Seedling facts for kids
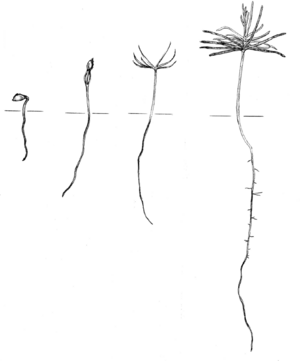
A seedling is a young plant that grows from a seed. It's like a baby plant! The journey of a seedling begins when the seed sprouts.
A typical young seedling has three main parts:
- The radicle is the first part to emerge from the seed. It grows downwards and becomes the plant's root.
- The hypocotyl is the part that grows upwards, pushing the seedling out of the soil. It will become the plant's main stem.
- The cotyledons are special leaves that are already inside the seed. They are often called "seed leaves." They provide food for the young seedling until it can grow its own true leaves and start making its own food through photosynthesis.
Plants are often grouped by how many cotyledons their seedlings have:
- Monocotyledons (or monocots) have just one cotyledon, which often looks like a blade or a narrow leaf. Examples include grasses, corn, and lilies.
- Dicotyledons (or dicots) have two cotyledons, which are usually round or oval-shaped. Examples include beans, sunflowers, and oak trees.
Gymnosperms, like pine trees, can have many cotyledons – sometimes up to eight! And some rare flowering plants, called acotyledons, don't have any cotyledons at all.

Contents
How Seedlings Grow: The Plumule
Another important part of a seed embryo is the plumule. This tiny part is what will grow into the main shoot of the plant, carrying its first true leaves.
There are two main ways seedlings can grow their plumule:
Epigeal Germination
In many seeds, like the sunflower, the plumule is very small and doesn't have any clear leaf shapes inside the seed. When these seeds sprout, the cotyledons are pulled up above the ground by the growing hypocotyl. The plumule then starts to grow and develop its true leaves once the cotyledons are in the sunlight. This is called epigeal germination.
Hypogeal Germination
Other seeds, like the broad bean, have a plumule with visible leaf structures even inside the seed. When these seeds sprout, the plumule grows up through the soil, but the cotyledons stay hidden below the surface. The plumule then emerges from the ground and develops its true leaves. This is known as hypogeal germination.
Images for kids
-
Seedling of a dicot, Nandina domestica, showing two green cotyledon leaves, and the first "true" leaf with its distinct leaflets and red-green color.
-
A few days old Scots pine seedling, the seed still protecting the cotyledons.
-
Seedling of Quercus robur sprouting from its acorn.
See also
 In Spanish: Plántula para niños
In Spanish: Plántula para niños








