Garibaldi Volcanic Belt facts for kids
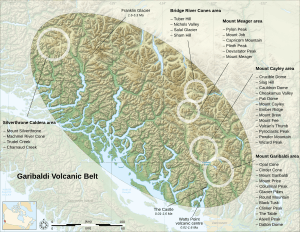
The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt is a chain of volcanoes found in British Columbia, Canada, and a small part of the northwestern United States. It is the northern section of a larger group of volcanoes called the Cascade Volcanic Belt. These volcanoes are known for being the most explosive in Canada. They are also the closest volcanoes to the busy southwest part of British Columbia.
Contents
How Were These Volcanoes Formed?
The volcanoes in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt were created by a process called subduction. This happens when two huge pieces of the Earth's crust, called tectonic plates, slowly crash into each other. In this area, the Juan de Fuca tectonic plate is sliding underneath the North American plate. This meeting point is just off the west coast of Vancouver Island. As one plate slides under the other, it melts, and this melted rock (magma) rises to the surface, forming volcanoes.
The volcanoes here are mostly stratovolcanoes. These are cone-shaped volcanoes built up by many layers of hardened lava, ash, and rock. They are typical of subduction zones.
Meet the Volcanoes of the Garibaldi Belt
Some of the most well-known volcanoes in this belt include Mount Garibaldi, Mount Cayley, and Mount Meager. Each of these has its own unique story and features.
Mount Garibaldi
Mount Garibaldi is a beautiful and iconic volcano. It stands tall and can be seen from many places in the region. It's a classic stratovolcano, meaning it has a cone shape built up over time by layers of volcanic material.
Mount Cayley
Mount Cayley is another significant volcano in the belt. It's known for its rugged peaks and is part of a larger group of volcanic features. The area around Mount Cayley shows signs of past volcanic activity, with interesting rock formations.
Mount Meager
Mount Meager is very important because it had the youngest explosive eruption in Canada. This happened about 2,350 years ago. This eruption was similar to the famous Mount St. Helens eruption in 1980 in the United States, and also like the ongoing eruption of Montserrat in the Caribbean. This shows that the volcanoes in the Garibaldi Belt are still active and can erupt powerfully.
Images for kids
-
North face of Mount Garibaldi. The Table is the flat-topped steep-sided edifice in the foreground rising above Garibaldi Lake.
-
South face of Pyroclastic Peak, the second highest peak of the Mount Cayley massif.
-
A volcanic hot spring near Meager Creek related to volcanism at the Mount Meager massif. This hot spring lies in one of the few hot spring clusters near Meager.
-
The Table, a flow-dominated tuya rising above the southwestern side of Garibaldi Lake.
-
Keyhole Falls, the largest waterfall along the Lillooet River. The solid-looking rock cliffs formed when a lava flow front repeatedly collapsed and collected downslope from the vent associated with the eruption of Plinth Peak 2,350 years ago.
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |