Second presidency of Donald Trump facts for kids
 |
|
Quick facts for kids
Second presidency of Donald Trump
|
|
|---|---|
| January 20, 2025 – present | |
| JD Vance | |
| Cabinet | Full list |
| Party | Republican |
| Election | 2024 |
| Seat | White House |
|
← Joe Biden •
|
|
Donald Trump's second term as the president of the United States began on January 20, 2025. He was inaugurated as the 47th president. Trump is a member of the Republican Party and was also the 45th president from 2017 to 2021.
He won the 2024 election against the Democratic candidate, Kamala Harris. Trump is the second president in U.S. history to serve two terms that were not back-to-back. At 78, he was also the oldest person to become president, a record he first set during his first term.
In his first few months, President Trump signed many executive orders, which are official instructions from the president. On immigration, he signed the Laken Riley Act into law and issued orders to increase security at the Mexico-U.S. border. He also started new procedures for the deportation of immigrants.
Trump created a group called the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE). Its job is to lower spending by the U.S. government and reduce the number of rules. This led to many government workers losing their jobs.
In foreign policy, Trump has worked to make the relationship between the U.S. and Israel stronger. He approved military strikes on nuclear sites in Iran. During the Russian invasion of Ukraine, his administration paused military help to Ukraine and asked for a ceasefire. He also started the process of leaving international groups like the World Health Organization and the Paris Climate Accords.
Because he won elections in 2016 and 2024, the 22nd Amendment of the U.S. Constitution says he cannot be elected for a third term.
Contents
The 2024 Election
Donald Trump announced he was running for president on November 15, 2022. He had been the 45th president from 2017 to 2021. In March 2024, he won the Republican Party's nomination. He chose Senator JD Vance of Ohio as his vice presidential running mate.
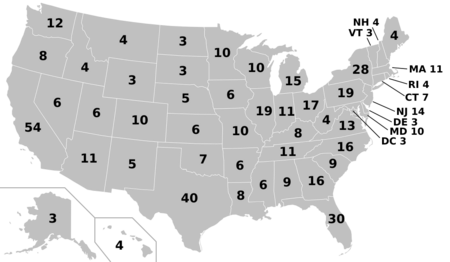
On November 6, 2024, news organizations projected that Trump had won the presidency. He won with 312 electoral votes, while Kamala Harris received 226. When he took office, he became the second president to serve two non-consecutive terms, after Grover Cleveland in 1893. In the same election, Republicans kept control of the House of Representatives and won control of the Senate.
Transition and Inauguration
The presidential transition is the period when the president-elect prepares to take office. Trump's transition team used ideas from the America First Policy Institute, a research group. During this time, Trump announced who he wanted for his cabinet and other top government jobs.
Trump was inaugurated on January 20, 2025. He was sworn in by Chief Justice John Roberts inside the Capitol Rotunda. In his first weeks, some of his actions led to public and legal discussions about government rules.
Administration
Cabinet
News media reported that Trump chose cabinet members who were very loyal to him. His cabinet was also described as one of the wealthiest in modern history, with more than 10 billionaires in government positions. He also appointed many people who had previously worked for Fox News.
Hiring Process
When the second Trump presidency started, teams were sent to government agencies to interview job applicants. The goal was to find people who were dedicated to the president's plans. On his first day, Trump signed an executive order about federal hiring. The administration asked federal workers to show their support for the president's goals. New hires were sometimes asked to give examples of how they helped Trump's 2024 campaign.
Advisors
Trump received advice from several people, including Elon Musk. Key advisors included Christopher Rufo for education and Stephen Miller for domestic policy and immigration.
Executive Orders
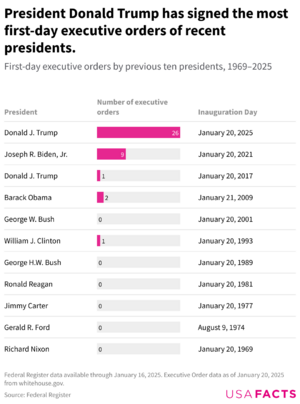
On his first day in office, President Trump signed 26 executive orders, the most ever for a president's first day. These orders covered many areas, including federal spending, immigration, and government programs. Many of these orders were challenged in court by groups who disagreed with them.
Domestic Policy
FEMA
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) provides help after disasters. In April, FEMA did not extend benefits for parts of Georgia and North Carolina hit by Hurricane Helene in 2024. After tornadoes hit Mississippi in March, it took over two months for the federal government to declare a major disaster. On May 23, the Trump administration approved disaster aid for areas in 8 states, including Mississippi.
Immigration
President Trump said he would bring back some immigration policies from his first term. This included new rules for travelers from certain countries and building more facilities for migrants. He appointed Tom Homan as the "border czar."
Soon after taking office, the Trump administration ended the CBP One mobile app service for migrants. He also reinstated the national emergency at the southern border. He gave immigration enforcement powers to more government agencies. On January 29, Trump signed the Laken Riley Act, which was the first law of his second term. He also ordered the expansion of a migrant operations center at Guantanamo Bay.
In February, the U.S. Border Patrol chief said that illegal border crossings had gone down by almost 90% since Trump's inauguration. In his first month, 37,660 people were deported.
Foreign Policy

President Trump's foreign policy is known as "America First." This means he focuses on what he believes is best for the United States. His relationships with other countries have been described as transactional, meaning he often makes deals. He has encouraged other countries to defend themselves more.
Europe
The Trump administration has argued that European countries should spend more on their own defense. During his campaign, he said he might not defend NATO allies if they did not meet the alliance's spending goals.
Trump has tried to help negotiate peace to end the war between Russia and Ukraine. In February 2025, he had phone calls with Russian President Vladimir Putin and Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy. The U.S. and Russia held a meeting in Saudi Arabia for peace talks. In March, Ukraine agreed to a 30-day ceasefire for strikes on energy infrastructure.
On July 9, Trump approved a military aid package for Ukraine after a major Russian attack. He said he was frustrated with Putin and was considering new tariffs on countries that trade with Russia.
Africa
The Trump administration's relationship with South Africa has been strained. Trump stopped all aid to the country.
In June 2025, President Trump helped make a peace deal between the Democratic Republic of Congo and Rwanda. The deal is meant to end a long conflict in the region. In exchange, the U.S. received rights to some of the area's minerals.
Asia
Middle East

In March 2025, the U.S. began airstrikes on Houthi targets in Yemen to protect ships in the Red Sea. In May, Trump announced a ceasefire deal with the Houthis.
Trump brought back a "maximum pressure" campaign against Iran to limit its nuclear program. On June 13, 2025, Israel bombed sites in Iran related to its nuclear program. On June 21, the U.S. also attacked three of Iran's nuclear sites. Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth said the goal was to damage the nuclear program without harming the Iranian people.
After the 2024 election, Trump pushed for an end to the Gaza war. Israel and Hamas agreed to a ceasefire on January 15, 2025.
Indian subcontinent

In February 2025, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Trump at the White House. In response to military strikes between India and Pakistan in 2025, Vice President Vance said the conflict was "none of our business."
Foreign Aid
The Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) made large cuts to the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), an agency that provides humanitarian aid. In January 2025, the administration stopped work on most USAID projects for 90 days.
After a Supreme Court ruling, the administration had to continue some projects. In March, Secretary of State Marco Rubio announced that 83% of USAID programs would be canceled. The remaining programs were moved to the Department of State.
In July 2025, Congress passed a bill to cut about $8 billion in foreign aid. However, funding for PEPFAR, a program that fights AIDS in other countries, was protected from the cuts.
Trade
President Trump is a strong supporter of tariffs, which are taxes on imported goods. He has placed tariffs on goods from many countries, especially China, Mexico, and Canada. This led to those countries placing their own tariffs on U.S. goods.
On April 2, 2025, a day Trump called "Liberation Day," he announced a 10% tariff on all goods imported into the U.S. After the stock market dropped, he paused the tariffs for 90 days. In May 2025, the U.S. and China agreed to lower tariffs on each other's goods for 90 days.
Business and Government
During his second presidency, Trump continued to own his businesses. This was different from some past presidents who sold their assets or put them in a blind trust. His businesses included the social media company Truth Social, real estate deals, and products with the Trump brand.
His family was also involved in the cryptocurrency industry. In January 2025, Trump launched a memecoin called $Trump. The coin's value grew very quickly. This mixing of private business with the presidency was discussed by government ethics experts.
In May 2025, it was announced that Trump planned to accept a $400 million luxury jet from Qatar. The jet would first be used as Air Force One and later be given to his presidential library. This plan was criticized by politicians from both parties.
See also
 In Spanish: Segunda presidencia de Donald Trump para niños
In Spanish: Segunda presidencia de Donald Trump para niños
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |