Tide facts for kids


A tide is the regular rise and fall of the ocean's surface. This happens mainly because of the strong pull of gravity from the Moon on Earth's oceans. Tides change how deep the water is in the ocean and in river mouths (called estuaries).
Tides also create moving water currents, which are sometimes called tidal streams or 'rip tides'. Knowing when the tides will change is very important for boats navigating near the coast. The area of the seashore that is covered by water at high tide and exposed at low tide is called the intertidal zone. This zone is a very important place for many sea creatures and plants.
The height of the tides changes a bit depending on the phases of the Moon. When there is a New Moon or a Full Moon, the tides are higher. This is because the Sun's gravitational pull adds to the Moon's pull. These extra-high tides are called "spring tides".
Contents
How Many Tides Happen Each Day?
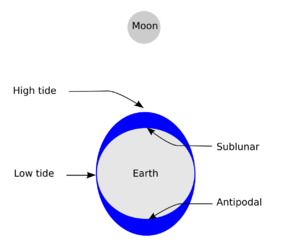
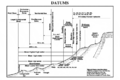
In most places around the world, you will see two high tides and two low tides every day. The highest point the water reaches is called the high tide. The lowest point is called the low tide.
When the water is coming in towards high tide, it's called a "flood tide". When the water is going out towards low tide, it's called an "ebb tide".
Why Do We Have Two Tides a Day?
The time between one high tide and the next is about 12 hours and 25 minutes. This is exactly half of a "tidal lunar day".
The Moon orbits the Earth in the same direction that the Earth spins. So, it takes a little longer than a regular day—about 24 hours and 50 minutes—for the Moon to be in the exact same spot in the sky above you again. During this time, the Moon has passed over your head once and been on the opposite side of the Earth once. This is why the strongest tidal pull happens about every 12 hours and 25 minutes.
How Does the Moon's Gravity Cause Tides?
The Moon's gravity pulls on the Earth. But gravity gets weaker the further away something is. So, the Moon pulls a little stronger on the side of Earth facing it. It pulls a little weaker on the side of Earth farthest from it.
This difference in pull makes the Earth "stretch" slightly along the line connecting Earth and the Moon. The solid Earth stretches a tiny bit. But ocean water is fluid, so it can move much more easily. It moves in response to this stretching force, especially horizontally.
As the Earth spins, the Moon's pull on any spot on Earth changes all the time. The ocean water is always moving to catch up with this changing pull. This constant change in the Moon's gravity causes the sea level to rise and fall in a regular pattern.
Other things, like air pressure and the Sun's gravity, also affect tides. However, in most places, the Moon's gravity has the biggest effect.
Images for kids
-
Low tide at Bangchuidao scenic area, Dalian, Liaoning Province, China
-
Low tide at Bar Harbor, Maine, U.S. (2014)
-
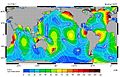
M2 tidal constituent. Red is most extreme (highest highs, lowest lows), with blues being least extreme. White cotidal lines converge in blue areas indicating little or no tide. The curved arcs around these convergent areas are amphidromic points. They show the direction of the tides, each indicating a synchronized 6-hour period. Tidal ranges generally increase with increasing distance from amphidromic points. Tide waves move around these points, generally counterclockwise in the N. Hemisphere and clockwise in the S. Hemisphere
-
Brouscon's Almanach of 1546: Compass bearings of high waters in the Bay of Biscay (left) and the coast from Brittany to Dover (right).
See Also
 In Spanish: Marea para niños
In Spanish: Marea para niños
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |