Absolute temperature facts for kids
Absolute temperature, also known as thermodynamic temperature, is a special way to measure how hot or cold something is. It uses a scale where the lowest possible temperature, called absolute zero, is set as 0.
The two main absolute temperature scales are Kelvin (used with Celsius degrees) and Rankine (used with Fahrenheit degrees).
Absolute zero is the coldest anything can ever get. At this temperature, tiny particles like molecules almost completely stop moving. It's the lowest temperature a gas thermometer can measure, and no electronic devices can work at this extreme cold.
What are some examples of absolute temperature?
Here are some common temperatures shown on the absolute scale:
- 0 °C (freezing point of water) is 273.15 K.
- 25 °C (a comfortable room temperature) is 298.15 K.
- 100 °C (boiling point of water) is 373.15 K.
- 0 K (absolute zero) is -273.15 °C.
How do you convert temperatures?
Converting between Celsius and Kelvin is quite simple!
- To change Celsius to Kelvin, you just add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature. So, K = C + 273.15.
- To change Kelvin to Celsius, you subtract 273.15 from the Kelvin temperature. So, C = K - 273.15.
Scientists around the world use the Kelvin scale. It's part of the International System of Units, which is a global standard for measurements. Kelvin is one of the seven basic units in this system.
Images for kids
-
Figure 4 In solid materials, particles move in a special way called phonons. This animation shows different types of these movements.
-
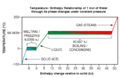
Figure 9 Even very close to absolute zero, helium stays a special kind of liquid called a superfluid. It only freezes if it's under a lot of pressure.