Second Battle of El Alamein facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Second Battle of El Alamein |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Western Desert Campaign | |||||||
 24 October 1942: British soldiers on the attack. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Allies: |
Axis: |
||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
195,000 men |
116,000 men 552 artillery pieces 496 Anti Tank Guns – 1,063 |
||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 13,560 casualties 332 – ~500 tanks 111 guns 97 aircraft |
30,542 casualties ~500 tanks 254 guns 84 aircraft |
||||||
The Second Battle of El Alamein was a very important battle during the Second World War. It took place in Egypt, near a place called El Alamein. This battle lasted from October 23 to November 5, 1942.
This battle was a major turning point in the North African Campaign. The Allied forces won a big victory. This stopped the Axis powers from taking over Egypt. It also protected the important Suez Canal and the Middle Eastern oil fields.
After this battle, the Axis commander, Erwin Rommel, and his Afrika Corps had to retreat. They moved all the way back to Tunisia and Libya.
Contents
Why the Battle Happened
The Western Desert campaign was a fight for control of North Africa. The Axis powers, led by Germany and Italy, wanted to take Egypt. This would give them control of the Suez Canal. The canal was a vital shipping route.
The First Battle of El Alamein had stopped the Axis advance. But they were still very close to Egypt. The Allies needed to push them back for good.
New Commanders and Plans
In August 1942, Lieutenant-General Bernard Montgomery took charge of the British Eighth Army. He was a new commander for the Allied forces. Montgomery planned a big attack to defeat the Axis.
The Axis forces were led by General Erwin Rommel. He was known as the "Desert Fox" because he was a clever commander. Rommel's forces were tired and low on supplies.
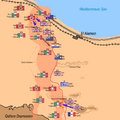
The Armies Face Off
The Allied forces had more soldiers and equipment.
- The Allies had about 195,000 men. They had over 1,000 tanks and many aircraft.
- The Axis forces had about 116,000 men. They had fewer tanks, around 547, and fewer aircraft.
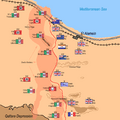
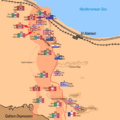
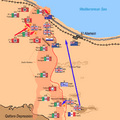
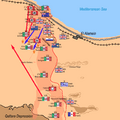
The battlefield was a narrow strip of desert. It was between the Mediterranean Sea and the Qattara Depression. This made it hard for either side to go around the other.
The Battle Begins: Operation Lightfoot
The battle started on the night of October 23, 1942. It began with a huge artillery barrage. Over 800 Allied guns fired for hours. This was called Operation Lightfoot.
The infantry (foot soldiers) then moved forward. They had to clear paths through Axis minefields. These minefields were very dangerous. The plan was for the infantry to open the way for the tanks.
Fighting in the Minefields
The fighting was very tough. The Axis forces had strong defenses. They had many anti-tank guns. The Allies faced heavy resistance. It took longer than expected to get through the minefields.
The Allied tanks struggled to advance quickly. Rommel's forces fought hard to stop them.
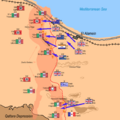
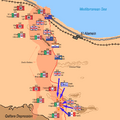
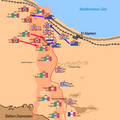
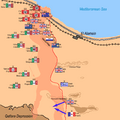
The Tank Battles and Counter-attacks
Over the next few days, there were fierce tank battles. The British tanks tried to break through the Axis lines. The Axis tanks, especially the German ones, fought back strongly.
Rommel launched several counter-attacks. He tried to push the Allies back. But the Allied forces held their ground. They kept pushing forward slowly.
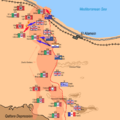
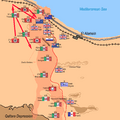
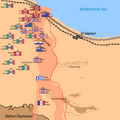
Operation Supercharge
After about a week of fighting, Montgomery launched a new attack. This was called Operation Supercharge. It began on November 2. This was a powerful push to break the Axis lines completely.
The Allied forces focused their attack on a narrow front. They used their tanks and infantry together. This attack finally broke through the Axis defenses.
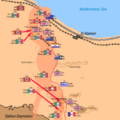
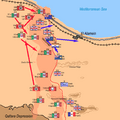
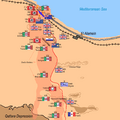
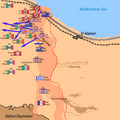
The Axis Retreat
Rommel realized his forces could not hold on. They were running out of fuel and supplies. Many of his tanks were destroyed. On November 4, Rommel decided to retreat.
The Allied forces chased the retreating Axis army. The retreat was long and difficult for the Axis. They lost many more soldiers and equipment.
Why This Battle Was So Important
The Second Battle of El Alamein was a huge victory for the Allies.
- It saved Egypt from being taken over by the Axis.
- It protected the vital Suez Canal.
- It stopped the Axis from reaching the Middle Eastern oil fields.
- It was the first major victory for the Allies against the Axis in North Africa.
- It showed that the Allies could defeat Rommel's forces.
This battle changed the course of the war in North Africa. It gave the Allies a big boost in confidence. It was a true turning point in the Second World War.
Images for kids
-
Erwin Rommel (left) in his Sd.Kfz. 250/3 command halftrack.
-
A British soldier puts his fingers up at German prisoners captured at El Alamein, 26 October 1942
See also
 In Spanish: Segunda Batalla de El Alamein para niños
In Spanish: Segunda Batalla de El Alamein para niños