Seawall facts for kids

A seawall is a strong wall built along the coast. Its main job is to protect land, homes, and fun places from the power of the sea. This includes protecting against tides, waves, and even huge tsunamis.
The coast is a very active place. Rivers, wind, and the sea itself are always changing it. Because of these strong natural forces, seawalls need regular care and sometimes have to be replaced.
There are many kinds of seawalls. Their design depends on the strength of the waves, the local weather, and what the land is used for. Seawalls are a type of hard engineering coastal protection. This means they are solid structures. However, building them can sometimes cause problems, like changing how sand moves along the coast. Because they are also expensive, people sometimes use other methods, like adding more sand to beaches.
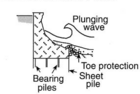
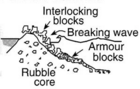
Seawalls can be made from different materials. Common ones include strong reinforced concrete, large rocks (boulders), steel, or wire cages filled with rocks called gabions. Other materials can be wood, vinyl, or even large sandbags made from natural fibers like jute. In the UK, a "sea wall" can also mean an earth bank used to create new land or a dike.
How Seawalls Work and Their Challenges
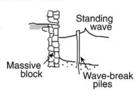
A seawall works by bouncing wave energy back into the sea. This reduces the power of the waves hitting the shore, which helps stop erosion.
However, seawalls have a couple of challenges:
- When waves hit a wall and bounce back, they can sometimes dig away the sand right in front of the wall. This can make the beach lower.
- Seawalls can also change how sand moves along the coast. This might cause erosion on unprotected beaches nearby.
Scientists have also looked at natural ways to protect coasts from tsunamis. For example, planting trees like Casuarina and coconut trees can act as a natural barrier. Studies show that a wall built offshore (away from the coast) could reduce tsunami wave heights a lot.
Different Types of Seawalls
The best type of seawall depends on the specific location and how much erosion is happening there. There are three main types of seawalls: vertical, curved or stepped, and mound.
Images for kids