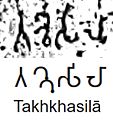Taxila facts for kids
Taxila is a very old town in Punjab, Pakistan. It was once a big city and an important center for learning and trade. For a while, it was even part of the Indo-Greek Kingdom.
Today, Taxila is famous for its amazing history. You can find a museum there with many ancient Buddhist items. There are also old ruins from the Gandhara Buddhist civilization, which was a very important culture long ago. Another interesting spot nearby is the Nicholson Memorial, a monument built to remember a British officer named John Nicholson.
Taxila's Ancient History
Taxila has a long and rich history, going back thousands of years. It was a crossroads for many different cultures and empires.
Early Beginnings of Taxila
People have lived in the Taxila area since the Stone Age. Later, it became a significant city because of its location on important trade routes. These routes connected different parts of Asia, making Taxila a busy place for merchants and travelers.
Taxila Under Different Empires
Over time, many powerful empires ruled Taxila.
Achaemenid Empire's Influence
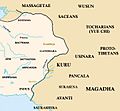
Around 500 BCE, Taxila became part of the Achaemenid Empire, a huge Persian empire. This brought new ideas and cultures to the city. It was a time of growth and connection with the wider world.
Alexander the Great's Arrival
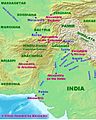
Later, in 326 BCE, Alexander the Great and his army arrived in Taxila. The local ruler, King Ambhi, welcomed Alexander. This event connected Taxila with the Greek world and led to new influences in art and architecture.
The Mauryan Empire
After Alexander, Taxila became an important city in the Mauryan Empire, one of the largest empires in ancient India. The famous emperor Ashoka is said to have been a governor in Taxila before he became emperor. During his rule, Buddhism spread widely, and many Buddhist buildings were constructed in Taxila.
Indo-Greek Rulers
After the Mauryan Empire, Taxila was ruled by Indo-Greek kings. These kings combined Greek and Indian cultures. They built new cities and minted coins that showed both Greek and Indian styles. The city of Sirkap, near modern Taxila, was one of their capitals.
Scythians and Parthians
Later, groups like the Scythians and Parthians took control of Taxila. They also left their mark on the city's culture and history.
Kushan Empire's Golden Age
Taxila reached a golden age under the Kushan Empire, especially during the rule of Kanishka. During this time, Taxila became a major center for Buddhism and the Gandhara art style. Many stupas (Buddhist shrines) and monasteries were built, and scholars came from far away to study here.
Decline of Taxila
The city began to decline after the 5th century CE. Invasions by the Hephthalites (also known as the White Huns) caused a lot of destruction. Trade routes also changed, and Taxila lost its importance as a major center.
Archaeological Discoveries in Taxila
Modern archaeologists have found many incredible things in Taxila. These discoveries help us understand what life was like in this ancient city.
Exploring Ancient Sites
Many ruins have been uncovered, including the remains of cities like Sirkap and Bhir Mound. These sites show how people lived, what their houses looked like, and how their cities were planned.
Sirkap City Ruins
Sirkap is one of the most famous archaeological sites in Taxila. It was built by the Indo-Greeks and later used by other rulers. The city was well-planned with straight streets and strong walls. Archaeologists have found temples, stupas, and houses here.
Dharmarajika Stupa
The Dharmarajika Stupa is a large and important Buddhist monument. It is believed to have been built by Emperor Ashoka. This stupa was a place of worship and held important Buddhist relics. Many smaller stupas and monasteries surround it.
Jaulian Monastery
The Jaulian monastery is another significant Buddhist site. It is located on a hill and offers great views. This monastery was a center for learning and meditation. Many statues and carvings have been found here, showing the beautiful Gandhara art style.
Museum of Taxila
The Taxila Museum displays many of the artifacts found in the area. You can see ancient coins, pottery, jewelry, and sculptures. These items tell the story of the different cultures that lived in Taxila over thousands of years.
Images for kids
-
Eastern border of the Achaemenid Empire
-
A map of Alexander's campaign in ancient India.
-
The Indo-Greek king Antialcidas ruled in Taxila around 100 BCE, according to the Heliodorus pillar inscription.
-
Jaulian, a World Heritage Site at Taxila.
-
Jaulian silver Buddhist reliquary, with contents. British Museum.
-
A Taxila coin, 200–100 BCE. British Museum.
-
Archaeological artifacts from the Indo-Greek strata at Taxila from John Marshall "Taxila Archeological excavations").
See also
 In Spanish: Taxila para niños
In Spanish: Taxila para niños