Tree fuchsia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tree fuchsia |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Onagraceae |
| Genus: | Fuchsia |
| Species: |
F. excorticata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Fuchsia excorticata |
|
 |
|
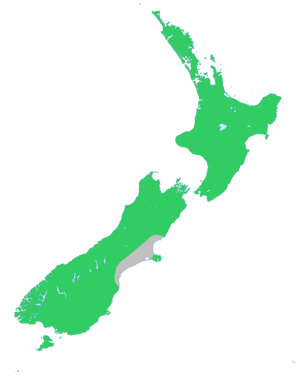
| Natural range of Fuchsia excorticata | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Fuchsia excorticata, also known as tree fuchsia or New Zealand fuchsia, is a special tree from New Zealand. Its Māori name is kōtukutuku. This tree is part of the Onagraceae family. You can find it all over New Zealand, even as far south as the Auckland Islands. It grows from sea level up to about 1,000 meters high, often next to rivers and streams.
It's easy to spot this tree because of its unique bark. The bark peels off in red, papery strips, showing lighter bark underneath. This is why its scientific name, excorticata, means "peeling bark." Tree fuchsia is the biggest type of Fuchsia tree, growing up to 15 meters tall. It's also one of the few New Zealand trees that loses its leaves in winter in the southern parts of the country.
Sadly, a creature called the common brushtail possum has caused problems for this tree. Possums love to eat tree fuchsia. They can eat so many leaves that the tree becomes bare and eventually dies. The tree fuchsia also produces small, dark purple berries. These berries are sweet and juicy. Māori people loved them and even gave the fruit its own name, kōnini. Early European settlers also used the berries to make jams and puddings.
Contents
What Does Tree Fuchsia Look Like?
Tree fuchsia is the largest type of Fuchsia in the world. It looks different from other fuchsia plants in New Zealand. This tree loses its leaves in winter and usually grows as a tree or a large bush. It often reaches about 12 meters tall.
Its bark is light brown or orange, very thin, and peels off like paper. The main trunk can be about 60 cm wide, with strong branches reaching out.
Leaves of the Tree Fuchsia
The leaves of the tree fuchsia have thin stems, about 1 to 4 cm long. The leaves themselves can be up to 10 cm long and 1.5 to 3 cm wide. They are usually oval-shaped with a rounded bottom.
The top surface of the leaves is smooth, except for the edges and veins. The edges of the leaves have small, saw-like teeth. The top of the leaf is usually dark green, and the underside is paler or silvery. Sometimes, the leaves can even have red or purple colors. In southern New Zealand, most trees are evergreen (they keep their leaves all year). But tree fuchsia is deciduous, meaning it loses its leaves in winter. So, in colder months, you can easily spot it because it has few or no leaves.
Flowers of the Tree Fuchsia
The flowers are usually bright red to purple. They often hang down from the main stem of the tree. Each flower grows alone. The four colorful outer parts of the flower, called sepals, are usually 5 to 16 mm long. The thin parts inside the flower, called filaments, are about 7 to 12 mm long and purplish. Tree fuchsia flowers are special because they can be either female or have both male and female parts.
Berries of the Tree Fuchsia
The berries are about 10 mm long and shaped like an oval. They are dark purple, almost black, when ripe.
Where Does Tree Fuchsia Grow?
Natural Global Range
Tree fuchsia is found only in New Zealand. This means it is endemic to New Zealand and doesn't grow naturally anywhere else in the world.
New Zealand Range
You can find tree fuchsia all over the North and South Islands of New Zealand. It also grows on Stewart Island and the Auckland Islands.
Habitat Preferences
Tree fuchsia is common in lowland and lower mountain forests. It especially likes to grow on the edges of forests, in open areas, and next to streams. These trees are very tough. Even if a forest is badly damaged, tree fuchsias often survive. They are also common in cold mountain areas in the South Island.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
The seeds of tree fuchsia are quite small. They can stay in the soil for a long time, but we don't know exactly how long they can survive. If the conditions are right, the seeds can sprout in just two weeks. In dark places, it might take up to eight weeks for them to grow. Because the seeds are so tiny, the young plants are delicate and can have a hard time growing strong.
Tree fuchsia is a gynodioecious species. This means some plants have flowers with both male and female parts, while others have only female flowers. The female-only plants have a harder time getting pollinated. This is because there aren't as many birds like tui and bellbirds, which are the main helpers for pollination. This tree flowers from August to December and produces berries from December to March.
Soil Preferences
Tree fuchsia can grow in soil found near rivers, called riparian soil. It can even be used to help improve areas where the soil and conditions are not very good. It likes moist soil and needs shade from other trees overhead.
Who Eats Tree Fuchsia?
Many local birds in New Zealand eat tree fuchsia. These include tui, bellbirds, kererū, and silvereyes. Tui and kererū eat the flowers and fruit, while other birds drink the nectar.
Sometimes, other plants like banana passionfruit and Buddleia can grow too much and push tree fuchsia out of its home. Animals like goats also eat tree fuchsia, but they don't cause as much harm as possums. Possums are a big threat because they eat the fruit and seeds, and they don't stop even when there aren't many seeds available.
Cultural Uses
The tree fuchsia, known as kōtukutuku by the Māori people, was very useful to them and to early European settlers in New Zealand. People ate the berries, and settlers made jams from them. Māori women also used the plant in steam baths after childbirth.
The bark of the tree contains substances called tannins. These were used to help make leather. Tree fuchsia was also used to make bright-colored dyes.
Related Pages
- Fuchsia arborescens, another tree commonly called the tree fuchsia.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Fucsia de Nueva Zelanda para niños
In Spanish: Fucsia de Nueva Zelanda para niños