Tidal range facts for kids
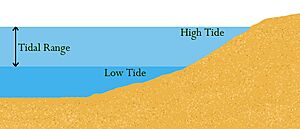
The tidal range is simply the difference in height between the high tide and the low tide. Imagine the ocean water rising and falling like a giant breath! These changes in sea level are called tides. They are mostly caused by the strong gravitational force of the Moon pulling on Earth's water. The Sun also has a pull, but it's weaker because it's much farther away. The Earth's rotation and other forces also play a part.
The size of the tidal range changes depending on the time and location.
When the Moon, Earth, and Sun are all lined up, their gravitational pulls combine. This creates extra-large tides called spring tides. During spring tides, the high tides are very high, and the low tides are very low. This happens twice a month: during a new moon (when the Moon is between the Sun and Earth) and a full moon (when Earth is between the Sun and Moon). The biggest spring tides often happen around the equinoxes.
When the Moon and Sun are at a right angle to the Earth, their pulls work against each other. This causes smaller tides called neap tides. During neap tides, the difference between high and low tide is much smaller. Neap tides also happen twice a month, during the first and third quarters of the lunar phases.
Scientists and experts at national hydrographic offices predict tides based on these astronomical movements. However, strong winds from storms or very low atmospheric pressure can sometimes make tides higher or lower than predicted. This can even cause local flooding in some areas.
The mean tidal range is an average measurement. It's the average height difference between all the high tides and all the low tides in a specific place.
Where Do Tides Show the Biggest Changes?
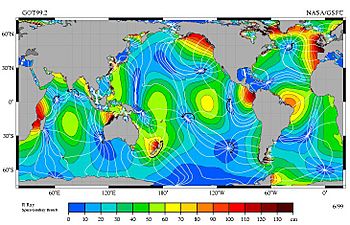
In the wide-open ocean, the typical tidal range is usually only about 1 metre (3 feet) (about 3 feet). You can see these smaller ranges in blue and green on the map to the right. But near coastlines, the tidal range can be very different! It can be almost zero in some places, or as huge as 11.7 metres (38.4 feet) (about 38 feet) in others.
Why such a big difference? It depends on how much water is near the coast and the shape of the land. If a bay or inlet is shaped like a funnel, it can squeeze the incoming tide. This makes the water rise much higher.
The place with the world's largest average tidal range is the amazing Bay of Fundy in Canada. Here, the water can rise and fall by an incredible 11.7 metres (38.4 feet)! That's taller than a three-story building! The highest ever recorded tide there was an astonishing 17.0 metres (55.8 feet) (about 56 feet). Other places with very large tides include Ungava Bay (also in Canada) and the Bristol Channel between England and Wales.
On the other hand, some seas have very small tidal ranges. These include the Mediterranean Sea, the Baltic Sea, and the Caribbean Sea. Imagine a spot in the ocean where the tide hardly moves at all! These special spots are called amphidromic points.
How Do We Classify Tidal Ranges?
Scientists have a way to classify tidal ranges based on their height:
- Micro-tidal areas have a tidal range lower than 2 metres (7 feet) (about 6.5 feet).
- Meso-tidal areas have a tidal range between 2 metres (7 feet) and 4 metres (10 feet) (about 6.5 to 13 feet).
- Macro-tidal areas have a tidal range higher than 4 metres (10 feet) (more than 13 feet).
See also
- King tide, an informal term for an especially high spring tide