hummingbird. Rufous hummingbirds are very small birds. They weigh about 2–5 g (0.071–0.176 oz), which is less than a penny! They are 7–9 cm (2.8–3.5 in) long and their wings spread about 11 cm (4.3 in) wide.
These birds eat nectar from flowers using their long tongues. They also catch insects while flying. Hummingbirds need to eat often during the day to stay active. At night, they go into a deep sleep called torpor to save energy. Because they are so small, bigger birds and animals that eat insects can be a danger to them.
Where Do They Live and How Do They Reproduce?
Rufous hummingbirds mostly live in open areas, on mountainsides, and at the edges of forests. You can find them in western North America, from southern Alaska all the way down through British Columbia, the Pacific Northwest, and into California. They build their nests further north (in Alaska) than any other hummingbird species.
The female hummingbird builds a nest in a safe spot, usually in a bush or a conifer tree.
Amazing Journeys: Migration
Rufous hummingbirds from the western parts of North America travel through the Rocky Mountains and nearby lowlands. They do this from May to September to find lots of wildflowers. Sometimes, they might stay in one area for the whole summer. When they do, these migrating birds, just like the ones that live there, often bravely protect their feeding spots from other birds.
Most rufous hummingbirds spend their winter in wooded areas in the Mexican state of Guerrero. To get there, they travel over 2,000 mi (3,200 km) overland from their summer homes. This is a huge journey for a bird that weighs only about 3 to 4 grams!
Many rufous hummingbirds that migrate to the southeastern United States and the Caribbean Islands are young birds or adult females. Adult males are rarely seen in these areas. Since young birds and females look very similar to Allen's hummingbirds, it can be hard to tell them apart without a very close look. Because of this, rufous hummingbirds seen migrating in the east are sometimes called "rufous/Allen's hummingbirds."
Protecting Rufous Hummingbirds
In 2018, the rufous hummingbird's conservation status was changed from "least concern" to "near threatened" on the IUCN Red List. This means they are getting closer to being endangered. One reason for this is that they rely on insects for food during winter. The number of insects around the world is going down because of pesticides and more intense farming. This affects the hummingbirds.
Also, because of climate change, many flowers that rufous hummingbirds eat from during their breeding season are blooming about two weeks earlier than they used to. This means that when the hummingbirds arrive at their breeding spots, they might be too late to find enough food.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Colibrí rufo para niños
In Spanish: Colibrí rufo para niños





