Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
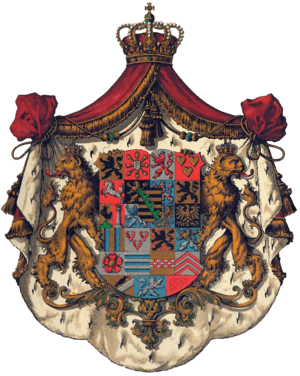
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
Sachsen-Coburg und Gotha
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1826–1918 | |||||||||||||
|
Anthem: Heil unserm Herzog, heil
|
|||||||||||||
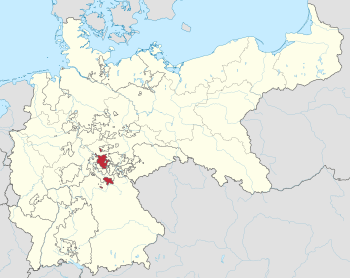
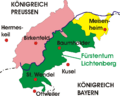
The Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
|
|||||||||||||
| Capital | Coburg and Gotha | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | German | ||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||
|
• Family lands reorganised
|
12 November 1826 1826 | ||||||||||||
|
• German Revolution
|
18 November 1918 | ||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||
| 1905 | 1,977 km2 (763 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||
|
• 1905
|
242000 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
The Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (in German, Sachsen-Coburg und Gotha) was a special type of country in Germany. It was a dual monarchy. This means one ruler governed two separate areas: the Duchy of Coburg and the Duchy of Gotha. The word "Saxe" shows that these lands were part of the larger region of Saxony. Many small countries in this area were ruled by members of the same royal family, the House of Wettin.
The royal House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha began in 1826. This happened when one branch of the Wettin family, the Dukes of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg, had no more male heirs. The remaining family members then divided their lands. The Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld gave up Saalfeld. In return, he received the Duchy of Gotha.
On November 12, 1826, Ernst III of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld became Ernst I Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. He was the first Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. He also held many other titles.
Ernst I had two sons. His younger son, Prince Albert, married his cousin, Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom. Because of this marriage, the royal family of the United Kingdom was called Saxe-Coburg and Gotha from 1901. This lasted until 1917, during the reign of Edward VII. The name was then changed to Windsor. This change happened because of strong anti-German feelings during World War I.
Contents
Rulers of the Duchy
Ernst I died in 1844. His older son, Ernst II, became the next Duke. Ernst II ruled until he died in 1893. He had no children. So, the Duchy's throne passed to the male descendants of his younger brother, Prince Albert. Prince Albert was Queen Victoria's husband.
Succession Rules
The Duchies had special rules. They did not want to be joined with Great Britain. Their laws prevented the King or the heir to the British throne from becoming Duke. This rule applied if other eligible male heirs existed. So, after Edward, Prince of Wales, the next in line was his brother, Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh.
Alfred's only son, also named Alfred, died in 1899. When Duke Alfred died in 1900, his nephew became Duke. This was Charles Edward the Duke of Albany. He was 16 years old and the son of Queen Victoria's youngest son, Leopold. Other family members, like Duke Arthur of Connaught, gave up their right to the throne.
The Last Duke
The new Duke, Charles Edward, started using the German version of his name: Carl Eduard. He ruled as Duke Carl Eduard. Until he turned 21 in 1905, a regent ruled for him. Carl Eduard kept his British title, Duke of Albany. However, he fought for Germany in World War I. Because of this, he lost his British titles in 1919.
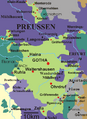
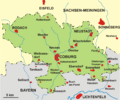
Carl Eduard reigned until November 18, 1918. At that time, a group called the Workers' and Soldiers' Council of Gotha removed him from power. This happened during the German Revolution. The two Duchies then became separate states. Soon after, they joined larger states. Saxe-Coburg became part of Bavaria. Saxe-Gotha merged with other small states. Together, they formed the new state of Thuringia in 1920, within the Weimar Republic.
Life in the Duchy
The main cities of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha were Coburg and Gotha. By 1914, the two duchies had these areas and populations:
| Duchy | Area (square kilometers) | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Sachsen-Coburg | 1,415 km2 (546.3 sq mi) | 74818 |
| Sachsen-Gotha | 562 km2 (217.0 sq mi) | 182359 |
| Total | 1,977 km2 (763.3 sq mi) | 257177 |
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha was unique. It was the only European country to send a diplomatic consul to the Confederate States of America. This was during the American Civil War. The consul was named Ernst Raven. He served in the State of Texas. The Confederate Government accepted him on July 20, 1861.
The Royal Family's Influence
Members of the Saxe-Coburg and Gotha family became kings in other countries. They ruled in Belgium and Bulgaria. They also married into almost all other royal families across Europe.
More than 50 years after Bulgaria became a republic, King Simeon returned. He was elected Prime Minister of Bulgaria. After World War I, the Kings of Belgium stopped using the name Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. However, they never officially changed their family name. Simeon of Bulgaria's legal name is Simeon Borisov Sakskoburggotski.
The Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha stopped being an independent country in 1918. This happened when Germany became a republic. Carl Eduard, the last Duke, lost his British titles. This was because he supported Germany in World War I. He died in 1954.
Gotha became part of the new state of Thuringia. Coburg joined Bavaria.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ducado de Sajonia-Coburgo y Gotha para niños
In Spanish: Ducado de Sajonia-Coburgo y Gotha para niños