United States Department of Education facts for kids

Seal of the United States Department of Education
|
|

Flag of the United States Department of Education
|
|
 Lyndon Baines Johnson Department of Education Building, Department Headquarters |
|
| Department overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | October 17, 1979 |
| Preceding agencies | |
| Jurisdiction | Federal government of the United States |
| Headquarters | Lyndon Baines Johnson Department of Education Building, 400 Maryland Avenue, Southwest, Washington, D.C., U.S. 20202 |
| Employees | 4,200 (2025) |
| Annual budget | $238.04 billion (2024) |
| Department executives |
|
| Key document |
|
The United States Department of Education is a part of the U.S. government that focuses on education. It started in 1980. The department officially began on May 4, 1980. It was created when the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare was split into two new departments. President Jimmy Carter signed the law to create it on October 17, 1979.
There was an earlier version of this department formed in 1867. However, it was quickly changed to the Office of Education a year later. Today, the official short name for the Department of Education is ED.
The Secretary of Education leads the Department of Education. In 2021, it had over 4,000 employees. This was the smallest staff among all U.S. government departments. In 2024, its budget was about $268 billion. This was a big increase from the $14 billion budget it had in 1979. In 2025, the department's budget was about four percent of all U.S. federal spending.
In early 2025, during Donald Trump's second term, the government announced plans to reduce the Department of Education's staff by half. President Trump signed an order on March 20, 2025, aiming to close the department as much as the law allowed. However, a U.S. district court in Boston stopped these actions on May 22, 2025. The Trump administration appealed this decision. A federal appeals court did not lift the block in early June 2025. But on July 14, 2025, the Supreme Court allowed the staff reductions to move forward.
Contents
What the Department of Education Does
The Department of Education has four main jobs:
- It sets rules for federal money given to students for education. It also gives out and checks on these funds.
- It gathers information about schools in America and shares research findings.
- It brings attention to important education issues across the country. It also suggests ways to improve education.
- It works to stop unfair treatment and make sure everyone has an equal chance to get an education.
The department also works with other government groups. For example, it helps ensure that young people who are homeless or have run away can get a proper education.
History of the Department
Early Years of Education Support
In 1867, President Andrew Johnson signed a law to create a Department of Education. The idea was to collect facts and numbers about schools. It would also give advice to schools, much like the Department of Agriculture helped farmers.
Henry Barnard and leaders of the National Teachers Association (now the National Education Association) first suggested this department. Barnard became the first United States Commissioner of Education. He left when the office was changed to a smaller part of the Department of Interior. This was because some worried it would have too much power over local schools. It became known as the United States Office of Education.
For many years, this office stayed small. It was part of different government groups, like the United States Department of the Interior. It was also part of the former Department of Health Education and Welfare (DHEW). In 1920, there was an attempt to create a full Department of Education with its own leader, but it did not succeed.
In 1939, the office moved to the Federal Security Agency and was renamed the Office of Education. After World War II, President Dwight D. Eisenhower made changes. The Federal Security Agency was closed, and most of its jobs moved to the new DHEW.
Becoming a Full Department
In 1979, President Carter wanted to create a Department of Education at the highest level of government. His plan was to move most of the education-related jobs from the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare to this new department. He also planned to move education jobs from other departments, like Defense and Justice.
Some people, especially in the Republican Party, did not want a cabinet-level Department of Education. They argued that the United States Constitution does not mention "education." They felt it was an unnecessary federal involvement in local school matters. However, others believed it was allowed under parts of the Constitution that deal with trade and spending. The National Education Association supported the new department, but the American Federation of Teachers did not.
In 1979, the Office of Education had 3,000 employees and a budget of $12 billion. When the Department of Education was created, Congress gave it a budget of $14 billion and 17,000 employees. During his 1980 presidential campaign, Ronald Reagan said he wanted to get rid of the department. Once he became president, he reduced its budget a lot. But in 1988, he asked for an increase in its budget.
Late 20th Century Changes
The Republican Party's plan in 1980 was to get rid of the Department of Education. President Ronald Reagan had promised to do this during his campaign. But he could not, because the United States House of Representatives was controlled by the Democrats. In 1982, he again said he would save money by closing the department.
By 1984, the Republican Party stopped calling for the department's closure. When President George H. W. Bush was elected in 1988, the Republican view became more like the Democrats'.
In 1994, Republicans gained control of Congress. Federal control and spending on education grew. Even though the Republican Party said they would abolish the department in their 1996 plans, this trend continued. Their plan stated that the federal government should not be involved in school lessons.
21st Century Education Focus
The George W. Bush administration made improving federal education a top goal. Between 2002 and 2004, the department's budget grew from $46 billion to $60 billion. It focused mainly on elementary and secondary education, especially through the No Child Left Behind Act.
In March 2007, President George W. Bush signed a law naming the department's main building the Lyndon Baines Johnson Department of Education Building.
In December 2015, President Barack Obama signed the Every Student Succeeds Act. This law updated and replaced the No Child Left Behind Act.
The department's 2023 budget was $274 billion. This money helped programs for students with disabilities, early childhood education, and financial aid like Pell Grants. This budget was lower than the $637.7 billion in 2022.
In March 2025, President Donald Trump signed an order to start closing the Department of Education. This was part of a long-term goal by some conservatives. The White House said the department would still manage "important tasks" like student loans. In April 2025, Linda McMahon, the Secretary of Education, announced that the department would restart taking money from the wages of students who had not paid their loans.
Changes to Fairness and Inclusion Programs
In February 2025, the Department of Education created a way for people to report concerns about programs that promote fairness and inclusion in schools. The government also warned that universities could lose federal money if they continued with certain programs related to diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI).
Investigations into Universities
In March 2025, the Department of Education's Office for Civil Rights announced that 60 universities were being investigated. These investigations looked into claims of unfair treatment. The investigations were based on a law that stops institutions getting federal money from treating people differently based on their background. These investigations happened during a time of increased focus on how universities handle student protests.
Efforts to Close the Department
Republicans have tried to close the Department of Education since the 1980s. There has been disagreement about the department from the start. Some teachers' unions did not like President George W. Bush's "No Child Left Behind" policies. Some conservative Republican candidates in 2016 did not like the Common Core standards supported by President Barack Obama.
Efforts to close the department gained strength during the coronavirus pandemic. This was partly due to a movement by parents who disagreed with school shutdowns. There was also opposition to certain education standards and policies for LGBTQ students. Some felt these policies went against parents' rights.
Project 2025, a plan from the Heritage Foundation, talks a lot about closing the Department of Education. It also suggests making public schools private and ending free school lunches. Project 2025 also aims to create a conservative school curriculum for all public schools. The plan also includes ideas for reducing the number of public school teachers. President Trump's policies have been compared to Project 2025.
Polls in February and March 2025 showed that about two-thirds of Americans did not support closing the department. Educators generally oppose it, believing the federal government plays an important role in American education. The National Education Association (NEA), which represents 2.8 million teachers, said that taking away the department's resources would hurt millions of students in low-income areas who need educational help.
Under Trump's Second Presidency
On March 3, 2025, Linda McMahon became the 13th Secretary of Education. President Trump said her main goal would be to close the Department of Education. McMahon agreed, saying the department was not needed.
On March 11, 2025, the government announced it would fire almost half of the Department of Education's staff. This would reduce the workforce from about 4,100 to 2,100 employees. President Trump signed an order on March 20, 2025, to close the department as much as the law allowed. However, the department cannot be fully closed without Congress's approval. A U.S. district judge blocked the mass layoffs on May 22, 2025. Although the Trump administration appealed, a federal appeals court did not lift the block on June 4, 2025. On July 14, 2025, the Supreme Court allowed the mass layoffs to proceed.
2025 Staff Changes and Reorganization
On March 11, 2025, the Department of Education announced a big reduction in its staff. This cut nearly half of its employees. Secretary of Education Linda McMahon said this was part of a plan to modernize the department. It included changes to Federal Student Aid (FSA) and the Office for Civil Rights (OCR). Remaining staff were put on paid leave starting March 21, 2025. They were scheduled to leave or retire by June 9, 2025. The department said these changes were needed to make things run smoother and reduce federal control in education. Some responsibilities would move to other federal agencies.
On March 20, 2025, Trump signed an order telling the Secretary of Education to "help close the Department of Education and give power over education back to the States and local communities." However, Congress created the department, so it needs Congress's approval to close it.
Staff Reductions
In February 2025, the U.S. Department of Education offered its staff money to resign or retire early. In March 2025, the department announced a plan to cut its workforce by half.
Effects of the Changes
Most of the job cuts happened in the Federal Student Aid office. This office handles financial aid and student loans. Cuts also affected the Office for Civil Rights, which protects students and teachers from unfair treatment. Secretary McMahon said that money for financial aid would not be affected. However, changes in staff could cause problems for those receiving aid.
The Trump administration promised that funding for schools, like Title 1 for schools with many low-income students, would be kept. However, almost all the experts who work with data for these programs were affected by the job cuts. The department's data team was reduced from over 100 people to just three.
The department manages tens of billions of dollars in loans to students and parents. It also oversees collecting about $1.6 trillion in outstanding loans from over 40 million borrowers as of March 2025. If the department were to close, experts thought other government groups, like the Treasury Department, would take over managing the loans. On March 21, 2025, Trump announced that managing all federal student loans and other "special needs" programs would move to other departments. He said the Small Business Administration would take over student loans. The Health and Human Services office would take on special needs and nutrition programs.
Responses to the Changes
Senators Elizabeth Warren, Bernie Sanders, and other Democratic senators wrote a letter against the mass layoffs in March 2025. They asked Secretary McMahon to bring the laid-off employees back. Representative Bobby Scott said that closing the department would "make existing differences worse." He also said it would "reduce accountability and put low-income students, students of color, students with disabilities, rural students and English as a Second Language students at risk."
Derrick Johnson, the head of the NAACP, criticized Trump's attempt to close the department. He said Trump was weakening basic parts of democracy.
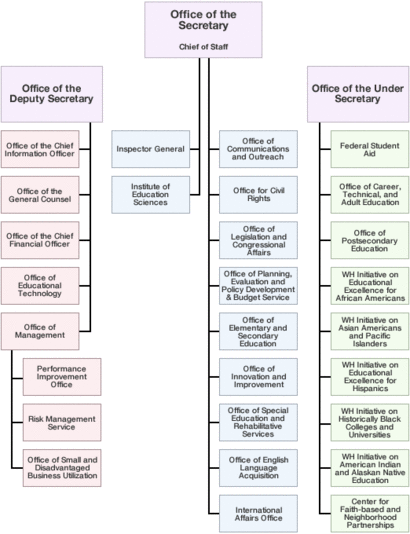
How the Department is Organized
| Program | |
|---|---|
| Secretary of Education | Office of Communications and Outreach |
| Office of the General Counsel | |
| Office of Inspector General | |
| Office of Legislation and Congressional Affairs | |
| Office for Civil Rights | |
| Office of Educational Technology | |
Institute of Education Sciences
|
|
| Office of Innovation and Improvement | |
| Office of the Chief Financial Officer | |
| Office of Management | |
| Office of the Chief Information Officer | |
Office of Planning, Evaluation and Policy Development
|
|
| Risk Management Service | |
| Deputy Secretary of Education | Office of Elementary and Secondary Education
|
| Office of English Language Acquisition | |
Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services
|
|
| Office of Innovation and Improvement | |
| Under Secretary of Education | Office of Postsecondary Education |
| Office of Career, Technical, and Adult Education | |
| Office of Federal Student Aid | |
| President's advisory board on Tribal Colleges and Universities | |
| President's advisory board on Historically Black Colleges and Universities | |
| Associated federal organizations | Advisory Councils and Committees |
| National Assessment Governing Board (NAGB) | |
| National Advisory Council on Indian Education | |
| Federal Interagency Committee on Education | |
| Advisory Commission on Accessible Instructional Materials in Postsecondary Education for Students with Disabilities | |
| National Board for Education Sciences | |
| National Board of the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education | |
| Federally aided organizations | Gallaudet University |
| Howard University | |
| National Technical Institute for the Deaf | |
Department Budget
|
| Budget of the Department of Education for FY 2024, showing its largest components |
For 2024, the U.S. Department of Education's budget was about $268 billion. It also manages about $1.7 trillion in federal student loan debt.
See also
 In Spanish: Departamento de Educación de los Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Departamento de Educación de los Estados Unidos para niños
- Council for Higher Education Accreditation
- Educational attainment in the United States
- Free Application for Federal Student Aid
- Federal Student Aid
- Higher education in the United States
- Student loans in the United States
Related Laws
- 1965: Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA)
- 1965: Higher Education Act of 1965 (HEA)
- 1974: Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
- 1975: Education for All Handicapped Children Act (EHA)
- 1979: Department of Education Organization Act
- 1984: Equal Access Act
- 1990: The Jeanne Clery Disclosure of Campus Security Policy and Campus Crime Statistics Act (Clery Act)
- 2001: No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB)
- 2004: Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
- 2009: Race to the Top
- 2015: Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)