Saturnalia tupiniquim facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Saturnalia tupiniquim |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
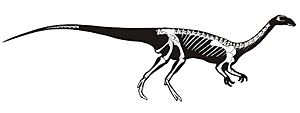
| Skeletal reconstruction showing known remains of all specimens | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Suborder: | †Sauropodomorpha |
| Subfamily: | †Saturnaliinae |
| Genus: | †Saturnalia Langer et al., 1999 |
| Species: |
†S. tupiniquim
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Saturnalia tupiniquim Langer et al., 1999
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Saturnalia was a type of dinosaur that lived a very long time ago. It is now extinct, meaning it no longer exists. This dinosaur was a very early member of the group called sauropodomorphs. These dinosaurs were usually plant-eaters with long necks.
Saturnalia lived during the Late Triassic period. This was about 233 million years ago. Its fossils have been found in southern Brazil, in a place called the Santa Maria Formation.
Contents
Discovering the Saturnalia Dinosaur
Scientists first found Saturnalia fossils in the mid-summer. They found three parts of skeletons in Brazil, in an area known as Paleorrota. The main fossil, called MCP 3844-PV, was a well-preserved skeleton without the head.
Two other partial skeletons were also found. One included part of a jaw with teeth. All these fossils came from a place called "Wald-Sanga." This area is part of the Santa Maria Formation.
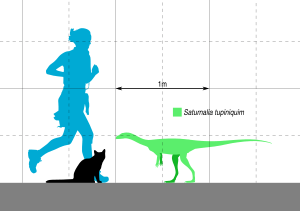
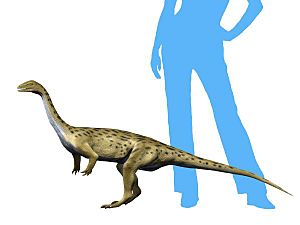
These fossils are very old, dating back about 228 million years. This makes Saturnalia one of the oldest true dinosaurs ever found. It was a small dinosaur, growing to about 1.5 meters (5 feet) long. It weighed around 4 kilograms (9 pounds), which is about the same as a small house cat.
Scientists used a special method to find out the exact age of the Santa Maria Formation. They found it was about 233.23 million years old. This means it is one of the oldest places where dinosaur fossils have been found.
How Saturnalia Got Its Name
The dinosaur Saturnalia was first named in 1999. The scientists who named it were Max C. Langer, Fernando Abdala, Martha Richter, and Michael J. Benton. They named the main type of this dinosaur Saturnalia tupiniquim.
The name Saturnalia comes from a Latin word. It refers to an ancient Roman festival called Saturnalia, which was a time of feasting. The dinosaur was given this name because its fossils were found during a similar festive period.
The second part of its name, tupiniquim, comes from the Portuguese and Guarani languages. It means "native." So, the full name means something like "native carnival dinosaur."
How Scientists Classify Saturnalia
Saturnalia has been a bit tricky for scientists to classify. This is because it has features that look like two different groups of dinosaurs. It has some traits of sauropodomorphs, which were often large plant-eaters. But it also has features similar to theropods, which were usually meat-eating dinosaurs.
In 1999, the scientists who first described Saturnalia placed it in the sauropodomorph group. However, later studies showed that its skull and hand bones looked more like theropods. This made some scientists wonder if it was a true sauropodomorph or a very early relative.
Another scientist, José Bonaparte, studied Saturnalia in 2007. He noticed it was very similar to another early dinosaur called Guaibasaurus. He put both dinosaurs into the same family, called Guaibasauridae.
Today, most scientists agree that Saturnalia is a very early sauropodomorph. It is considered a "basal" sauropodomorph. This means it is one of the first and most basic members of that dinosaur group. It might even be part of the Guaibasauridae family, which is also placed at the very beginning of the sauropodomorph family tree.
See also
 In Spanish: Saturnalia tupiniquim para niños
In Spanish: Saturnalia tupiniquim para niños