Squamish volcanic field facts for kids
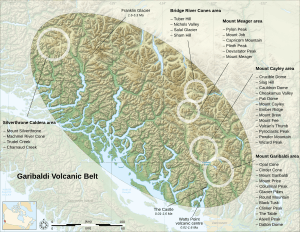
The extent of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt showing the location of the Squamish field volcanoes.
|
|
| Country | Canada |
|---|---|
| Province | British Columbia |
| Region | Garibaldi Volcanic Belt |
| Coordinates | 50°07′13″N 123°17′26″W / 50.12028°N 123.29056°W |
| Length | 3 km (1.9 mi) |
| Width | 1 km (0.62 mi) |
The Squamish volcanic field is a small group of volcanoes in British Columbia, Canada. It's located on the South Coast of the province. This volcanic area is about 3 kilometers (2 miles) long. It stretches from Howe Sound near Britannia Beach to the Squamish River.
It's the very southern tip of a larger group of volcanoes called the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt. This belt is part of the Canadian Cascade Arc. The volcanoes here are smaller than the big, cone-shaped ones (called stratovolcanoes) found elsewhere in the Garibaldi Belt. They are mostly made of rock types called dacite and basaltic andesite. The field gets its name from the nearby town of Squamish.
Contents
What is the Squamish Volcanic Field?
The Squamish volcanic field is a special area where volcanoes have erupted. It's not just one big volcano, but a collection of smaller ones. This field is shaped like a long, narrow strip, running north to south. It's only about 3 kilometers (2 miles) long and 1 kilometer (0.6 miles) wide.
Where is it Located?
This volcanic field is found in a beautiful part of Canada. It's on the South Coast of British Columbia. You can find it near Howe Sound, which is a large fjord. The field stretches from the eastern side of Howe Sound to the western side of the Squamish River. This area is also close to the Sea to Sky Highway.
Part of a Bigger Volcanic System
The Squamish volcanic field is the southernmost part of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt. This belt is a long chain of volcanoes. It's also part of an even larger system called the Canadian Cascade Arc. This arc includes many volcanoes that stretch through parts of North America.
Types of Volcanoes and Rocks
The volcanoes in the Squamish field are not as large as some of the famous stratovolcanoes. Stratovolcanoes are tall, cone-shaped volcanoes like Mount Fuji. The volcanoes here are smaller. They are made up of different kinds of volcanic rock.
The main type of rock found here is called dacite. There is also some basaltic andesite. These are both types of igneous rock, which means they formed from cooled lava.
When Was it Active?
The Squamish volcanic field has at least two main areas where eruptions happened. These are called the Watts Point volcanic centre and the Monmouth Creek complex. Scientists believe the most recent eruptions happened a very long time ago. This was during a period called the Pleistocene epoch.
During the Pleistocene, Earth experienced many ice ages. The eruptions in the Squamish field likely happened when there was a lot of ice around. This type of eruption, where volcanoes interact with glaciers, is called glaciovolcanism. It means the lava erupted under or next to ice.

