Siege of Frankenthal facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Siege of Frankenthal |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Palatinate phase of the Thirty Years' War | |||||||
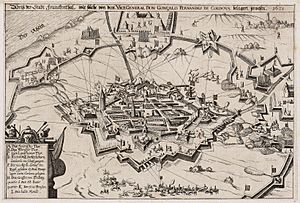 1625 engraving of the siege |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
The Siege of Frankenthal was an important event during the Thirty Years' War. It was part of a bigger fight called the Palatinate campaign. A Spanish army, led by Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba, surrounded the fortified city of Frankenthal. The city was defended by a mostly English army, commanded by John Burroughs. The siege lasted for a long time, from 1621 until March 20, 1623. Finally, King James I of England ordered the city to surrender.
Background to the Siege
Frankenthal's Importance
In the early 1600s, the city of Frankenthal was very important. It was located in a region called the Electoral Palatinate. This area was like a small country within the Holy Roman Empire. Its ruler, Frederick IV, Elector Palatine, decided to make Frankenthal stronger. He improved the city's walls and defenses. He also made other cities like Heidelberg and Mannheim into strong fortresses. Frankenthal played a key role in protecting the Palatinate.
Start of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War began in 1618. It started when the Kingdom of Bohemia rebelled against Ferdinand II. Ferdinand was the Holy Roman Emperor, a powerful ruler in Europe. The people of Bohemia offered their crown to Frederick V, Elector Palatine. Frederick V was the son of Frederick IV, who had strengthened Frankenthal.
When Frederick V accepted the crown, it made the conflict much bigger. His decision brought the Electoral Palatinate directly into the war. This meant that the fighting, which started in Bohemia, now spread to other parts of Europe, including the Palatinate region where Frankenthal was located.
See also
 In Spanish: Sitio de Frankenthal para niños
In Spanish: Sitio de Frankenthal para niños

