RNA facts for kids
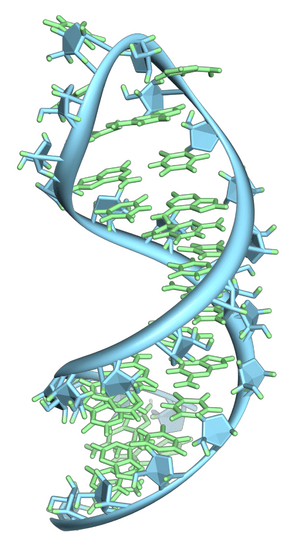
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. It is a very important molecule found in all living things. RNA is a bit like DNA, but it has some key differences.
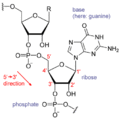
DNA has two strands twisted together, but RNA usually has only one single strand. RNA also uses slightly different building blocks, called bases. These bases are:
In RNA, adenine often pairs with uracil, and guanine often pairs with cytosine. DNA uses a base called thymine instead of uracil.
RNA also contains a different type of sugar called ribose, while DNA has deoxyribose. These differences make RNA more active and suitable for taking part in cell reactions.
In most living things, DNA holds all the genetic information. But in some viruses, like HIV, RNA carries the genetic information instead.
Contents
How RNA Helps Make Proteins
Messenger RNA
One of RNA's main jobs is to carry instructions for making proteins. Think of it like a messenger! These instructions tell the cell which amino acids to use and in what order. This type of RNA is called messenger RNA (mRNA).
Here's how it works: 1. A section of DNA in the cell's nucleus acts as a blueprint. 2. An enzyme called RNA polymerase reads this DNA blueprint and makes a copy of it as an mRNA molecule. This process is called transcription. 3. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes are like tiny protein factories. 4. At the ribosome, the mRNA's instructions are read. The sequence of bases in the mRNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids. These amino acids then link together to form a protein. This step is called translation.
DNA stays safely inside the nucleus because it's a very long molecule. mRNA is smaller and can move around the cell easily to deliver its messages.
Two other types of RNA also help in making proteins: transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a small RNA molecule. Its job is to carry specific amino acids to the ribosome. There is a different tRNA molecule for each type of amino acid. Each tRNA has a special spot where an amino acid can attach. It also has an "anti-codon" that matches a "codon" (a three-base code) on the mRNA. For example, the codons UUU or UUC on mRNA tell the cell to add the amino acid phenylalanine.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a key part of the ribosomes. Ribosomes are made of rRNA and proteins. rRNA helps the ribosome bind to mRNA and carry out the process of making proteins. Ribosomes are very common in the cell's cytoplasm, and rRNA makes up a large part of all the RNA in a cell.
Small Nuclear RNAs (snRNAs)
Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) work with proteins to form structures called spliceosomes. These spliceosomes help with a process called alternative splicing. Genes often have sections called exons that contain the instructions for proteins. Spliceosomes can join these exons together in different ways. This means that one gene can actually make several different proteins!
How RNA Controls Genes
Some types of RNA act like switches, controlling when and how much a gene is used.
Micro RNAs (miRNA)
Micro RNAs (miRNA) are small RNA molecules that can control how genes work. They often do this by attaching to mRNA molecules and either blocking them or causing them to break down faster. This process is called RNA interference.
Small Interfering RNAs (siRNA)
Small interfering RNAs (siRNA) are very small, double-stranded RNA molecules. They can stop specific genes from working. The discovery of siRNAs has been very important for medical research and developing new medicines.
Other Types of RNA
Retrotransposons
Retrotransposons are sometimes called "jumping genes." They can make copies of themselves and move to different places in the cell's genome (its complete set of DNA). They do this in two steps: first, they copy themselves from DNA to RNA, and then from RNA back to DNA. This new DNA copy is then inserted into a new spot. Retrotransposons act a lot like some retroviruses, such as HIV.
Viral Genomes
Many viruses, like the flu virus, use RNA as their genetic material instead of DNA. When these viruses infect a cell, their RNA takes over the cell's machinery. It forces the cell to make more viral RNA and the protein coats needed to build new viruses.
Images for kids
-
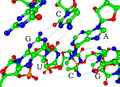
How bases pair up in a siRNA.
See also
 In Spanish: Ácido ribonucleico para niños
In Spanish: Ácido ribonucleico para niños